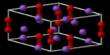
Colemanite [(Ca2B6O11·5H2O) or (CaB3O4(OH)3·H2O)] is a borate mineral found in evaporite deposits of alkaline lacustrine environments. It is a white crystalline mineral, typically occurring as glassy prisms, consisting of hydrated calcium borate.
Colemanite is a secondary mineral that forms by alteration of borax and ulexite. It is a borate mineral, which forms by the alteration of ulexite and borax. It was first discovered in 1884 from the Furnace Creek in Death Valley. The mineral was named after William Tell Coleman, owner of Harmony Borax mine where the mineral was first found.
General Information
- Category: Inoborates
- Formula: Ca2B6O115H2O
- Crystal system: Monoclinic
- Crystal class: Prismatic (2/m) (same H-M symbol)

Properties
Colemanite can either be colorless, or can be found in a range of colors including white, yellowish-white, gray, and gray-white. It has a transparent to translucent appearance, perfect cleavage, white streak, and vitreous luster. The relative hardness of colemanite is 4.5, and its density is 2.42 g/cm3.
- Color: Colorless, white, yellowish, grey
- Crystal habit: Massive granular to coarsely crystalline, most commonly nodular.
- Fracture: Brittle uneven to subconchoidal
- Mohs scale hardness: 4.5
- Luster: Vitreous
- Streak: White
- Diaphaneity: Transparent to translucent
- Specific gravity: 2.42
- Optical properties: Biaxial (+)
Occurrence
Colemanite occurs as a common constituent in borate deposits, formed in arid alkaline lacustrine environments that are deficient in carbonate and sodium. It is closely associated with Celestine, calcite, gypsum, kernite, luneburgite, gowerite, ginorite, nobleite, priceite, searlesite, ulexite, and howlite.
It was first described in 1884 for an occurrence near Furnace Creek in Death Valley and was named after William Tell Coleman (1824–1893), owner of the mine Harmony Borax Works where it was first found.
Uses
Colemanite is an important ore of boron and was the most important boron ore until the discovery of kernite in 1926. It has many industrial uses, like the manufacturing of heat-resistant glass.
Information Source