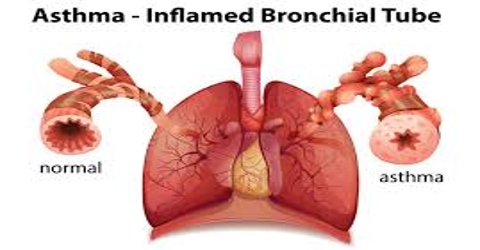
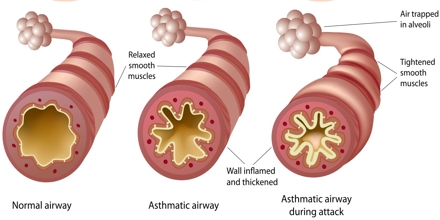
Asthma is a disease disturbing the airways that bring air to and from your lungs. People who undergo from this chronic situation are said to be asthmatic. If you have asthma your airways are constantly irritated. They become even more swollen and the muscles around the airways can tighten when something triggers your symptoms. This makes it complicated for air to move in and out of the lungs, causing symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath and/or chest tightness.

What happens during an asthma attack?
- The muscles around your airways tighten up, narrowing the airway.
- Less air is able to flow through the airway.
- Inflammation of the airways increases, further narrowing the airway.
Asthma Symptoms
Asthma is characterized by irritation of the bronchial tubes with enlarged assembly of sticky secretions inside the tubes. People with asthma experience symptoms when the airways tighten, inflame, or fill with mucus. Common asthma symptoms include:
- Coughing, especially at night
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness, pain, or pressure
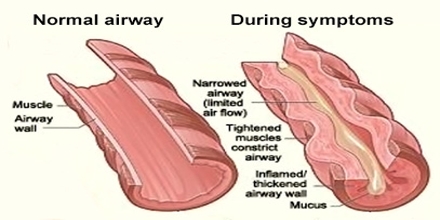
The exact cause of asthma is unknown
People with asthma have inflamed (swollen) and “sensitive” airways that become narrow and blocked with sticky mucus in response to definite triggers.
Factors such as a genes, air contamination, chlorine in swimming pools and modern hygiene standards have been suggested as possible causes, but there’s not presently enough facts to be assured whether any of these do cause asthma.
Treatment
There’s presently no cure for asthma, but treatment can help manage the symptoms so you’re able to live a regular, active life. For both adults and children, asthma can generally be controlled with medications taken by an inhaler.
The main treatments are:
- avoiding asthma triggers whenever doable
- short-acting reliever inhalers – inhalers used when needed to quickly relieve asthma symptoms for a short time, by relaxing the breathing tubes
- preventer inhalers – inhalers used regularly every day to reduce inflammation in the breathing tubes and stop asthma symptoms occurring
- combined preventer and long-acting reliever inhalers – inhalers used regularly every day which help stop asthma symptoms occurring and relax the breathing tubes for a longer period
Conclusion
Asthma has no cure. Even when you feel well, you still have the disease and it can flare up at any time. Asthma affects people of all ages, but it most often starts during childhood. In the United States, more than 25 million people are known to have asthma. About 7 million of these people are children. However, Asthma can be controlled with proper treatment.