INTRODUCTION: Industrial training is an indispensable part to study practically running processing technology of an industrial unit for student of textile technology, processing machines and equipment are not in continuous running condition .so it only provide demonstration of mechanical features and processing technology of the material in accomplishment of the theory their of but not of the situational variables to achieve practical knowledge two month long mid – course industrial training in knit composite mill was arrange for us. These enable us to avoid the gap between theory & practical knowledge. The incumbent was deputed to ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD. for practical mill training programmed arranged by own university authority guidance of MD. GIASS UDDIN and head of the department DR.MUSTAFIZUR RAHMAN.
ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD
ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD. is formed with a knitting section, dyeing section, quality control department, finishing section & garments. Current production is knitting section is almost 4 ton/day & flat bed knitting is almost 10000 Pcs/day. Current production is dyeing section is almost 4.5-5 ton/day. Production in garments section is depending on the order of buyers.
GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD.
Name : ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD.
Type : 100% Export oriented knit composite knit dyeing factory.
Year of established :
Location : Gazipur Sadar,gazipur.
Address
Head office : Silver Tower(16th Floor)
52,Gulshan Circle,Gulshan-1,Dhaka-1212.
Phone:9289514-15.
Web:WWW.one composite.com.
Factory : Bishuya Kuribari, Gazipur Sadar,Gazipur.
Phone:9289514-15. Fax:928917.
Sponsors : One Bank
Gulshan Branch.
Product Mix :
Single Jersey
Double Jersey or Heavy Jersey
Plain Interlock
1×1 Rib
2×2 Rib
Lycra Rib
Fleece Fabric
Fleece Terry
Lycra Single Jersey
Polo PK
Back PK
CVC (Cheap Value of Cotton) [% of Cotton is more in Blend]
Collar & Cuff
PC dyeing
Production capacity
Knitting : 120 ton/month
Dyeing : 150 ton/month
Finishing : 250 Ton/month
Garments : 7 million Pcs/ month
History of project Development
Construction : 2001
Dyeing section set up : 2003
Garments section set up : 2003
Different Department : Knitting section
Quality control department.
Knit dyeing section
Garments
Physical Infrastructure :
Physical infrastructure of One Composite Mills Ltd. is a complex structure.
The kitting & dyeing section is made by brick wall &
Tin shaded .The finishing, Q.C, Store, Garments is made by
brick wall & tin shaded.
MANPOWER MANAGEMENT
Organogram of the man power MANAGEMENT
Admin manager
Admin officer
Account officer
Store officer
Store assistant
Store helper
Office peon
Cleaner
Loader
Sweeper
Organogram of the man power (PRODUCTION)
General Manager
Manager (Dyeing & Finishing)
Asst. Manager (Dying Section)
Shift in charge
Supervisor
Operator
Helper
Organogram of the man power for OTHER
Security in charge
Security supervisor
Security
MACHINE DESCRIPTON:
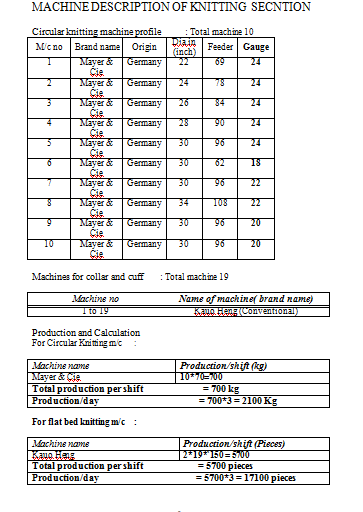
AUTO STRIFE
M/c no : 9, 10
Model : SMI -1
Diameter : 30 inch
Gauge : 24
Velocity maximum : 22 rpm
Feeder : 48
Cam : 48
Cam track : 2
Maximum color use : 6
Here the work is done by jack, Jack gives pressure to design of cam then its gives pressure on cam track & probably the design is formed here. The problem is we don’t get actually how the design formed.
MACHINE DESCRIPTION OF DYEING SECTION
Machine no : 01
Brand name : Thies
Manufacturer : Germany
Chamber : 1
Reel speed : 220 MPM
Capacity : 250 Kg
Maximum operating Temp : 1400C
Maximum operating pressure : 3 bar
Machine no : 02& 03
Brand name : Thies
Manufacturer : Germany
Chamber : 2
Reel speed : 224 MPM
Capacity : 350 Kg
Maximum operating temp : 1400C
Maximum operating pressure : 3 bar
Machine no : 04
Brand name : Thies
Manufacturer : Germany
Chamber : 3
Reel speed : 230 MPM
Capacity : 500 Kg
Maximum operating temp : 1400C
Maximum operating pressure : 3 bar
Machine no : 05
Brand name : Thies
Manufacturer : Germany
Machine capacity : 750 Kg
Chamber : 3
Reel speed : 280 MPM
Maximum working temp : 1400C
Liquid ratio : 1:6
Maximum working pressure : 3 bar
Machine capacity:
Machine no | Capacity(Kg) |
01 | 250 |
02 | 350 |
03 | 350 |
04 | 500 |
05 | 750 |
| Total 2200 | |
Total capacity =2200Kg =3.2ton (approximately)
Production per day =2.2 X 3 = 6.6 ton (approximately)
Sample dyeing capacity = (20+35+25) Kg=80 Kg
Numbers of motors in dyeing machine:
Machine no | Winch motor | Dosing motor | Mixing motor | Main pump |
01 | 1 | 01 | 01 | 01 |
02 | 2 | 01 | 01 | 01 |
03 | 2 | 01 | 01 | 01 |
04 | 3 | 01 | 01 | 01 |
05 | 03 | 01 | 02 | 01 |
Dyeing parameter
Dyeing pH
- Bleaching bath pH : 10.5-11.5
- After beaching bath pH : 5.5-6.5
- Initial dye bath pH : 5.5-6.5
- Addition of dye pH : 5.5-6.8
- After of salt pH : 6.5-7.5
- After soda dosing pH(after 10 min) :10.3-11.2
- After Dyeing pH : 5.0-6.0
- Fixing bath pH : 4.5-5.5
Fixation time
- Light shade : 30-40 min
- Medium shade : 45-50 min
- Deep shade : 50-60 min
M: L ratio : 1:6 to 1:9
The amount of Gluber salt, Soda ash, & Caustic soda on the basis of shade percentage:
For Drimarine –CL/K/HF & Remazol-RR
Name | <0. 01-0.1% | 01-0.5% | 0.5-1% | 1above |
G. salt (g/l) | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
Soda ash (g/l) | 4 | 6 | 9 | 12 |
FLOW CHART FOR FINISHING
Dewatering
↓
Drying
↓
Turning
↓
Compacting
↓
Brushing
↓
Quality Control
↓
Delivery
MACHINE DESCRIPTION OF FINISHING SECTION
The machines that are used in Tube lines are given bellows
- Dewatering m/c
- Dryer
- Compactor
The machines that are used in Tube form in ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD. are given bellow:
M/c no: 1
Machine name : Dewatering Machine
Brand name : FABCON
Origin : America
Pressure range : 0- 40 bar
Speed : 0-30 M/min
Over feed Speed : 0-20 M/min
Capacity : 12 ton
Working Principle of De Watering Machine:
At first the dyed fabric is placed to the turning table, then the fabric is feed to the cloth lifter which is drive by motor. Then the fabric is feed to the feed roller. Then the fabric is passed to the extracting nip. Then the fabric is passed to the padding nip. These are also drive by a motor. Then the fabric is passed to the conveyer belt. Then passed to the cloth folder & supply to the trolley, then supply to the drier.
Calculation of De watering percentage that we had done is given below:
Before padding, the G.S.M of fabric =10
After padding, the G.S.M of fabric =5.33
Amount of de watered =10 – 5.33 = 4.67
So % of water at de watering = (4.67/10)*100 = 46.7
When the pressure is applied 5.5 bar
Mc no: 2
Machine name : Dryer m/c
Brand name : Syncro
Temperature : 120-1300C for white and 130-1600C for color
Fabric
Over feed : 20-20% as required.
Speed : 6-40 m/min.
Conveyor belt speed : 30 m/min
M/c no: 3
Machine name : Compactor m/c
Brand name : Fabcon
Origin : America
Temperature : 100-1500C
Over feed : 2-8 %
Speed : 15-30 m/min
Cylinder pressure : 5 bar
M/c no:4
Machine name : Brushing Machine
Brand name : Sucker Muller
Origin : Germany
Capacity :7 Ton
M/c no:5
Machine name : Air Turning M/c
Brand name : Dong Nam Industrial Co.Ltd.
Origin : Korea
Model No :DNAT-400
LAB MACHINE SPECIFICATION
M/c No: 1
Machine name : Spectrophotometer
Brand : Data color
Origin : America
M/c No: 2
Machine name : Gyro wash
Brand : James H.Heal & Company Ltd.
Origin : England
Temperature : 100° c
M/c No: 3
M/c Name : Accudry
Origin : England
Brand : James H.Heal & Company Ltd.
Temperature : 80° c
M/c No: 4
M/c Name : Electrolux Wascator
Brand : James H.Heal & Company Ltd
Origin : England
Temperature : 100°
RAW MATERIALS
Raw materials for knitting section:
- Ø Cotton (combed)
- Ø Lycra
- Ø PC
- Ø CVC
- Ø Dyed yarn
Source:
- Square Textile
- One tex
- Padma textile
- Shohagpur textile
- Rahamat textile
- Hanif spinning mill
Raw materials for dyeing section:
Types:
Mainly raw materials for One Composite Mills Ltd. are:
1. Gray fabric
A.100 % cotton
B. PC
C. Melange
D. CVC
E. Polyester, etc
2. Dyes
3. Chemicals
4. Auxiliaries, etc.
Source:
Dyes & chemicals are mainly imported from India & local market. Etc.
Production planning, sequence & operation
Introduction and basic procedure of planning and control:
A planned work brings success. With out planning nothing is complete within the required time. So planning has its own importance which is intolerable. Planning gives a scheduled task and control completes it successfully. But production planning and control is not an easy task. Its basic working procedure is as follows-
- Taking orders from marketing division.
- Analyzing the orders.
- Planning for knitting the fabric
- Planning for dyeing the fabric
- Planning for finishing the fabric.
It is only a basic procedure. It may change according to the type of order. Sometimes, the order is places only for finishing the material or only for dyeing the white goods. Then some steps are committed for planning procedure.
- Taking orders from marketing division:
One Composite Mills Ltd. marketing division supplies fabric orders to the One Composite Mills Ltd. planning and control division by a specific format.
- Analyzing the orders:
This section analyzes the orders according to buyers order quantity, type of orders (i.e. type of fabric, color to be dyed etc), delivery date etc. Then it selects which M/C to use, no of M/C to use, time required for production etc. This section plans for required quantity of fabric to be knitted (order quantity + 6% of order quantity), Knitting balance, fabric to be dyed. Dyeing balance, RFD (Ready for delivery), RFD balance, delivery fabric & delivery balance.
- Planning for knitting:
This section plans for knitting production. It selects M/C for knitting the fabric for specific type of fabric, type of yarn used, required GSM, width etc. It also gives delivery data for knitted fabric.
- Planning for dyeing the fabric:
Production planning for dyeing is called ‘Batch plan’. According to the batch no and color, width, style and construction the batch plan is made. For easy understand this section gives some batch cards. Batch cards are serialized according to the priority of delivery.
E. Planning for finishing the fabric:
Finishing schedule is same as the dyeing. After dyeing the material goes to the finishing section with the batch plan. Finished data is written to the batch card and is informed to the planning section.
However, this section always enforces to all the departments to finish all the works within the delivery time given by the buyers. This section delivers materials by truck, micro bus, ship, etc to the customer within the mean time. Thus it plays a very important role in the success of the company.
Batch section
Position of batch section in production line as follows:
Knitting Grey Fabric
Batch Section
Dyeing
Finishing
Finished Fabric
Function or purpose of batch section:
- To receive the grey fabric roll from knitting section or other source.
- To prepare the batch of fabric for dyeing according to the following parameter:
- Order sheet (Received from buyer)
- Dyeing shade (Color or white, Light or Dark)
- M/C capacity
- Fabric structure
- Yarn type, etc.
- To send the grey fabric to the dyeing floor by trolley with batch card.
- To keep records for every previous dyeing.
Proper batching criteria:
- Ø To use maximum capacity of existing dyeing m/c
- Ø To ensure every dyeing m/c running in full production.
- Ø To minimize the m/c washing time or preparation time.
- Ø To keep the no of batch as less as possible for same shade, etc.
Batch management:
Primary batch is done by the dyeing manager. Batch section in charge receives this primary batch plan from dyeing manager. Then the works is adjusting, according to m/c condition.
Remarks:
Proper batch can minimize the batch to batch shade variation. It can near or same dyeing condition for every batch of same shade. Thus it improves the dyeing quantity minimize dyeing cost a lot.
Scouring process for 100% cotton knit fabric
Recipe:
Detergent : 1g/l
Anti-creasing agent : 1g/l
Sequestering agent : 0.8g/l
Stabilizer : 0 .4g/l
Caustic Soda : 2.5g/l
Peroxide (H2O2) : 3.5%
Acetic Acid : 1.2g/l
Peroxide Killer : 0.35g/l
Process procedure:
Filling water into m/c
↓
Fabric load in m/c
↓
Raise the temperature of 500C
↓
Addition Auxiliaries (Detergent, Sequestering agent, Anti-creasing agent, Stabilizer)
↓
Alkali dosing in 10 min
↓
Raise the temperature of 700C
↓
Addition of hydrogen peroxide (inject)
↓
Raise the temperature of 980C, run time 60min
↓
Cooling at 750C
↓
Drain out
↓
Hot wash at 98°c*10 min.
↓
Cooling
↓
Drain out
↓
Neutralization with acetic acid at 60°c*10 minute
↓
Drain
↓
Enzyme wash at 55°c 50min PH-4.5
↓
Raise temp. at 800C*10min.
↓
Rinse
↓
Drain
↓
Peroxide killer at 40°c*10min.
↓
Drain
Dyeing Process for 100% cotton knit fabric:
Fill the m/c with water
↓
Fabric load
↓
Addition Auxiliaries (Leveling agent, Sequestering agent, Anti-creasing agent) and run time 10 min.
↓
Dye dosing for 20 min. (linear dosing) and run time 10min.
↓
Salt dosing for20 min. and run time 10min.
↓
Soda dosing for 40min. runtime 20min.
↓
Raise the temperature of 600C with gradient 20C/min and running time 60 min. (Here batch sample match standard sample)
↓
Rinse 1 or 2 times depend upon dye shade and running time 10 min
↓
Bath drain
↓
Filling water into m/c
↓
Addition Acetic Acid for neutralization (cheek PH; should be 5.0-6.0), run time 10min
↓
Rinse 10min
↓
Drain out
↓
Filling water into m/c
↓
Addition of soaping agent and raise the temperature of 600C and running time 10 min
↓
Rinse 10 min
↓
Drain out
↓
Filling water into m/c
↓
Acid treatment at room temp. for 10min.
↓
Addition of softener for softening the fabric at 45°c and running time 20 min
↓
Over flow rinse
↓
Fixing at 40°c*20min.
↓
Rinse
↓
Unload fabric
Dyeing process for Blend Fabrics(Cotton/Polyester):
Polyester part Dyeing:
Fill the m/c
↓
Addition of auxiliaries(PH controller, leveling agent PH 4.5)
↓
Color dosing at 60°c*20min.
↓
Raise the temp 100°c(1°gradian/min.)
↓
Raise the temp. 130°c run time 30min.
↓
Cooling at 80°c
↓
Sample cutting
↓
Reduction clearing at 105°c*20min.(Detergent, caustic soda, hydrose)
↓
Cooling
↓
Cold wash
↓
Acid treatment, PH 7-8
↓
Drain
↓
Rinse
Cotton Part Dyeing:
Same as 100% cotton fabric dyeing Dyeing faults:
Dyeing faults are given below
- Patchy dyeing effect:
Reasons:
- Entanglement of fabric.
- Faulty injection of alkali.
- Faulty color addition
- Due to hardness of water.
- Due to improper salt addition, etc
- Roll to roll variation or Meter to Meter variation:
Reasons:
- Yarn lot mix.
- Faulty heat setting.
- Hardness of water.
- Faulty m/c speed, etc
- Dye-stain:
Reasons:
- Un dissolved dye particle in bath.
- Un dissolved caustic soda particle in bath.
- Crease mark:
Reasons:
- If pump pressure & reel speed is not equal
- Due to high speed m/c running.
- Rub mark:
Reasons:
- Due to reel cranking.
- Due to sharp point of nozzle.
- Due to sharp delivery roller, etc
- Nozzle to Nozzle variation:
Reasons:
- Pump pressure & reel speed is not equal
QUALITY ASSURANCE SYSTEM
Quality assurance procedure may be divided into two major parts:
- Online quality control
- Offline quality control
Online quality control:
Online quality control comprises with the raw material control & the process control.
Raw material control:
As the quality product depends upon the raw material quality. So we must ensure the best quality of raw material with an economical consideration.
- The fabric must be with out faults, with proper absorbency, whiteness as per requirement of the subsequent process.
- The chemicals should be with a known concentration with a higher degree of purity.
- All the m/cs engaged should be higher a precision.
Process control:
The method chosen for process must be provided with the necessary accurate parameters. Here the specific gravity, water level, PH, temperature at each stage is cheeked.
Finished fabric inspection:
Finished fabrics are inspection by 4 point system.
Formula is following:
= B *3240/L*W
Or = B*100*0.9*36/ L*W
Where,
L= Total length in meter
W= Fabric width in inch
B= Total Plenty point
Offline quality control:
The final product should pass against the norms given by buyer. The following tests are generally done-
ü GSM test
ü Shade cheek
ü Shrinkage test
ü Spirality test
ü Wash fastness test
ü Rubbing fastness test
ü Perspiration test
ü Durability test, etc.
In One Composite Mills LTD. laboratory two material are testing (i.e. Quality control)
- Fabric testing
- Raw material Testing
- Fabric testing:
- Physical test
- chemical test or color fastness test
- Physical tests name are following:
1.1 GSM
1.2 Durability test
1.3 Sprility /Squeness test
1.4 Garments durability test
1.5 Shrinkage test
- Chemical test/ color fastness tests name are following:
Color fastness to wash
Color fastness to water
Color fastness rubbing
Color fastness to perspiration
- Raw materials test:
- Water : PH & Hardness Test.
- Gluber salt : PH & Hardness Test.
- Acetic Acid : Strength Test
- NaOH : Purity Test
- Na2CO3 : Strength Test
- H2O2 : Strength Test
Which may occurs on certain substances as result of the optical brightener present in the detergent. Check under UV light
1.3 SPIRALITY TEST:
Purpose:
To measure the Spirality that is when the horizontal alignment of a fabric changes its relationship to the length, causing distortion
Calculation:
For specimen which shrink in length
Determine the average of the measurement & this called S i.e.
S = (S1+S2) / 2
Then use this value of S in the formula
Spirality = {(S X L) / 100} + S
Where, L is the average shrinkage length.
Example:
Spirality = {(S X L) / 100} + S
= {(31.5 X 7) / 100} + 31.5 = 33.7 mm
For specimen which stretch in length:
Spirality = S – {(S X L) / 100}
Where, L is the average stretch length
Example:
Spirality = S – {(S X L) / 100}
= 31.5 – {(31.5 X 7) / 100} = 29.3 mm
Another Formula measured in percentage. The formula is following:
Spirality % = (S X 100) / L
| Where, L is the Actual fabric length. |
Example:
Spirality % = (S X 100) / L
= (31.5 X 100) / 470 = 6.70%
And also Spirality measured in degree.
CHEMICAL TEST
COLOR FASTNESS TO WASH:
- A. Purpose:
The resistance of the loss of color of any dyed or printed material to washing is referred to as its wash fastness.
- B. Apparatus: Gyro wash, Grey scale, Multi fiber.
- C. Method: Buyer requirements.
- D. Test specimen:
For Fabric : Fabric Size 10 cm X 4 cm
For Yarn : Yarn Weight 0.8gm
Multi Fiber fabric : Multi Fiber fabric size 10 cm X 4 cm
- E. Assessment:
Color change: The original and tested dyed samples are placed side by side, oriented in the same direction along with the color change grey scale and compare the contrast between the treated dyed sample and the same untreated sample with the appropriate pair of color change grey scale. If there is no color change, then it is ratting 5.
Color staining: Again, compare the contrast between the untreated white fabric and the stained white fabric with the appropriate pair of gray –white samples of the Grey scale for staining.
RUBBING TEST:
- Purpose:
The fastness test to rubbing is used on a variety of fabrics to evaluate the transfer of surface dye from the test fabric when it applied surface friction or rubbed against a rough surface.
- Apparatus: Crock-meter and Grey scale.
- Procedure:
At first the sample is placed with tap under the metallic mounting plate. Then the crocking cloth is set in the crocking pin (peg) with clip. Then the test specimen is rubbed to & fro (10 X 10 rubs, 1rub/sec) by means of crock meter finger. Finally the crocking cloth is removed from the peg. In case of wet rubbing test, the crocking cloth is dried at room temperature.
- Evaluation:
Compare the contrast between untreated and treated white crocking cloth with the staining grey scale.
Again, color contrasts of rubbed and unrubbed dyed samples are compared with color changing grey scale.
For both type of rubbing test, the fastness is rated from 1 to 5, Were 1 means worst rubbing fastness and 5 means excellent rubbing fastness.
Maintenance:
Machine, Buildings and other facilities are subjected to deterioration due to their use and exposure to environmental condition .Process of deterioration, if unchecked, culminates in rendering these service facilities unserviceable and brings them to a standstill Industry, therefore has no choice but to attend them from time to repair and recondition them so as to elongate their life to extent it is economically and physically possible to do so.
It is in this in the context that maintenance assumes importance as an engineering function. It is made responsible for provision of a condition of these machines, buildings and service that will permit uninterrupted implementation of plans requiring their use.
Objectives of maintenance:
- To keep the factory plants, equipments, machine tools in an optimum working condition.
- To ensure specified accuracy to product and time schedule of delivery to customer.
- To keep the downtime of machines to the minimum thus to have control over the production program.
- To keep the production cycle within the stipulated range.
- To modify the machine tools to meet the need for production.
Maintenance of machinery:
Maintenance
Preventive Maintenance Break down Maintenance
Mechanical Electrical Mechanical Electrical
UTILITIES SERVICES
Following utilizes are available :
- Electricity
- Steam/Boiler
- Gas
1 ELECTRICITY
In OCML electricity is provided by own generator of the industry. It has no electric sub- station.
There are both gas & diesel generator.
Technical details about the generator:
Machine no: 01
Type of generator : Gas generator (old)
Brand name : WAUKESHA
Manufacturer : USA
Model no : MTG 846
Capacity : 750 kw
Volts : 415
Phase : 3
Power factor : 0.8
Frequency : 50 Hz
AMPS : 1304
Governed Speed : 1000 rpm
Machine no: 02
Type of generator : Gas generator (New)
Brand name : WAUKESHA
Manufacturer : USA
Model no : VHP 5904 GSID
Capacity : 900 kw
Volts : 415/220 V
Phase : 3
Power factor : 0.8
Frequency : 50 Hz
AMPS : 1565
Governed Speed : 1000 rpm
Machine no: 03
Type of generator : Diesel Generator
Brand name : DATE
Manufacturer : Mexico
Model no : HC1434 F
Capacity : 288 kw
Volts : 415 V
Phase : 3-4
Power factor : 0.8
Frequency : 50 Hz
Governed Speed : 1000 rpm
Diesel Consumption : 55 Lit/ hr
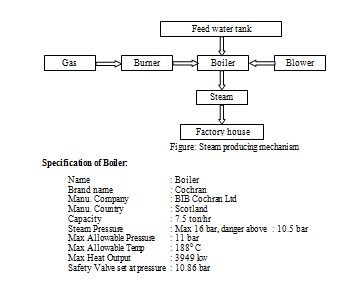
2. STEAM
Steam:
Boiler is used to produce steam from water.
Steam Producing Mechanism:
Steam is produced from water. Water is supplied from soft water tank and is reserved in feed water tank, situated above the boiler. Gas is supplied to burner. Burner produces a flame with the help of boiler. So heat is produced. Water is supplied to the boiler. Because of heat, steam is produced. It is then supplied to different m/cs at a certain pressure.
EFFLUENT
TREATMENT PLAN
EFFLUENT TREATMENT PLAN (capacity-30 M3/hr)
Description of the ETP process:
Equalization tank consist raw effluent. At the beginning, raw effluent is led to the mixing tank/reaction tank by pumping.
- In mixing tank, Lime and Ferus sulphate are added with effluent; blower is used to mix properly.
- At the end of the reaction the solution is led to the flocculation tank where poly Electrolite/ poly Acrylamide is added for further reaction; blower is used here too.
- From the flocculation tank solution is drained to Tube settler-1. Here, sludge is divided and placed in the sludge sump.
- After the operation of Tube settler-1, the solution is brought to PH correction chamber where HCL is mixed to control the required PH.
- After the completion of PH correction the solution is led to the biological reaction tank-1 & 2. In this tank BACTERIA MEDIA is used to absorb the harmful insects that exist in effluent. A bit amount of DAP (Di-amonium phosphate) + Urea (2:1) is also used here as food of bacteria.
When the plant is stopped the mixture (DAP + Urea) is to use more.
DO (Dissolved Oxygen) is to cheek and control in both the reaction tank. The tested temperature is approx. 400C here.
- From the biological reaction tank water is again drained to Tube settler-2. Like Tube settler-1, sludge is divided here too and placed in the sludge sump.
- The main action of filter feed sump is to accelerate the cleaner effluent and make it flow the pressure sand filter and Activated carbon filter for final filtration. After the filtration the treated water is drained out in the air.
Before draining out the treated water, the BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) and COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) are to cheek and keep it in required range. The tested temperature of the outlet water is approx.380C.
- The less contaminated liquid that is obtained from different operations except dyeing is stored in the less contaminated reservoir. It needs filtering too before drain out.
- In another operation, liquid sludge is collected from sludge sump and makes it inject into Sludge thickening tank.
- In sludge thickening tank, divination of raw sludge is occurred by centrifuge hydro extractor and the filtrated liquid is led to the equalization tank further processing.
- The centrifuge hydro extractor is used to convert the sludge into cake which is later brought to the air by the help of hand-drum. After hydro extracting, the rest substance is drained to the equalization tank for further processing.
- The tested temperature of the equalization tank is approx. 420C. Here, blowers perform to maintain proper circulation of the effluent.
FUNCTIONS OF DIFFERENT INGREDIENTS USED IN E.T.P PLANT:
Lime : Lime is used to change the color of effluent and to increase the transparency of water.
Ferus Sulphate: Ferus Sulphate is used for the agglomeration of the foreign matters present in the effluent.
Poly Electrolite: Poly Electrolite helps to make the agglomerated materials be gummy for easy deposition below the surface of water.
Hydrochloric Acid: Hydrochloric Acid is used to sustain the required PH of the treated water.
Water quality of E.T.P:
Parameter | Permissible concentration |
BOD | < 50 ppm |
COD | < 200 ppm |
Color | Colorless |
Temperature | Max m 380C |
PH value | 6 – 9 |
Total Dissolved solid (TDS) | < 2500 ppm |
Total suspended solid (TSS) | < 100 ppm |
Dissolved oxygen (DO) | 4.5 – 8 |
STORE
&
INVENTORY CONTROL
STORE AND INVENTORY CONTROL
Frequency of inventory control:
v Monthly inventory control.
v Annual inventory control.
Scope of inventory control:
- Raw materials
- Dyes store
- Others chemicals store
- Grey fabrics
- Finished fabrics
- Spare parts
- General store
- § Capital equipment
- § Accessories
- § Stationary
- § Maintenance parts.
Inventory system for raw materials:
- Raw materials partially received from production planning &directly form head office.
- Material receiving & inspection repot (MRIR) is prepared. Received quantity is mentioned & noted down.
- Submitted to QC department. Some are OK & few rejected.
- Entry of data of goods in DATATEX.
- Goods are arranged according to OK or rejected group.
- Department gives store requisition to be house.
- As per requisition materials supplied & this record is noted down.
Stages of Grey Fabric Inventory Control:
v After knitting production
v Grey inspection
v Warehouse
v Batch preparation
v Dye house.
Stages of Finished Fabric Inventory Control:
Þ finished section
Þ After final inspection
Þ Warehouse
STORE CAPACITY:
Item | Amount |
Dyes | 4-5 tons |
Chemicals | 17 tons |
Grey fabrics | 15-20 tons |
Yarn storage | 30tons |
Remark:
2. The inventory system of OCML covers both knitting & dyeing inventories.
3. The space is noticed to be insufficient considerably.
4. An expansion of space is thus desired for sound inventory.
COST ANALYSIS
Costing of the product:
Costing system mainly describes how the cost of the final product is fixed by the company/beneficial. According to buyer/customers requirement at first the fabric is collected from local and foreign suppliers. Then it is calculated how much dyestuff and chemical is required to the end of the processing of that specific fabric. After that, the final cost is fixed including some profit. Then the unit price is offered to the buyer for approves it.
Costing of the product is done by the consideration of the following factors:
ü Amount of raw materials consumed.
ü Direct Labor.
ü Indirect Labor.
ü Factory cost.
ü Office and administrative cost.
ü Sales and distribution cost.
ü Profit, etc.
Remarks:
The costing of product is a secret matter of the industry. They are not interested to flash the cost related data. So, we could not collect the price of product and costing of the product.
MARKETING ACTIVITIES
Consumer of product:
- Ø TEXEBO
- Ø ARTMAL
- Ø TESCO
- Ø BGEX
- Ø MOTHER CARE
- Ø S. OLIVER
Country of export:
- England
- Germany
- USA
- France
Marketing Strategy:
Marketing Strategy is a very important factors to the sale the products to buyer. If the marketing strategy is not so develop, it will be very hard to reach the goal. In case of garments marketing the dealings with buyer is a very important factor. In ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD. Mainly senior marketing officers, merchandiser & higher officials deals with the buyer. There are some fixed buyers of the industry. These buyers give their orders continuously all over year. The marketing officers & the merchandiser communicate with the buying house to collect the orders. By both side understanding the rate& the order are fixed.
Duties & responsibilities of marketing officer:
Dealing with the buyer & convince the buyer is the main duty of marketing officer. A marketing officer also has some other duties. The main duties & responsibilities of marketing officer are given bellow-
1) To prepare cost sheet by dealing with the buyer.
2) To make different steps by discussing with the high officials & merchandiser.
3) To maintain a regular & good relationship between commercial officer & merchandiser.
4) To maintain a communication with the buyers and buying house.
5) Communicate with better criteria of the products.
Actually the responsibilities & duties of marketing officer begin from getting order of buyer & end after receiving goods by buyer. So, he should be always smart, energetic & sincere.
Remarks:
ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD. Has a well learned marketing & merchandising team. They always communicate with the buyers. ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD Has some fixed buyers. The marketing section also looks the quality & quantity buyers.
VISION
&
SUGGESTION
OUR VISION
ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD. is a well-planed versatile project. The administrative, management, and chain of command – all are well organized. They are devoted to satisfy the customer by their activities. However, some of the points we want to mention for the good of ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD.
Some suggestions:
- During the transport of the fabric in the dyeing floor also during the loading of the m/c, fabrics are soiled for the contact with floor. This makes the fabric dirty. It may require more scouring & bleaching agent or may create stain making it faulty.
- Due to storage of Textile Engineers, night shifts sometime continue production without any production officer, As a result in some cases quality level drops.
- The machines of the finishing section should be modernized.
- The dyeing floor is watery most of the time; it should be cleaned all the time.
- A very important point is that we collected sample in different stages of our training. We asked the involved persons to cut some sample pieces for us. The samples were cut very much more than we required. This is noticeable. A huge amount of fabric goes to wastage. No doubt, this lessens the overall efficiency.
Conclusion: AUST has given a change to perform the industrial attachment in ONE COMPOSITE MILLS LTD. This attachment, act as a bridge to minimize the gap between theoretical and practical knowledge. Undoubtedly, this attachment taught us more about textile technology, industrial management & production process. Besides it gave us the first opportunity to work in an industry. We believe that, the experience of this industrial attachment will help us in our future career as textile technologist/engineer.
















