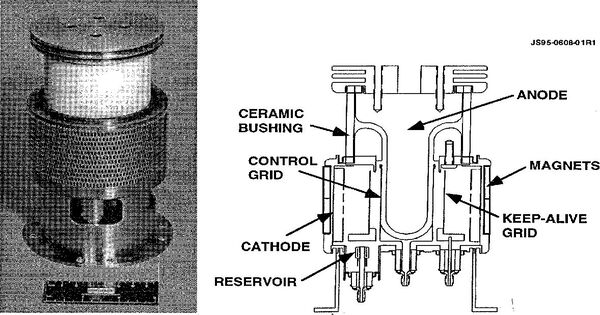
A crossatron is a high-power pulsed modulator device made up of a cold cathode gas-filled tube that incorporates features from thyratrons, vacuum tubes, and power semiconductor switches. This switch can operate at voltages of more than 100 kilovolts thanks to the use of deuterium gas fill to improve the Paschen breakdown voltage, axial molybdenum cathode corrugations to offer a larger current capability and a molybdenum Paschen shield.
It is a cold-cathode, gas-filled tube used in electronics. It functions similarly to a thyratron, but with a few notable changes. The terminal curvature of the Paschen shield and the adjacent section of the anode are chosen to produce a voltage stress at the curved Paschen shield surface in the range of 90-150 kV/cm in response to a 100-kV difference. In comparison to a hydrogen-filled thyratron, the crossatron has a longer attainable lifetime and higher dependability due to its cool cathode.
It has rapid start-up times and performs well under high temperatures, radiation, electromagnetic pulses, and repeated overvoltage and overcurrent events. Crossatron switches are used in power conditioning for high-voltage phase-control rectifier service, high-frequency DC-to-AC inverter modulation, voltage regulation, command charging, and fault protection.
Here are some key points about Crossatron:
- Cold Cathode: Unlike many other vacuum tubes which require heating of the cathode to emit electrons, Crossatrons operate with a cold cathode, meaning they don’t need heating elements to function. This feature makes them more efficient and reliable for certain applications.
- Gas-filled: Crossatrons are filled with a gas, often hydrogen or a mixture of hydrogen and other gases. The gas plays a crucial role in the operation of the tube, aiding in the initiation and maintenance of the discharge.
- Triggering Mechanism: Crossatrons can be triggered into conduction by various methods, including applying a high-voltage pulse to the anode or cathode. Once triggered, they can conduct a significant amount of current.
- High-Power Switching: These tubes are often used in high-power switching applications where rapid and reliable switching of high currents is required. They find applications in areas such as radar systems, high-energy physics experiments, and certain types of industrial equipment.
- Reliability: Crossatrons are noted for their dependability and extended life when compared to other types of vacuum tubes. This is due in part to their cold cathode design, which avoids the requirement for heating elements that degrade with time.
Pulsed power applications include high-speed capacitor and pulse-forming network discharge, repeating inductive-energy-storage circuit opening, square wave pulse modulation in hard-tube modulators, and fault protection.