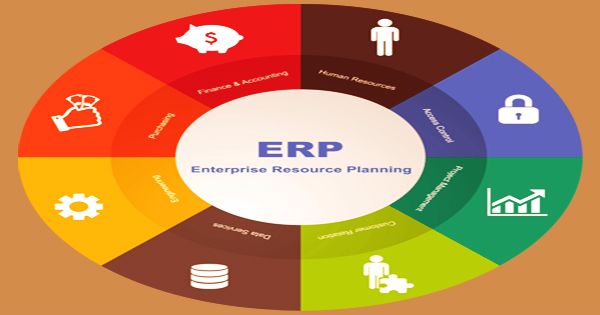
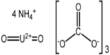
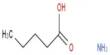
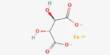
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a software framework used for the management and maintenance of a company’s functions. For businesses, many ERP software applications are relevant because they help them incorporate resource planning by combining all the processes required with a single framework to operate their businesses. ERP is generally alluded to as a classification of business the executives programming regularly a set-up of coordinated applications that an association can use to gather, store, oversee, and decipher information from numerous business exercises. The errands are normally done continuously.
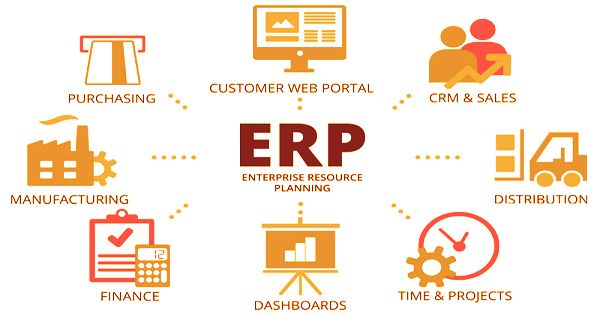
Functions of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Using standard databases managed by a database management system, ERP actually offers an organized and continuously updated view of core business processes. Planning, ordering inventory, sales, marketing, finance, human resources, and more can also be combined with an ERP software framework. ERP software is part of the IT business, and it is now considered a multi-billion-dollar industry due to its utility and popularity. Without an ERP application, every division would have its framework enhanced for its particular undertakings. With ERP programming, every office actually has its framework, yet the entirety of the frameworks can be gotten to through one application with one interface.
The ERP framework incorporates different organizational structures and allows error-free transactions and development simpler, thus improving the effectiveness of the company. ERP apps often allow various departments to more efficiently interact and exchange information with the rest of the business. It gathers data about the action and condition of various divisions, making this data accessible to different parts, where it very well may be utilized gainfully. ERP programs are generally known as a business the executive’s programming. They include a large group of utilizations that cooperate to:
- Gather data
- Store it for future reference
- Manage and sort the information for easier access
- Interpret the data for use by the business
By linking knowledge about development, finance, delivery, and human resources together, ERP applications will help a company become more self-aware. For businesses looking to change how effectively they work, ERP offers a variety of services. To provide the fastest and most reliable services, the system used is continuously updated. However, it varies from conventional system architecture to build an ERP system. Since it interfaces various advances utilized by each aspect of a business, an ERP application can dispense with expensive copy and inconsistent innovation. The cycle regularly coordinates creditor liabilities, stock control frameworks, request checking frameworks, and client information bases into one framework.
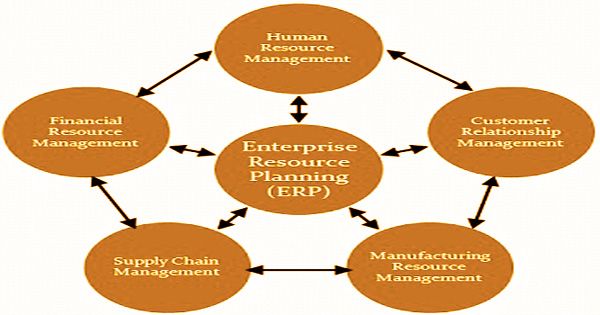
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
As the name suggests, the primary objective of ERP is to control the different resources within the business to ensure that they are used in a cost-effective manner. It is also designed to ensure that all resources are appropriately used. Not all ERP packages were produced from a manufacturing core; ERP vendors started to assemble their packages with components of finance and accounting, maintenance, and human resources in different ways. ERP contributions have developed throughout the years from conventional programming models that utilize physical customer workers to cloud-based programming that offers far off, electronic access.
In the 1990s, ERP systems experienced rapid growth; “ERP II” was coined in 2000 in an article by Gartner Publications entitled ERP Is Dead Long Live ERP II. It identifies web-based software that provides employees and collaborators (such as suppliers and customers) with real-time access to ERP systems. ERP works especially well for controlling and handling items such as the production capacity of a company, the amount of cash, the raw materials at its disposal, payroll details, and purchase orders. An ERP framework doesn’t generally wipe out failures inside the business. The organization needs to reevaluate the manner in which it’s composed, or, more than likely it will wind up with inconsistent innovation.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software-accounting, revenue, ordering, and manufacturing-encompasses several different areas within a business. Owing to the inability of an organization to abandon old working processes that are incompatible with the program, ERP systems typically struggle to achieve the goals that motivated their implementation. Most ERP frameworks fuse best practices; this implies the product mirrors the merchant’s understanding of the best method to play out every business cycle. A few organizations are likewise hesitant to relinquish old programming that functioned admirably previously. The key is to forestall ERP ventures from being part into numerous littler undertakings, which can bring about cost, invades. The data inside an ERP framework shows the necessary data to customers in order to keep them aware of the ability of the organization to operate and generate revenue.
Information Sources: