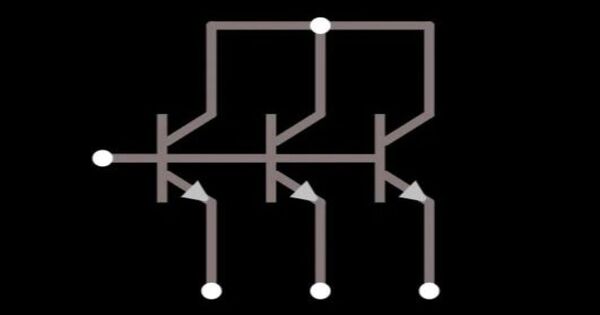
A multiple-emitter transistor is a type of bipolar transistor that is commonly used as the input to TTL NAND logic gates in integrated circuits. Input signals are sent to the emitters. It is a particular form of transistor with several emitter regions coupled to a single base and collector. If any one or more of the base-emitter junctions is forward biased, the voltage presented to the next stage is reduced, allowing logical operations to be performed with a single transistor. This arrangement enables several input signals to be integrated and amplified in a single device.
Multiple-emitter transistors replace the diodes in diode-transistor logic (DTL) to create transistor-transistor logic (TTL), allowing for faster switching and lower power dissipation. Logic gate use of multiple-emitter transistors was patented in the United Kingdom in 1961 and in the United States in 1962.
Multiple-emitter transistors are commonly utilized in logic gates and digital circuits for performing logical operations. They are also employed in analog circuits where several input signals must be added together or if signal amplification is necessary.
Applications
The multiple-emitter transistor can be utilized in a variety of applications that need the combination of several input signals or the steering of current. One common application is in digital logic circuits, where it can serve as a foundation for complicated logic gates.
A famous example of a multiple-emitter transistor is the ECL (Emitter-Coupled Logic) transistor, which is frequently employed in high-speed digital circuits due to its high switching rates and noise immunity. ECL logic circuits frequently use multiple-emitter transistors to efficiently perform complex logic tasks.
Multiple-emitter transistors can be either bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or field-effect transistors (FETs), depending on the technology employed. They are commonly found in integrated circuits where space efficiency is critical, as they can perform numerous functions in a small package. Overall, multiple-emitter transistors provide variety in circuit design and might be useful in applications that need many input signals or high-speed operation.