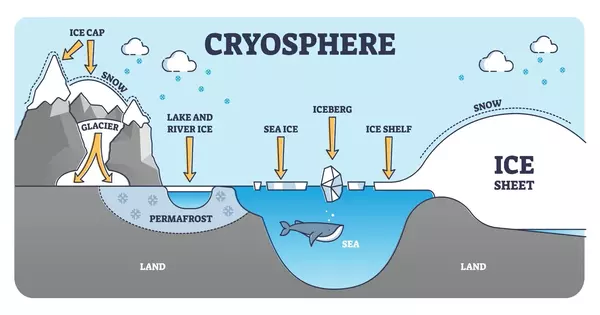
The cryosphere is the part of the Earth’s surface where water exists in its solid form, including snow, ice, glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets, sea ice, and permafrost. It plays a crucial role in the Earth’s climate system as it reflects a significant portion of the incoming solar radiation back to space, regulating the Earth’s temperature.
The cryosphere refers to the frozen parts of the Earth’s surface, including snow, glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets, sea ice, and permafrost. These frozen areas play a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate and supporting ecosystems around the world.
The cryosphere is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, with rising temperatures causing the melting of glaciers and sea ice, the thawing of permafrost, and other significant changes that can have far-reaching effects on the planet’s ecosystems and human societies. Understanding the cryosphere and how it is changing is essential for predicting the future impacts of climate change and developing effective strategies for mitigating its effects.
\Changes in the cryosphere can have significant impacts on the environment and human societies, such as sea level rise due to melting glaciers and ice sheets, changes in water availability, and alterations in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. The cryosphere is currently undergoing significant changes due to global warming, which is causing the melting of glaciers and ice sheets, and reductions in the extent and thickness of sea ice in many regions of the world.
The cryosphere is an essential component of the global climate system, generating significant connections and feedbacks through its influence on surface energy and moisture fluxes, clouds, precipitation, hydrology, atmospheric and oceanic circulation. The cryosphere influences the global temperature and climate model responses to global changes through various feedback processes. Ice covers approximately 10% of the Earth’s surface, although this is fast reducing. The term deglaciation refers to the disappearance of cryospheric characteristics. Cryology is the study of cryospheres.