Form of Letter of Credit:
A letter of credit (L/C) may be two forms. These as below:
- Sight payment credit.
- Deferred payment credit.
(i) Sight payment credit:
The most commonly used credits are sight payment credits. These provide for payment to be made to the beneficiary immodestly after presentation of the stipulated documents on the condition that the terms of the credit have been complied with. The banks are allowed reasonable time to examine the documents.
(ii) Deferred payment credit:
Under a deferred payment credit the beneficiary does not receive payment when his presents the documents but at a later date specified in the credit. On presenting the required documents, he received the authorized banks written undertaking to make payment of maturity. In this way the importer gains possession of the documents before being debited for the amount involved.
In terms of its economic effect a deterred payment credit is equivalent to an acceptance credit, except that there is no bill of exchange and therefore no possibility of obtaining money immediately through a descant transaction. In certain circumstances, how ever, the banks payment undertaking can be used as collateral for an advance, though such as advance will normally only be available from the issuing or confirming bank. A discountable bill offers wider scope.
4.4.1.bTypes of Letter of credit:
The letter of credit can be either recoverable or irrecoverable. It needs to be clearly indicated hether the letter of credit recoverable or irrecoverable.When threr is no indication then the letter of will be deemed to be a recoverable L.C .The details as follows:
Irrevocable letter of credit —cannot be cancelled or amended without the consent of all parties, including the beneficiary. This is the most common type of documentary credit in the international trade of goods
Revocable letter of credit —can be cancelled by the issuing bank without warning to the beneficiary
Government letter of credit —That letter of credit, which are done by the Defense Ministry and other Ministries of the government.
Master or mother letter of credit — The L/C which come from out side the country to the exporter from importer that is mother or master letter of credit.
Other classes of letter of credit:
Confirmed letter of credit —a ‘confirming’ bank (either in Australia or overseas) agrees to pay you under a documentary credit, whether or not payment is received from the issuing bank
Transferable letter of credit —the original beneficiary of the documentary credit can transfer their rights to a second beneficiary on the same or similar terms as the original documentary credit (the original beneficiary may be an intermediary between you and your ultimate buyer)
Revolving letter of credit —allows automatic reinstatement of the documentary credit after the amount for the original shipment has been paid, so subsequent shipments to your buyer are covered by a single documentary credit
Standby letter of credit —a contingency documentary credit which you can draw on if your buyer, using another payment method, defaults in making a payment to you under the export contract
Back to back/complementary letter of credit —where your buyer is the beneficiary of a separate documentary credit (in their capacity as a seller under a separate sales contract), they can sometimes use this credit as security to apply to their bank for a complementary documentary credit to cover their payment under an export contract with you
FOREIGN COUNTRY BANGLADESH
|
|
|
|
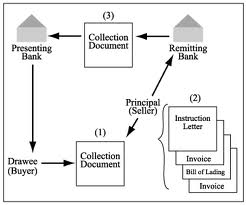
Figure: Back to Back Credit Procedure
Clean or open letter of credit — The letter of credit, which provides assurance of payment bill of exchange without submission, of any export documents that is called clean letter of credit.
At sight letter of credit— That letter of credit, which expires ninety days i.e. with in this period the documents must be sending to the negotiating bank .
Deferred payment letter of credit —That letter of credit, which expires one hundred & eighty days i.e. with in this period the documents must be sending to the negotiating bank .
Contract letter of credit
Refinance letter of credit
Marginal letter of credit
Traveler’s Letter of credit
Red clause—pre-shipment finance that allows you (the beneficiary) to receive an advance from the advising bank of all or part of the amount owed to you under a documentary credit so you can buy raw materials or other inputs required to manufacture the product for export.
Acceptance Credit- With an acceptance credit payment is made in the form of a tern bill of exchange drawn on the buyer, the issuing bank or the pendent bank. Once he has fulfilled the credit requirements, the beneficiary can demand that the bill of exchange be accepted and returned to him. Thus the accepted bill takes the place of a cash payment.
4.4.1.c Parties to a Letter of Credit:
The applicant
The applicant is the party that induces the Banks to issues the letter of credit. The applicant is normally obligated to reimburse the Bank for any payment made under letter of credit.
The Issuing Bank
The issuing Bank is the Bank that issues the letter of credit. The issuing Bank undertakes an absolute obligation to pay upon presentation of documents drawn in strict conformity with the terms and condition of the letter of credit.
The Advising Bank
An advising Bank simply advises a letter of credit without any obligation on its part. However, the advising Bank shall take reasonable care to check the apparent authenticity of the credit that it advises. The advising Bank is typically a Bank in the Beneficiaries.
The Beneficiary
The beneficiary is the party entitled to drawn payment under the letter of credit. The beneficiary will have to present the required documents to avail payment under the letter of credit.
The Confirming Bank
The confirming Bank confirms that the issuer has issued a letter of credit. The confirming Bank becomes directly obligated on the credit to the extent of its confirmation and by confirming the Bank receives the rights and obligation of an issuer. It is to be noted that confirmation is normally done by the advising bank or by a third Bank in the Beneficiary locate.
The Nominating Bank
The Bank where drafts drawn under the credit are payable. In case of a usance credit where drafts are to be accepted by this Bank.
The Negotiating Bank
The Bank that negotiates document under letter of credit upon presentation. Typically advising Bank as nominated as negotiating Bank.
The Reimbursement Bank
The Bank nominated by the issuing Bank to provide reimbursement to the negotiating Bank or sometimes the payee Bank.
The Transferring Bank
A Bank is specifically authorized in the credit as a Transferring Bank. Typically Advising Bank is nominated as Transferring Bank. Such as Bank is authorized to make the documentary credit available in whole or in part to one or more other Beneficiary.