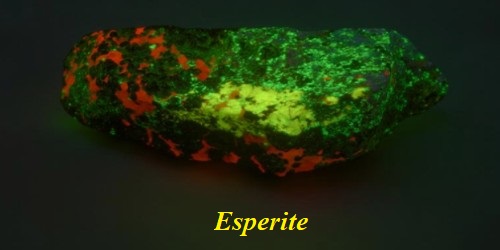
Esperite is a rare complex calcium lead-zinc silicate [PbCa3Zn4(SiO4)4] related to beryllonite and trimerite that used to be called calcium larsenite. It is one of the 70 some fluorescent minerals from Franklin and Sterling Hill, New Jersey. It will fluoresce a nice yellow color under short-wave ultraviolet light. It was named in honor of Esper F. Larsen Jr. (1879–1961), petrologist of Harvard University.
General Information
- Category: Silicate mineral
- Formula: [PbCa3Zn4(SiO4)4]
- Crystal system: Monoclinic
- Crystal class: Prismatic (2/m) (same H-M symbol)
Properties
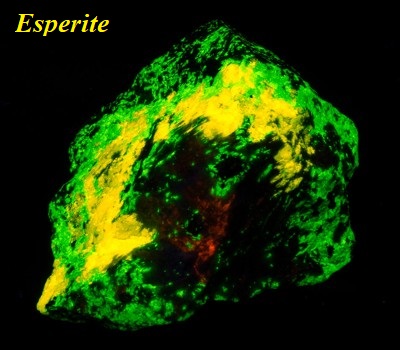
Esperite has a white, greasy appearance in daylight and is much prized for its brilliant yellow-green fluorescence under a shortwave ultraviolet light. It is found in association with calcite, franklinite, willemite, hardystonite, and clinohedrite.
- Color: White
- Crystal habit: Typically massive
- Fracture: Conchoidal, brittle
- Mohs scale hardness: 5 – 5.5
- Luster: Vitreous
- Streak: White
- Diaphaneity: Subtranslucent to opaque
- Specific gravity: 4.28 – 4.42
Occurrence
Esperite is found in significant quantities only at Franklin and Sterling Hill, New Jersey. It has also been found as prismatic crystals up to 1 mm in length at the El Dragon Mine, Potosi, Bolivia in association with allophane, chalcomenite, clinochalcomenite, and barite.
Association: Willemite, zincite, hardystonite, glaucochroite, andradite, franklinite, clinohedrite, leucophoenicite, larsenite, copper.
Information Source: