The Hubble Space Telescope is a large space telescope. On April 24, 1990, the space shuttle Discovery launched it into orbit. Hubble orbits the Earth at a height of about 535 kilometers (332 miles). It measures the length of a large school bus and weighs the equivalent of two adult elephants. Hubble travels at about 5 miles per second, which is equivalent to traveling from the east coast to the west coast of the United States in 10 minutes. Hubble runs on solar power.
Consider entering a room at night, turning off all the lights, and closing the shades. However, an unsettling glow emanates from the walls, ceiling, and floor. The light is barely bright enough to see your hands ahead of your face, but it persists. Sounds like a scene from “Ghost Hunters,” doesn’t it? No, this is the real deal for astronomers. However, finding something close to nothing is difficult.
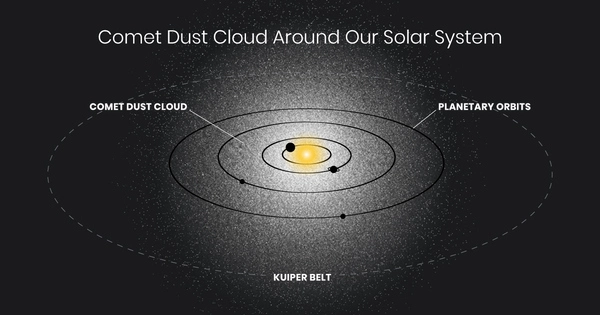
One possible explanation is that a shell of dust envelops our solar system and reflects sunlight all the way out to Pluto. When cleaning the house, it’s not uncommon to see airborne dust caught in sunbeams. This, however, must have a more exotic origin. Because the glow is so evenly distributed, comets — free-flying dusty snowballs of ice — are the most likely source. They fall in from all directions, spewing out a cloud of dust as the ices sublimate due to the heat of the Sun. If true, this would be a previously unknown architectural element of the solar system. It remained invisible until the arrival of very imaginative and curious astronomers, as well as the power of Hubble.
If our analysis is correct there’s another dust component between us and the distance where New Horizons made measurements. That means this is some kind of extra light coming from inside our solar system.
Tim Carleton
Aside from a tapestry of glittering stars, and the glow of the waxing and waning Moon, the nighttime sky looks inky black to the casual observer. But how dark is dark?
To find out, astronomers decided to sort through 200,000 images from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and made tens of thousands of measurements on these images to look for any residual background glow in the sky, in an ambitious project called SKYSURF. This would be any leftover light after subtracting the glow from planets, stars, galaxies, and from dust in the plane of our solar system (called zodiacal light).
When researchers completed this inventory, they found an exceedingly tiny excess of light, equivalent to the steady glow of 10 fireflies spread across the entire sky. That’s like turning out all the lights in a shuttered room and still finding an eerie glow coming from the walls, ceiling, and floor.

The researchers say that one possible explanation for this residual glow is that our inner solar system contains a tenuous sphere of dust from comets that are falling into the solar system from all directions, and that the glow is sunlight reflecting off this dust. If real, this dust shell could be a new addition to the known architecture of the solar system.
This idea is bolstered by the fact that in 2021 another team of astronomers used data from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft to also measure the sky background. New Horizons flew by Pluto in 2015, and a small Kuiper belt object in 2018, and is now heading into interstellar space. The New Horizons measurements were done at a distance of 4 billion to 5 billion miles from the Sun. This is well outside the realm of the planets and asteroids where there is no contamination from interplanetary dust.
New Horizons detected something a bit fainter that is apparently from a more distant source than Hubble detected. The source of the background light seen by New Horizons also remains unexplained. There are numerous theories ranging from the decay of dark matter to a huge unseen population of remote galaxies.
“If our analysis is correct there’s another dust component between us and the distance where New Horizons made measurements. That means this is some kind of extra light coming from inside our solar system,” said Tim Carleton, of Arizona State University (ASU).
“Because our measurement of residual light is higher than New Horizons we think it is a local phenomenon that is not from far outside the solar system. It may be a new element to the contents of the solar system that has been hypothesized but not quantitatively measured until now,” said Carleton.
Hubble veteran astronomer Rogier Windhorst, also of ASU, first got the idea to assemble Hubble data to go looking for any “ghost light.” “More than 95% of the photons in the images from Hubble’s archive come from distances less than 3 billion miles from Earth. Since Hubble’s very early days, most Hubble users have discarded these sky photons, as they are interested in the faint discrete objects in Hubble’s images such as stars and galaxies,” said Windhorst. “But these sky-photons contain important information which can be extracted thanks to Hubble’s unique ability to measure faint brightness levels to high precision over its three decades of lifetime.”