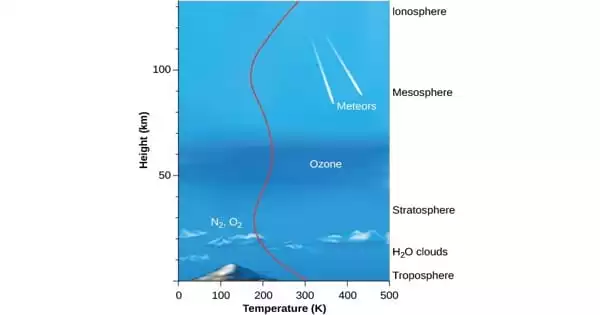
Environmental degradation is defined as the disintegration of the earth or the deterioration of the environment as a result of the consumption of assets such as air, water, and soil; the destruction of habitats; and the extinction of species. It is defined as any modification or aggravation to nature’s turf that is deemed harmful or unpleasant.
Some environmental life species necessitate large areas in order to offer food, living space, and other assets. These are known as location specific animals. When the biome is fragmented, enormous portions of living space vanish. It becomes more difficult for wildlife to acquire the resources they require to survive. The environment goes on, even though the animals and plant life are not there to help sustain it properly.
Causes of Environmental Degradation –
(1) Land Disturbance and Ruinous Agricultural Practices
Land deterioration is a more fundamental cause of environmental degradation. Many weedy plant species, such as garlic and mustard, are both foreign and obtrusive. A disruption in their environmental circumstances allows them to begin growing and spreading. These plants have the ability to take over nature and eliminate the local flora. As a result, there is a territory with a single dominant plant that does not provide adequate food resources for all environmental organisms. As a result of these invasive species, the entire environment may be destroyed.
Intensive agricultural techniques have resulted in a decrease in the quality of the majority of our natural settings. The majority of farmers convert woods and grasslands to croplands, lowering the quality of natural forests and vegetation cover. The increasing demand to turn lands into resource regions for producing high-value foods, crops, and cattle has resulted in the devaluation of natural habitats such as forests, wildlife, and fertile fields.
(2) Pollution
Pollution, in any form, is destructive to the environment, whether it be in the form of air, water, land, or noise. Air pollution pollutes the air we breathe, causing health problems. Water contamination reduces the quality of water available for drinking. Land pollution is caused by human activity and resulting in the destruction of the earth’s surface.
When exposed to constant loud sounds such as horns of vehicles on a busy road or machines making loud noise in a factory or mill, noise pollution can cause irreversible harm to our ears.
(3) Overpopulation
Rapid population increase places a demand on natural resources, resulting in environmental degradation. Because of improved medical facilities, the mortality rate has decreased, resulting in an increase in lifetime. More people simply equals more demand for food, clothing, and shelter. More land is required to cultivate food and house millions of people. This leads to deforestation, which contributes to environmental damage.
As the human population grows, so does the demand for natural resources. This frequently leads to over-exploitation of natural resources and contributes to environmental deterioration.
(4) Landfills
Landfills contaminate the ecosystem and wreak havoc on the city’s beauty. Due to the high amount of waste generated by families, industries, factories, and hospitals, landfills have been established within the city. Landfills endanger both the environment and the people who live in them. When landfills are burned, they emit a foul odor and significantly harm the environment.
It also disrupts the interaction food chains of animals since the toxins pollute plants and rivers that the animals ingest. Aside from the terrible odor from landfills and the frequent burning of rubbish, living in such situations is intolerable.
(5) Deforestation
Deforestation is the removal of trees in order to make space for additional residences and industry. Rapid population expansion and urban sprawl are two primary drivers of deforestation. Other sources of deforestation include the use of forest area for agriculture, animal grazing, fuelwood harvesting, and logging. Deforestation contributes to global warming because reduced forest size returns carbon to the environment.
(6) Natural Causes
Avalanches, quakes, tidal waves, hurricanes, and wildfires can completely smash surrounding animal and plant groupings, rendering them unable to survive in those locations. This can occur either through physical demolition as a result of a singular calamity or through the long-term degradation of assets caused by the introduction of an intrusive foreign species into the environment. The latter is common following tidal waves, when reptiles and beetles wash ashore.