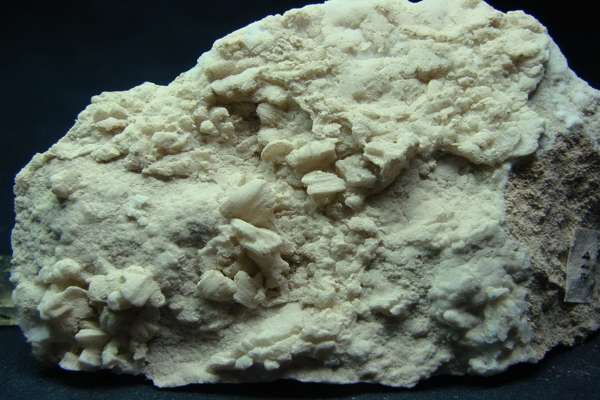
Niter is an unusual mineral belonging to the nitrates group. It is also known as, nitre, which is the mineral form of potassium nitrate, KNO3, also known as saltpeter or saltpetre. It is found in the form of efflorescence in hot, dry regions. The color of nitratine varies from colorless to white, with a reddish-brown tint, or lemon-yellow tint, or gray, due to impurities. Historically, the term niter was not well differentiated from natron, both of which have been very vaguely defined but generally refer to compounds of sodium or potassium joined with carbonate or nitrate ions.
It is named after the Nitrogen content in the chemical composition, and it was discovered in 1821 in the Tarapaca region in Chile.
General Information
- Category: Nitrates, oxide mineral
- Formula(repeating unit): KNO3
- Crystal system: Orthorhombic
- Crystal class: Dipyramidal (mmm)
- Color: White

Properties
Niter is a colorless to white mineral crystallizing in the orthorhombic crystal system. It exhibits a hardness of 1.5 to 2. It is soluble in water, tastes bitter, and is a pungent chemical. Its deliquescence is above 80%.
- Crystal habit: Druse or acicular
- Cleavage: Very good on {001}; good on {010}
- Fracture: Brittle
- Mohs scale hardness: 2
- Luster: Vitreous
- Streak: White
- Diaphaneity: Transparent
- Specific gravity: 2.10 (calc.)
- Solubility: Soluble
Occurrences
Nitratine is mainly bedded in the deposits formed in playas, in caves, deposited from seeping groundwater, leaching nitrates from overlying rocks, especially in dry, cold environments.
It usually is found as massive encrustations and efflorescent growths on cavern walls and ceilings where solutions containing alkali potassium and nitrate seep into the openings. It occasionally occurs as prismatic acicular crystal groups, and individual crystals commonly show twinning. Niter and other nitrates can also form in association with deposits of guano and similar organic materials.
Uses
Niter was used to refer specifically to nitrated salts known as various types of saltpeter (only nitrated salts were good for making gunpowder) by the time niter and its derivative nitric acid were first used to name the element nitrogen, in 1790.
Information Source: