The law of substitution has several limitations as follows:
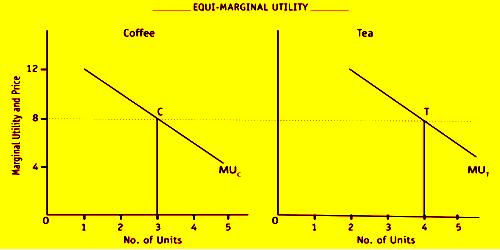
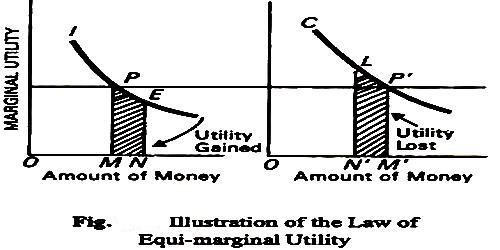
The law of substitution is also known as the law of equi-marginal utility or the law of maximum satisfaction. This law was first developed by H.H Gossen. Therefore, this law is also known as second law of Gossen. Prof. Marshall has developed and given the present shape of this law.
We know human wants are unlimited but the resources to fulfill the wants are limited. A rational consumer always tries to maximize his satisfaction by spending his limited money income. Consumer can maximize his satisfaction if he is able to equalize the marginal utility derived from the consumption of different units of several commodities by spending his all limited money income so that this law is known as law of maximum satisfaction or law of equi-marginal utility.
Ignorance of Consumer
If the consumer is ignorant or blindly follows custom or fashion, he will make a wrong use of money. If the consumer is ignorant about the availability of substitute goods in market then he can’t substitute the commodity having high M.U instead of low. Due to his ignorance, he may not be aware of other more alternatives. In this case no substitution takes place and this law does not apply.
Commodities Indivisible
The law of substitution is based on the assumption that commodities are divisible and substituable. This is an unrealistic assumption. Though commodities may be divided according to the convenience of the consumer, it is not possible to divide all commodities in small units. There are certain commodities like fan or a radio which cannot be used in case of the indivisible commodities.
Utility not Measurable
This principle of maximum satisfaction is based on the unrealistic assumption of the cardinal measurement of utility and the constancy of the marginal utility of money. Utility can’t be measured in terms of numbers. It can only be expressed in terms of range i.e. high or low.
Customs and Fashion
Sometimes people are slave of customs or fashion and they are unable to become rational. In the case of commodity related to custom and fashion this law is not applicable because while purchasing such commodity they don’t care about equalizing M.U from different commodity. Without being rational a consumer cannot substitute one thing for another. This is another limitation of this law.
Unlimited Resources
The law of substitution has no place when the resources are unlimited as in the case of free gift of nature. If there is shortage of goods in market there is no any question to equalize the M.U from several commodities. In such cases, there is no need to re-arrange expenditure because they can be used without any cost.
Choice Uncertain
The alternatives open to the consumer also assumed to be certain. But consumer choices are uncertain and even risky. In fact, it is expected utilities that determine consumer’s choices of the various combinations he can buy with a given money income.
No Fixed Accounting Period
There is no definite budget period in the case of individuals. Even if there is a fixed accounting period, the application of this principle is rendered difficult by the varying degrees of durability of the goods consumed. A durable goods is available for consumption in several succeeding accounting periods.
Information Source: