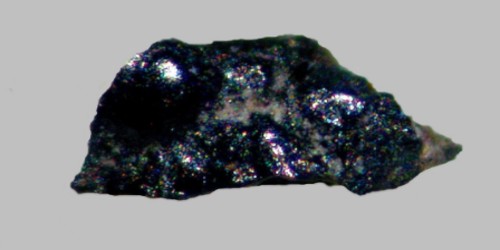
Chvaleticeite is a monoclinic hexahydrite manganese magnesium sulfate mineral and soft monoclinic mineral with formula: (Mn2+, Mg)[SO4]·6(H2O). It occurs in the oxidized zone of manganese silicate deposits with pyrite and rhodochrosite that have undergone regional and contact metamorphism. It is defined as the manganese dominant member of the hexahydrite group.
Chvaleticeite is named after the city Chvaletice, Bohemia, in the Czech Republic.
General Information
- Category: Sulfate mineral
- Formula: (Mn2+, Mg)[SO4]·6(H2O)
- Crystal system: Monoclinic
- Crystal class: Prismatic (2/m) (same H-M symbol)

Properties
Chvaleticeite and minerals like it have been studied for their hydrogen bonding and incongruent melting properties as they are predicted to form in the relative environments of Mars and other bodies in the solar system.
- Color: White, pale pink, yellowish green
- Crystal habit: Efflorescence coatings, minute granular
- Cleavage: Poor
- Mohs scale hardness: 1.5
- Luster: Vitreous
- Streak: White
- Diaphaneity: Translucent to transparent
- Specific gravity: 1.84
Occurrence
Chvaleticeite was discovered in a sulfate paragenesis in the oxidation zone of the Upper Proterozoic volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposit of pyrite-manganese ores at Chvaletice.
It was found in association with melanterite (it can form by partial dehydration), Mg-jokouite, Mg-ilesite, rozenite, copiapite, and gypsum. This paragenesis allows heptahydrates and tetrahydrates to dominate over pentahydrates and hexahydrates. Chvaleticeite is completely soluble in water.
Association: Melanterite, magnesian–manganoan melanterite, epsomite, magnesian–ferroan mallardite, magnesian jokokuite, magnesian ilesite, rozenite, copiapite, gypsum (Chvaletice, Czech Republic); apjohnite, copiapite, epsomite, gypsum (J´achymov, Czech Republic).
Information Source: