You may have heard a lot about antioxidants in juxtaposition with good health and avoiding diseases. Antioxidants have gotten enormous press, and fairly so. But how do they work once inside our bodies, and what are various sources of antioxidants?
All living organisms develop oxygen to metabolize and use the dietary nutrients in order to create energy for continued existence. Oxygen thus is a very important factor for living. Oxygen meditates chemical reactions that metabolize fats, proteins, and carbohydrates to create energy.
Once an antioxidant finds its way into the body, typically through the foods we eat, it slows down, or even prevents, the oxidation of other molecules. When molecules in the body oxidize, they can generate free-radicals, or cellular byproducts. It is very usual to have these free-radicals in the body, but in excess, they can wreak havoc on our cellular structures.

Foods High In Antioxidants
There are some nutrients in food that include antioxidants. Vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta carotene are among the mainly studied nutritional antioxidants.
Vitamin C is the most significant water-soluble antioxidant in extracellular fluids. Vitamin C helps to counterbalance ROS in the water or aqueous phase before it can attack the lipids. Vitamin E is the most important lipid soluble antioxidant. It is important as the chain-breaking antioxidant within the cell membrane. It can protect the membrane fatty acids from lipid peroxidation. Vitamin C in addition is capable of regenerating vitamin E.
The following is my short-list for antioxidant-rich Foods. Try to incorporate as many as possible into your daily diet. Remember, organic, raw, fresh and local is always best:
Corn, Lemon, Dates, Chiles, Garlic, Grapes, Mangos, Squash, Almonds, Berries, Carrots, Peppers, Spinach, Broccoli, Tomatoes, Olive Oil, Green Tea, Pineapple, Red Beets, Coconut Oil, Wheat Germ, Hempseed Oil, Sweet Potatoes, Raw Nuts & Seeds, Whole Grain Brown Rice etc.
What are antioxidants used for?
Antioxidants may play a function in the management or prevention of several medical conditions, such as some cancers, macular degeneration, Alzheimer’s disease, and some arthritis-related conditions.
Free radicals
These free radicals are capable of attacking the healthy cells of the body. This may lead to damage, disease and severe disorders. Cell damage caused by free radicals appears to be a most important contributor to aging and diseases like:
- cancer
- heart disease
- decline in brain function
- decline in immune system etc.
Overall, free radicals have been implicated in the pathogenesis of at least 50 diseases.
Since free radicals surround an unpaired electron they are unbalanced and reach out and capture electrons from other substances in order to neutralize themselves. This originally stabilizes the free radical but generates another in the procedure. Soon a chain reaction begins and thousands of free radical reactions can happen within a few seconds on the primary reaction.
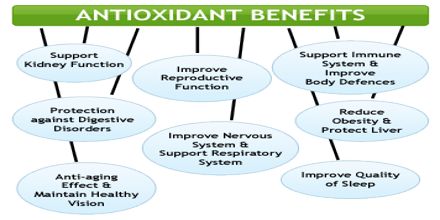
Benefits of Antioxidants
Antioxidants come up habitually in discussions about good health and preventing diseases. These dominant substances, which typically come from the fresh fruits and vegetables we eat, prohibit, the oxidation of other molecules in the body. The benefits of antioxidants are very significant to good health, because if free radicals are left unchallenged, they can cause a broad range of illnesses and chronic diseases.
- Skin Health Benefits
When skin is exposed to high levels of ultraviolet light, photo-oxidative damage is induced by the formation of different types of reactive species of oxygen, including singlet oxygen, superoxide radicals, and peroxide radicals. These forms of reactive oxygen damage cellular lipids, proteins, and DNA, and they are considered to be the primary contributors to premature aging of the skin, photodermatoses, and skin cancers.
- Immune System Support
Singlet oxygen can compromise the immune system, because it has the ability to catalyze production of free radicals. Astaxanthin and Spirulina have been shown to enhance both the non-specific and specific immune system, and to protect cell membranes and cellular DNA from mutation.
Additional Ways Antioxidants Help Benefit
Increasing one’s antioxidant intake is essential for optimum health, especially in today’s polluted world. Because the body just can’t keep up with antioxidant production, a good amount of these vitamins, minerals, phytochemicals, and enzymes must come from one’s daily diet. Boosting your antioxidant intake can help provide added protection for the body against:
- Heart problems
- Eye problems
- Memory problems
- Mood disorders
- Immune system problems
Antioxidant deficiencies
A diet low in fats may impair absorption of beta carotene and vitamin E and other fat-soluble nutrients. Fruits and vegetables are important sources of vitamin C and carotenoids. Whole grains and high quality vegetable oils are major sources of vitamin E.
Many plant-derived substances are known as “phytonutrients,” or “phytochemicals”. These also possess antioxidant properties. Phenolic compounds such as flavonoids are such chemicals. These are found in several fruits, vegetables, green tea extracts etc.

Antioxidants within the human body
Apart from diet, the body also has several antioxidant mechanisms that can protect itself from ROS mediated damage. The antioxidant enzymes – glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) are such enzymes. They require micronutrient cofactors such as selenium, iron, copper, zinc, and manganese for their activity. It has been suggested that an inadequate dietary intake of these trace minerals may also lead to low antioxidant activity.