Many changes occur in our daily lives we are unaware of, such as the sourness of milk, the rusting of iron, the stretching of a rubber band, the toasting of bread, the melting of wax, the lighting of a match, and so on. All of the changes that occur around us are either physical or chemical in nature. Physical changes are those that alter the physical properties of a substance without altering its internal structure.
A chemical change, on the other hand, is one that affects the internal structure of the substance, resulting in the formation of a new substance. So, read the article to understand the distinction between physical and chemical change.
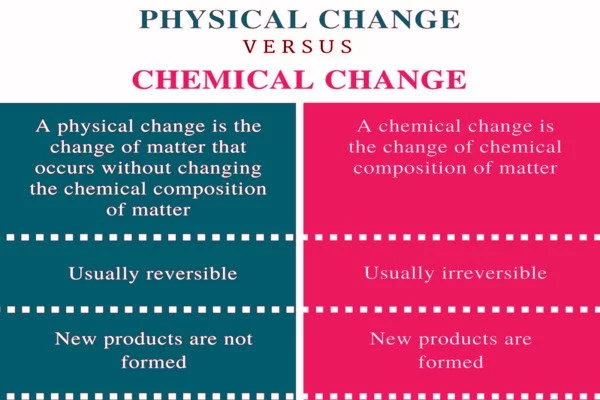
Difference between Physical Change and Chemical Change –
PHYSICAL CHANGE
- Physical change is defined as a change in which molecules are rearranged but their internal composition remains unchanged. Physical Change is defined as a change in which molecules are rearranged but their internal composition remains unchanged. Some common examples of physical change include vaporization, condensation, and the freezing/melting/boiling of water.
- Physical change is a process in which a substance’s physical properties, such as shape, size, color, volume, appearance, state (i.e. solid, liquid, gas), and so on, change without changing its molecular composition. These are volatile changes that can be reversed using simple physical methods.
- Physical changes are only temporary and easily reversed. Only the form of the substance is altered here, and no new product is created. Simple physical techniques can be used to recover the original matter.
- The same element or compound exists before and after the change, implying that the object’s original characteristics remain unchanged. Melting wax, boiling water, dissolving sugar in water, chopping wood, crumpling paper, and so on.
- Changes in the physical attributes of the substance, such as shape, size, appearance, texture, odor, density, and so on, are observed during the physical change. No or very little energy is absorbed or released in the form of heat, light, or sound energy.
CHEMICAL CHANGE
- Chemical Change is the process by which a substance transforms into a new substance with a different chemical composition. Chemical Change refers to the process by which a substance transforms into a new substance with a different chemical composition. Chemical changes include combustion, metabolism, egg cooking, and so on.
- Chemical change is defined as the process by which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged or combined to form a new substance. When a substance undergoes a chemical change, its chemical properties change and it is transformed into a different substance with a different chemical composition. Some signs of chemical change include the evolution of energy, the formation of bubbles, changes in odor, and temperature changes.
- In nature, chemical changes are permanent, which means they cannot be reversed even by reversing conditions. Here, a completely different product is formed, with properties that differ greatly from those of the reacting substances. Because the original matter no longer exists, it cannot be recovered.
- Alternatively, it is known as a chemical reaction, in which the substances involved are known as reactants and the result of the reaction is known as a product. Because of the formation of the new product, the energy change is one of the characteristics of a chemical change. Once the chemical change occurs, it cannot be undone. For instance, adding vinegar to baking soda, bleaching a stain, fermenting grapes, and so on.
- Chemical change involves the change in chemical properties of the substance, i.e. change in its chemical nature. Wherein enormous energy is absorbed or given out as heat, light, or sound energy