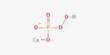
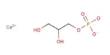
Calderite is a mineral in the garnet group with the chemical formula (Mn2+, Ca)3(Fe3+, Al)2(SiO4)3. It was named after James Calder, an early writer on the geology of India. It belongs to the garnet group. It is dark reddish brown to dark yellowish in color and generally granular massive in form.
It was named for geologist James Calder who worked on the geology of India. The name was first applied to a rock in manganese deposits in Katkamsandi, Hazaribagh district, Bihar and at Netra, Balaghat district, Madhya Pradesh, India. later transferred to its predominant mineral. In 1909 it was described as a mineral from Otjosondu, Otjozondjupa Region, Namibia.
General Information
- Category: Silicate mineral
- Formula: (Mn2+, Ca)3(Fe3+, Al)2(SiO4)3
- Crystal system: Cubic
- Crystal class: Hexoctahedral (m3m)

Properties
Calderite can be identified in the field by its color variations, such as dark yellow and reddish-yellow. Its transparent to translucent form has no cleavage. This mineral has a vitreous luster, with a white streak. The density of calderite is 4.08 g/cm3.
- Color: brownish red to brownish yellow
- Cleavage: None
- Mohs scale hardness: 6.5-7.5
- Luster: Vitreous
- Streak: white
- Diaphaneity: transparent to translucent
- Specific gravity: 3.756
Occurrence
Calderite occurs in a manganese deposit, and in an iron formation. It is often associated with minerals such as pyrolusite, aegirine, hematite, rhodochrosite, rhodonite, quartz, and kutnohorite.
Information Source;