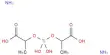
Edingtonite is a white, gray, brown, colorless, pink or yellow zeolite mineral. Its chemical formula is BaAl2Si3O10·4H2O. It is a grayish-white zeolitic mineral, in tetragonal crystals. It is a hydrous silicate of alumina and baryta. It is an unusual mineral in that it has two polytypes or two phases that are not yet recognized as separate minerals. It has varieties with tetragonal, orthorhombic or triclinic crystals.
Whilst some claim it was named after Scottish mineral collector James Edington (1787–1844), most sources (including the knowledgable mineralogist Haidinger) credit Thomas Edington FRSE (1814-1859), a Scottish geologist and mineralogist of greater fame.
General Information
- Category: Tectosilicate
- Formula: BaAl2Si3O104H2O
- Color: Brownish gray, Colorless, Gray, White, Pink
- Crystal system: Orthorhombic, some are tetragonal
- Member of: Zeolite Group

Properties
- Cleavage: {110} Perfect
- .Density: 2.69 – 2.7, Average = 2.69
- Diaphaneity: Transparent to translucent
- Fracture: Uneven – Flat surfaces (not cleavage) fractured in an uneven pattern.
- Hardness: 4-5 – Fluorite-Apatite
- Luster: Vitreous (Glassy)
- Streak: white
- Mohs scale hardness: 4 – 5
- Optical properties: Biaxial (-)
The structure actually contains open channels that allow water and large ions to travel into and out of the crystal structure. The size of these channels controls the size of the molecules or ions and therefore a zeolite like edingtonite can act as a chemical sieve, allowing some ions to pass through while blocking others.
Information Source: