Fabric Inspection:
When the fabrics are received from the dyeing and finishing section, it needs to be checked, because, faulty fabrics can be supplied from dyeing and finishing. But the cutting section has to check it. Otherwise the end products will be faulty. For this, the fabric is being inspected by the quality inspector of the cutting section. They check the fabric fully and find out the faults. Then mark it so that, these faulty portion of the fabric can be rejected during spreading and cutting. Then the fabric is being stored for relaxation.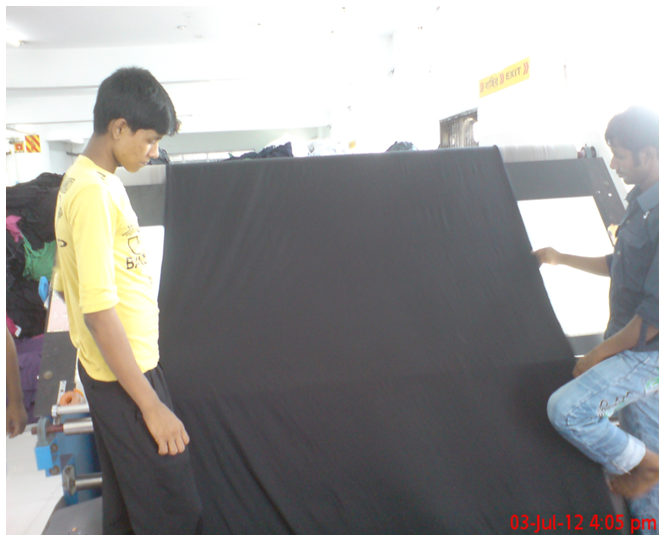
Fig: Finished Fabric Inspection
Fabric Relaxation:
When the fabric comes from the dyeing and finishing, the fabric remains a slightly hot. In dryer, stenter and compactor heat is applied on fabric. So moisture is removed from the fabric and it is not in actual condition. But if we keep the fabric in normal temperature and pressure for a certain time, the fabric absorbs moisture from the atmosphere and regains its original nature. This process is called fabric relaxation. Another cause of fabric relaxation is to maintain the dimensional stability of produced garments. When the fabric is being processed in different finishing machines, it goes under certain heat and pressure to give it proper shape. But when the heat and pressure is being withdrawn, the shape may change. So, if the dimension is became stabilized before cutting, no chance of strain in garments. So relaxation is very necessary before cutting.
Fig: Fabric Relaxation
Relaxation Period:
Fabric relaxation is performed for a certain period. This time is varied from fabric to fabric. But the minimum time of relaxation is twelve (12) hours. This time also may vary according to the buyer’s recommendation.
After fabric relaxation, different tests are performed for maintaining the proper quality.
Relaxed Loop Elongated Loop: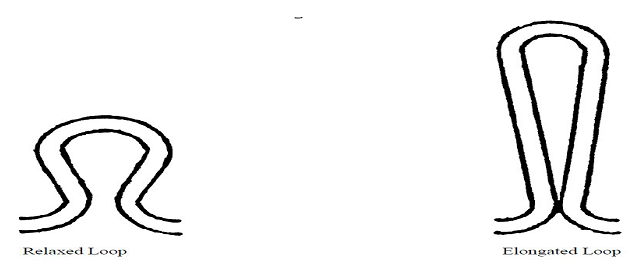
Test Cutting & Approval:
After testing the fabric, if it is seemed that, the fabric quality is ok, and then test cutting is done. Here a little amount of fabric is cut and sewed in sewing section. Then the garments are compared with the approved sample. Sewing allowance and other measurements are also observed. If everything is ok, then the approval is given and the fabric is ready for bulk production.
Marker Making:
For industrial garments preparation, marker making is a very important chapter for highest usage of fabric and for lowest wastage of fabric. In Divine Textiles Limited there is a strong team working for marker making in cutting section of each floor. This is a process which is performed to draw the pattern pieces on the fabric before cutting. This may be done by drawing the pattern pieces on the fabric directly or by drawing the pattern pieces on a thin marker paper and then placement the paper onto the fabric lay. So, we can define the marker as bellow. Marker is a thin paper which contains all necessary pattern pieces for all sizes for a particular style of garments in such a way that, fabric wastage would be least. The representation or drawing of the arrangement of identified garment pattern relevant to the cutting of a batch material. The marker is placed on the material and provides guideline for cutting. Marker may be on fabric or held in computer data files. Marker width is equal to the minimum fabric width and its length depends on the no of pattern sizes that will be drawn.
Preparations of Marker Making:
Before the marker making, some preparatory processes would be followed. In Divine Textiles Limited these processes are followed strictly:
- Marking Grain Line: Before marker making, the grain line of pattern and fabric must be marked.
- Fabric Measurement: Before marker planning, the fabric must be measured carefully. Because, marker width is relevant to the minimum fabric width.
- Fabric Faults: Fabric faults would be also under consideration. In a fabric roll, where any faults found, that points must be avoided for quality production and to least the fabric wastage.
- Cutting Table: Marker planner should consider the cutting table length before making marker. Marker length must be less than the cutting table length.
Methods of Marker Making:
There are two methods of marker making:
- Manual method
- Computerized method
In Divine Textiles Limited, manual method is used for marker making. Here marker is produced in two ways:
Marker drawn directly on fabric lay.
Marker drawn on marker paper.
Marker drawn directly on fabric lay:
This is the oldest and mostly used method for marker making. In this processes fabric is spreaded on cutting table and setting up all pattern pieces directly on to the fabric. Marking is done by chalk, pencil or pen. In order of this method, needs more time and experience.
Marker drawn on marker paper:
In this process marker is made on marker paper. All the pattern pieces are laid on a thin marker paper and drawn it. Then the marker paper in placed on fabric lay and used for fabric cutting. Before planning the marker, fabric length and width must be taken under consideration.
An analytical comment:
In this factory, manual method is used for marker making. The advantages of computerized method are given bellow comparing with the manual method:
Advantages:
- More suitable for large scale production than the manual method.
- Marker efficiency is higher than manual.
- Least wastage of fabric.
- Low production cost.
- Low labor cost.
- If required, print out of the marker could be got.
- Grading of the pattern could be done automatically.
- Few time consumption.
- Marker can be prepared quickly than manual.
Disadvantages:
- Initial investment is higher than manual.
- More skilled operator is needed than manual. I think everything has its positive and negative sides. But in comparison, the advantages of computerized marker are more than the manual. It increases the efficiency, workability and production of the factory. It saves valuable time and least fabric wastage. Thus saves money too. Moreover it attracts buyers with its modern facilities.
So, I think, it would be better to use computerized marker making system i.e. Computer Aided Design (CAD) instead of manual method. So the factory can think about it.
FABRIC SPREADING:
The appropriate type of spreading surface is determined by the fabric type, spreading equipment, cutting method, cutting equipment, and the firm’s quality standards. Spreading requires a flat, smooth surface. If the spreading surface doubles as a cutting surface, it also must be level. Spreading and cutting may be done on the same surface, but automated cutting often requires spreading and cutting to be done in adjacent but separate locations.
Spreading and cutting surfaces are available in standard widths that correspond to fabric width. Narrow fabric can be spread on a wider table. A spreading surface needs to be about 10 inches wider than the fabric. Spreading tables may have tracks or rails placed along one or both sides of a tabletop or just a few inches off the floor. This track helps guide and control the spreader as it moves up and down the length of the table. With some types of equipment, the table tracks are geared to synchronize the movement of the spreading machine with fabric unrolling, in order to regulate tension.
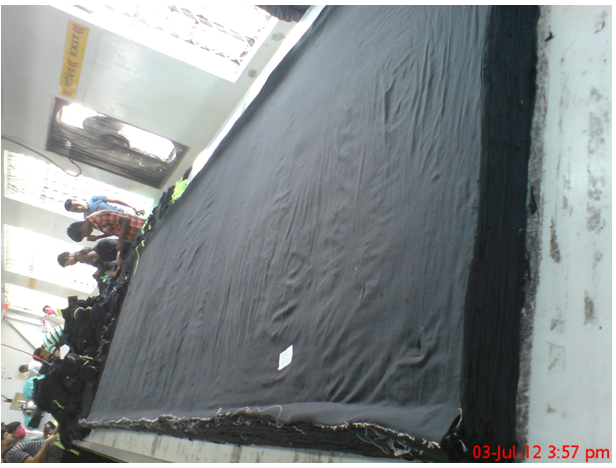

Fig: Fabric spreading
Spreading tables may also be very specialized for certain types of fabric and cutting equipment. Pin tables have rows of pins located below the surface that can be extended through slats to hold fabric in a precise location for accurate matching of pattern repeats. Vacuum tables are used to compress lay-up and prevent shifting or movement during cutting. A spread is covered with a plastic film that forms a seal over the lay-up when a vacuum is applied. A lay-up of quilted fabric can be compressed as much as 75 percent when the vacuum is used. This allows more plies in the lay-up and restricts the movement of slippery fabrics for more accurate cutting.
Cutting equipment may be moved to a lay-up as another lay-up is prepared further down the table, or fabric can be spread on one surface and then transferred to the cutting surface. Air flotation tables, when activated; allow easy movement of a lay-up onto an adjacent cutting area. A layer of air between the table surface and the bottom layer of paper reduces friction and allows a lay-up to be moved easily without putting stress on the fabric or the operators. Spreading tables with conveyor zed surfaces carry the fabric to the cutting machine so that no time is wasted. Ideally one lay-up can be cut while is being spread. Conveyors may be used with computerized cutting systems, large die presses, and laser cutters.
Garments Spreading Machines:
Fig: Automatic spreading Machine with fabric control devices
The fundamental purpose of spreading machines is to superimpose layers of fabric in a smooth, tension-free manner for accurate and efficient cutting. Manually operated spreading machines can be as simple a roll bar mounted on four wheels that is pushed up and down a spreading table by an operator. Manual spreaders travel only as fast as an operator moves them, while some of the faster automated machines can spread 100-150 yards per minute. Spreading speed can only be utilized on long spreads with few defects. Spreading speed may affect productivity, quality, and cost of the operation, but it should not be the primary focus for purchase of new equipment. Manual spreading machines may be used by small firms as the primary spreading device and by large firms for short spreads. As spreading machines become more sophisticated, they are motor driven and have fabric control devices included increasing productivity, decreasing variability, and making spreading more cost-efficient.
Fabric control device during garments spreading:
Fabric control devices are mechanisms that control fabric as it is carried up and down the table:
(i) Tensioning mechanisms,
(ii) Positioning devices,
(iii) End treatment systems.
(i) Tensioning involves synchronizing the rate of spreading with the rate fabric is unrolled. A positive feed system utilizes a covered roller that is driven and timed to the movement of the machine. It prevents the momentum of a large roll from continuing to unwind when the machine slows down or stops. Roller covers of different materials may be used to give better gripping power for different types.
(ii) Positioning devices and sensors monitor position and control fabric placement during spreading. These devices improve the quality of a spread. Electronic edge sensors monitor selvages as fabric is spread. A deviation from the proposed alignment triggers a motor that shifts the roll to the correct position. Alignment can be held to one-eighth inch tolerance with these devices.
(iii) Width indicators may sound an alarm to alert the operator whenever fabric becomes narrower than the established width. Width variations are analyzed to determine where in the marker they fall, whether the fabric will still fit the marker, or whether the variation should be treated as a defect and removed.
(iv) End treatment devices are used with spreaders but are separate and placed at the end of the spread. The specific end treatment equipment needed depends on whether the spreading mode is face-to-face or face-one-way. A face-to-face spread utilizes an end catcher and folding blade that work together. These are mechanical parts, mounted at opposite ends of the marker to catch and hold the fabric as the blade shapes and creases the fold. An over feed device may be built into the spreading unit, which automatically feeds extra material when a fold is to be made. End treatments have a major impact on fabric waste. There must be enough fabric at the end of a lay to retain it in place.
FABRIC CUTTING:
After completing the fabric spreading then the fabric cutting is started. To cut out pattern pieces of garment components as per exact dimension of the patterns from a fabric lay is called fabric cutting. The term fabric cutting is only applicable for garments manufacturing technology.
Fabric cutting should be done accurately as per exact dimension of the pattern pieces in the marker. Accurate cutting depends on methods of cutting and marker planning. If manual cutting method is used, then cutting accuracy depends on sharpness of knife, skill ness of operator, and attentiveness of operator. Computer controlled cutting and die cutting have their self cutting accuracy.
During fabric cutting, the friction between the fabric and the blade produces temperature in the blade; the temperature may be up to 300°C. If the fabric contains synthetic fibers, e.g. nylon, polyester, acrylic or their blends, then fused edge may result in the fabric. As because most of those fibers melt at around 250°C. Therefore, sticking of cut edge of fabric will increase the fabric wastage Moreover, the fused edge after cooling will form hard bid, which will be problem of irritation during use of garments.
To avoid the problem of fused edge formation, the following steps may be taken
– Reduce the height of the lay;
– Reduce the cutting speed;
– Use anti-fusion paper in the lay at regular interval;
– Lubricate the knife during cutting.
Surface of the cutting table depends on methods of fabric cutting. The table surface should be capable to support the lay as well as to ensure that all the plies are cut at a time during fabric cutting.
Whatever the cutting method is used for fabric lay cutting, it should be ensured that the shape of the cut components from top to bottom lay are of exact size and shape, otherwise the garments produced will be defective.
Fabric cutting methods are as follows:
| Manual Method | Computerized Method |
| Scissor | Knife Cutting |
| Round knife | water jet |
| Band knife | Laser cutting |
| Straight knife | Plasma torch cutting |

Fig: Scissor
Fig: Metal Hand Gloves
Summary Working Procedure in Cutting Section:
- Follow production planning.
- Sample collect from sample section with pattern and garments approved.
- Lay order sheet/ratio sheet fill up by cutting section (fabric width, Item, Coloretc.).
- Lay order sheet fill up ok then send to cad section for marker making.
- Marker making ok.
- Fabric requisition from cutting section to store for cutting according to plan.
- Fabric is coming in cutting table as per marker and cutting plan.
- Fabric matches to trim card by merchandiser approved fabric width & length as per marker.
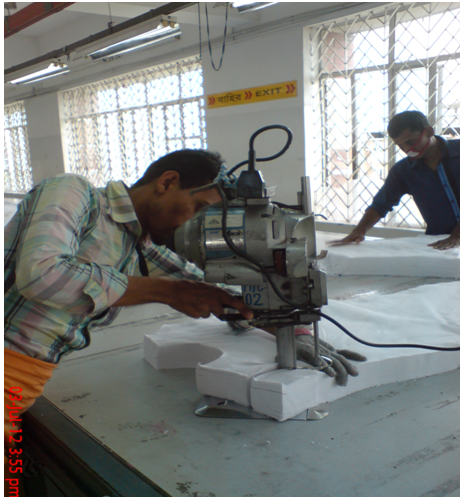

Fig: Straight knife cutting machine
- Then layering starts manual & machines all fabric. Pocketing and interlining.
- After lay then spread marker upon on the fabric.
- Marker check by pattern in quality people.
- Keep all document make & style. Color. And size wise send report to store & sewing line.
- Before cutting cutter man attach clamp. Gum tap on the layer.
- If marker have drill mark then need to drill.
- Cutting start by cutter man.
- Then group and ratio wise stricken.
- As per lay order sheet make bundle chart and send to i.e. Section for bundle card printing.
- As per bundle chart wise numbering.
- Then panel check.
- If have any fault need to replace cut bundle roll and shad wise then bundle and send to line by input girl.
- If have any fusing, embroidery than send to this section.
When the cutting process is complete, the entire garment components are inspected for required production.
Spreading and Cutting Stage Problem:
Effect Cause Lack of Sufficient fabric Relaxation
Operators are not allowing sufficient time for relaxation
Too many no of plies during spreading
Ply height was found to be more than 7” Excessive dragging during spreading
Higher dragging tension maintained between spreader roller to lay
Blunt knife edges Edges of knife are not sharp and it leads to uneven shaping
Sticker Tagging:
After complete the cutting, the fabric is tagging by the sticker. The sticker tagging is an important part in this section. Due to fabric numbering or batching the sticker is tag on the cutting fabric surface.

Fig: Sticker Tagging for Batching
Bundling:
After cutting the fabric lay and tagging the sticker, all the garments components in stack form is shorted out as per size and color. To avoid mistake in sorting, it is better to use code number on each pattern.

Fig: Sorting / Bundling
When sorting / bundling are complete, all the garment components are sending to the sewing section.