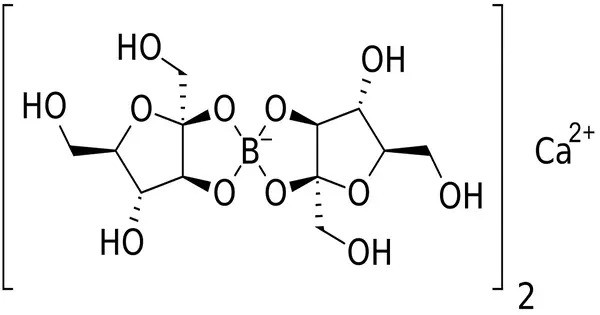
Calcium fructoborate is a salt of an organoboron compound containing boron (and fructose and calcium). Its structural formula is Ca[(C6H10O6)2B]2. is a form of boron, an essential trace mineral found in the body. It is a compound that combines boron with fructose, a simple sugar. The calcium part of the compound enhances its stability and absorption in the body.
It is naturally found in some plants, and is also manufactured and promoted as a dietary supplement. It is believed to be a more bioavailable form of boron compared to other forms like boron citrate, as the fructose in the compound helps the body absorb it more efficiently.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C24H40B2CaO24
- Molar mass: 774.26 g·mol−1
- Solubility: It has moderate solubility in water, though the exact solubility can depend on the concentration and specific formulation.
- Stability: It is relatively stable under normal conditions, but like many compounds containing boron, it may degrade under extreme conditions (e.g., high temperatures or acidic environments).
Health Benefits
- Joint Health: Calcium fructoborate is often marketed as a supplement for supporting joint health. It is thought to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce symptoms of osteoarthritis.
- Bone Health: Boron, in general, plays a role in bone metabolism, supporting calcium and magnesium utilization and helping to maintain strong bones.
- Hormonal Balance: Boron has been suggested to have a role in maintaining proper hormone levels, including testosterone and estrogen, which are crucial for various bodily functions.
- Antioxidant Properties: Some studies suggest that calcium fructoborate may have antioxidant effects, potentially protecting cells from oxidative damage.
Occurrences
In Nature: Calcium Fructoborate is naturally found in certain plants, particularly in the roots, stems, and fruits of some vegetables and fruits, as well as in small amounts in the soil. Boron is found in various forms in soil and plants, but when it binds with fructose, it forms Calcium Fructoborate.
Food Sources: It is found in trace amounts in fruits and vegetables, particularly in foods rich in boron, such as apples, pears, grapes, avocados, and almonds. Some plant-based foods, like leafy greens and vegetables, can provide small amounts of boron and, by extension, the potential for calcium fructoborate to be present.
Usage
Typically, it is used in dietary supplements designed to support joint health, bone strength, and general wellness. It’s also available in some multivitamins or bone-health formulas.
Safety
Generally, boron is safe when consumed in appropriate amounts. However, excessive intake of boron can be toxic, so it’s important to follow dosage instructions and consult with a healthcare professional if considering supplementation.