Keilite is an iron-magnesium sulfide mineral [chemical formula- (Fe, Mg)S)] that is found in enstatite chondrites. It is an isometric-hexoctahedral gray mineral containing calcium, chromium, iron, magnesium, manganese, sulfur, and zinc
It is the iron-dominant analog of niningerite. It is named after Klaus Keil (born 1934).
General Information
- Formula: (Fe2+, Mg)S
- Luster: Metallic
- Crystal System: Isometric
- Name: Named after Klaus Keil, Professor at the University of Hawaii, Honolulu, USA.
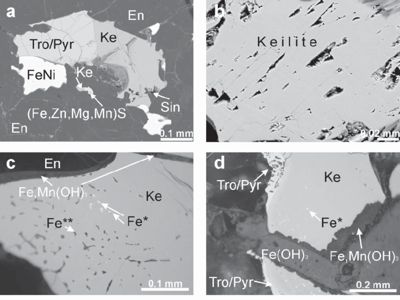
Fig: Keilite
Properties of Keilite
Keilite is an iron-magnesium sulfide mineral that is found in enstatite chondrites. It is the iron-dominant analog of niningerite. It is named after Klaus Keil.
- Cleavage: None
- Color: Gray.
- Diaphaneity: Opaque
- Habit: Microscopic Crystals – Crystals visible only with microscopes.
- Luster: Metallic
- Transparency: Opaque.
Occurrences – An accessory mineral in enstatite chondrite meteorites.
Examples of keilite occurrences are enstatite chondrites and the Zakłodzie meteorite. It appears to be confined to impact-melt influenced enstatite chondrites that were quenched. There are also some meteorites interpreted as impact-melt breccias that don’t contain keilite. This is explained as a deeper burial after impact, which slowed cooling and enabled retrograde reactions (diaphoresis) to take place.
Association: Niningerite, enstatite, kamacite, troilite.
Information Source;
















