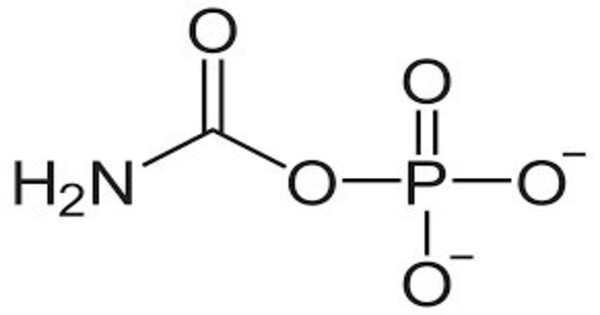
Carbamoyl phosphate is an anion of biochemical significance. It is a chemical compound with important roles in biological systems, especially in the urea cycle and the synthesis of pyrimidines. In land-dwelling animals, it is an intermediary metabolite in nitrogen disposal through the urea cycle and the synthesis of pyrimidines.
It plays a key role in converting ammonia, a toxic byproduct of protein metabolism, into urea, which is then excreted from the body. Its enzymatic counterpart, carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I), interacts with a class of molecules called sirtuins, NAD dependent protein deacetylases, and ATP to form carbamoyl phosphate. CP then enters the urea cycle in which it reacts with ornithine (a process catalyzed by the enzyme ornithine transcarbamylase) to form citrulline.
Properties
- Chemical Formula: C3H7NO6
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 105.1 g/mol
- Solubility: It is soluble in water due to its ionic nature.
- pH Stability: The compound is typically stable in neutral to slightly alkaline solutions.
Occurrences
Biological Systems:
- Urea Cycle: Carbamoyl phosphate is a key intermediate in the urea cycle (also known as the ornithine cycle), which is a crucial metabolic pathway for removing excess ammonia from the body. It is synthesized in the mitochondria of liver cells by the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I).
- Pyrimidine Biosynthesis: Carbamoyl phosphate is also involved in the de novo synthesis of pyrimidines, where it provides the carbamoyl group for the formation of carbamoyl aspartate in the initial steps of pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis. This reaction is catalyzed by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPS II), which is present in the cytoplasm of cells.
Applications
- Carbamoyl phosphate plays a critical role in the urea cycle, which is a fundamental metabolic pathway in the liver. It reacts with ornithine to form citrulline, a key step in detoxifying ammonia and producing urea for excretion.
- Carbamoyl phosphate and its derivatives are used in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals. For example, it can be used in the production of carbamoyl phosphate analogs that have potential therapeutic applications.
- It is a key intermediate in the industrial production of urea, which is used as a fertilizer, as well as in the manufacture of plastics and resins.
- It is used in various chemical syntheses, including the preparation of carbamoylated compounds, which have applications in agrochemicals and specialty chemicals.