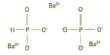
Kogarkoite is a sodium sulfate fluoride mineral with formula Na3(SO4)F. It is a pale blue monoclinic mineral. The crystal is monoclinic and is a type of naturally occurring antiperovskite. Kogarkoite is named after the Russian petrologist Lia Nikolaevna Kogarko (born 1936) who discovered the mineral.
Kogarkoite was first described in 1973 for an occurrence on Alluaiv Mountain, Lovozero Massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia. On Alluaiv it occurs in pegmatitic veins in nepheline syenite.
General Information
- Category: Sulfate mineral
- Formula: Na3(SO4)F
- Crystal system: Monoclinic
- Crystal class: Pyramidal (2/m) (same H-M symbol)

Fig: Kogarkoite
Properties
It has a pale blue colour, a specific gravity of about 2.67 and a hardness of 3.5.
- Colour: Colorless, pale sky-blue, pale pink, lilac
- Crystal habit: Tabular crystals, granular, earthy aggregates, pseudorhombohedral
- Mohs scale hardness: 3.5
- Lustre: Vitreous to dull
- Streak: White
- Diaphaneity: Transparent to translucent
- Specific gravity: 2.66
- Optical properties: Biaxial (+)
Occurrence
It occurs with sodalite in syenite xenoliths in an alkali intrusive complex at Mont Saint-Hilaire, Canada. In Hortense Hot Spring, Chaffee County, Colorado, it occurs as a sublimate. It occurs at Lake Natron near Ol Doinyo Lengai, Tanzania and Suswa Volcano, Lake Magadi, Kenya.
Information Source: