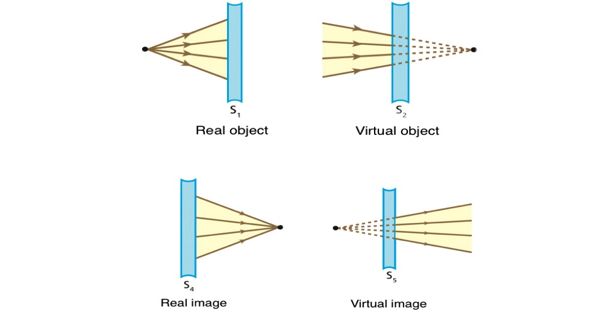
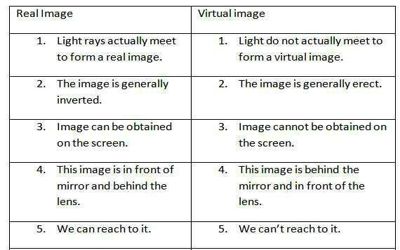
Real image and virtual image are the two classifications of the image that is formed by reflection or refraction of light rays. A real image is formed when rays converge, whereas a virtual image occurs where rays only appear to diverge.
The real image implies the representation of an actual object, produced when the light rays arising from a single source converge at a particular (real) point. These are formed on the front side of the mirror. On the contrary, the virtual image can be understood as the image produced due to the apparent divergence of rays of light from a definite point. These are assumed to be formed at the backside of the mirror. In general, real images are inverted, whereas virtual images are erect.
Difference between Real Image and Virtual Image –
REAL IMAGE
- A real image can be defined as the image produced by the reflection or refraction when the light rays arising from the object converge at a specific point.
- A real image is an image that is formed when the light rays meet at a particular point after reflection from the mirror.
- The real image is produced by the actual intersection of the rays of light. Hence they can be captured on the screen.
- A real image can be described as a reproduction of a real object formed at the point where the light rays originating from a particular object converge. It can be obtained on the screen when the screen is set in the plane of the image. The image formed on the cinema screen, of the theatre with the use of the projector is the practical example of a Real image.
- A concave mirror or a converging lens is used to produce a real inverted image, wherein the object should be located in front of the lens or mirror, at a place farther than the focus. Depending upon the position of the object, the size of the image may vary, i.e. it can be diminished or enlarged.
- The concave mirror is used in producing a real image.
VIRTUAL IMAGE
- A virtual image refers to an image produced when the light rays originating from an object only appear to strike at a certain point.
- Virtual image refers to the image which forms when the light rays appear to meet at a definite point, after reflection from the mirror.
- There is an imaginary intersection of the rays of light in the case of a virtual mage, so it cannot be cast on the screen.
- The virtual image is understood as an optical image that is produced from the apparent divergence of the rays of light emanating from a point on an object. So, an upright image is formed at the point where the rays only seem to diverge, but do not converge in reality.
- A diverging lens or convex mirror is used to produce a virtual image that is diminished in size when compared to the actual size of the object. However, it can also be formed by the converging lens and concave mirror, when the object is between focus and pole.
- Virtual images are produced by a plane mirror, convex mirror, and sometimes by concave mirror also.
Information Source: