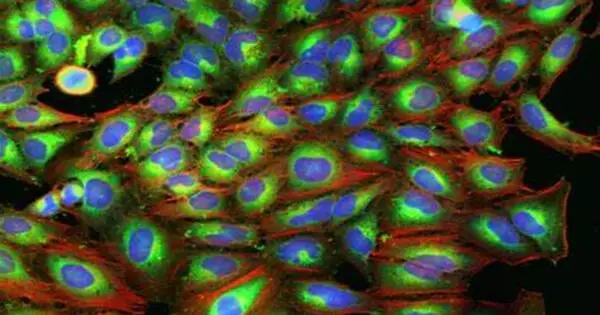
The Cell Painting assay is a high-content, high-throughput imaging technique for capturing a diverse range of cellular phenotypes in response to various perturbations. It entails staining cells with a combination of fluorescent dyes that target specific cellular structures or components, allowing the visualization of multiple cellular features at the same time. The goal is to obtain detailed information about cell morphology and function, which can be used in a variety of applications such as drug development, toxicity testing, and understanding cellular pathways. Many pharmaceutical companies, including Recursion Pharmaceutical and AstraZeneca, have used this method to profile compounds.
Methodology
Cells are stained with six fluorescent dyes that identify different cellular compartments, including nuclei, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and actin, in the Cell Painting assay. The images are then captured in high resolution using automated fluorescence microscopy, and image analysis algorithms are used to extract thousands of morphological features. These characteristics serve as the foundation for the morphological profile for each perturbation.
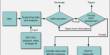
Here’s a basic overview of the Cell Painting Assay process:
- Cell Culture: Cells are cultured and treated according to the experimental design. The cells are typically grown on a glass-bottomed microplate for imaging purposes.
- Fixation: Cells are fixed to preserve their structure. This step involves the use of a fixative such as formaldehyde.
- Staining: A set of fluorescent dyes is used to stain different cellular components. These dyes can target various cellular structures such as the nucleus, cytoskeleton, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria. Each stain emits light at a specific wavelength, allowing for the identification and quantification of different cellular structures simultaneously.
- Image Acquisition: The stained cells are imaged using a fluorescence microscope equipped with appropriate filters for each fluorophore. Multiple images are typically acquired for each well to capture the different staining channels.
- Image Analysis: Using specialized image analysis software, the acquired images are then processed and analyzed. Based on the intensity and localization of fluorescent signals, this software identifies and quantifies various cellular features. The analysis can reveal details about cell morphology, organelle structure, and other cellular properties.
Applications
The Cell Painting assay has become a powerful tool in the field of drug discovery due to its ability to capture a wide range of cellular responses. Researchers can identify potential drug candidates, toxicity, and the mechanism of action of existing drugs by comparing the morphological profiles of cells treated with different compounds.
The assay, when combined with genetic perturbations, can be used to determine gene function or to understand the underlying mechanisms of genetic diseases. Researchers can gain insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic interventions by observing how cells from disease models differ in their morphological profiles from healthy cells.
Advantages
The Cell Painting Assay is useful because it provides a detailed picture of cellular morphology and function. It enables researchers to evaluate the effects of compounds on multiple cellular structures at the same time, providing a more comprehensive understanding of cellular responses to experimental conditions.