Companies can improve their revenue and profitability by implementing an asset acquisition strategy. In most countries, acquiring an asset also entails the acceptance of certain obligations. This strategy occurs when a firm purchases another company’s assets rather than shares, as opposed to a typical acquisition strategy that involves stock purchases. Be that as it may, in light of the fact that the gatherings can deal over which resources will be obtained and which liabilities will be expected, the exchange can be unmistakable in its construction and result than a consolidation, blend, or stock buy.
When compared to organic growth, this method provides a faster rate of growth. The goals of an asset acquisition strategy are to promote expansion through external methods rather than organic development from within the company. Likewise, to extend abroad, interior development requires a comprehension of nearby traditions, rules, and guidelines, which are regularly past the organization’s information. In an asset acquisition strategy an organization picks the resources, and now and then liabilities, it wishes to acquire, rather than a conventional obtaining where it purchases the whole organization.
There are several reasons for them to pursue this method. Some companies aim to boost their existing product or service lines’ economies of scale. The buyer solely buys and assumes the assets and liabilities that it specifies and agrees to purchase and assume, subject to any legal or contractual obligations imposed on the buyer. This is generally not quite the same as a stock securing or consolidation where the purchaser procures every one of the resources and liabilities (counting obscure or undisclosed liabilities) of the objective organization as an issue of law.

Risk and possible losses are reduced by selecting certain assets and liabilities. Other businesses, such as multinational corporations, may want to expand into new geographic markets. Asset acquisition techniques are very effective when it comes to failed firms’ assets. The Internal Revenue Services (IRS) states that the price paid for all of the assets should be allocated to each individual asset using the residual method.
The capacity to single out explicit resources and liabilities furnishes the purchaser with adaptability. The purchaser doesn’t squander cash on undesirable resources and there is less danger of the purchaser accepting obscure or undisclosed liabilities. Acquisition plans, in general, are a way for a firm to expand by buying other companies or business units from other companies.
Following are the objectives of the asset acquisition strategy:
- Achieve profitable growth. Acquisitions enable a more comprehensive and integrated corporate reach. This allows the acquirer to enhance revenue, market share, and streamline operations.
- Strengthening core competencies. The key skills of a target can be synergized by acquisition to promote competitiveness in technology, human capital, and operational capabilities.
- Add to the business portfolio. Acquirers use the conglomerate approach to take up a number of unconnected firms. Diversification decreases the chance of one of the enterprises failing.
- Continuing growth. It’s possible that the acquirer is in a mature industry. As a result, diversifying into new industries is one method to continue to provide value to shareholders. Taking over a business in a thriving sector is one possibility.
An obtaining procedure gives a way to an enormous organization in a full-grown area to progress gradual deals or benefit development, or for a more modest firm to speed up strides toward a size target. However, because the buyer must spend time identifying the assets and liabilities it intends to purchase and absorb, asset acquisitions become more complicated. A company’s assets, as well as its liabilities, are the focus of an asset acquisition plan.
Since the two organizations can choose which resources and liabilities ought to be traded, a resource procurement procedure takes into account more adaptability in structure than a stock buy. Additionally, the acquirer and target firm must agree on how the purchase money will be distributed among the assets in the transaction. In comparison to internal growth strategies, this technique provides rather rapid growth.
Acquirers can move quickly to a better market position. They can also improve the value of a company’s stock and its operational success. When compared to a stock acquisition plan, an asset acquisition approach allows the acquiring firm to pick and choose the elements of a company it loves and believes would help its business. Contingent upon the circumstance encompassing the bankrupt organization, utilizing this methodology as opposed to purchasing the business and its resources out and out could cost less forthright, while as yet giving adequate awards toward the back.
Choosing which assets, and occasionally liabilities, to purchase helps to avoid any unanticipated concerns that were not revealed prior to the transaction, which might sour the deal or cause more troubles than the acquisition is worth. Asset acquisition is a less common method of progressively gaining control of a target firm. As the objective turns out to be more reliant upon the new proprietor of those resources, the chance to procure the remainder of the activity, either by acquiring a controlling interest through stock buys or purchasing the organization inside and out, can frequently be cultivated with generally little exertion.
Large firms benefit from economies of scale, income, and financial resources, allowing them to make more money. When stock buyout proposals are rejected by the target firm, an asset acquisition might be beneficial. Such a methodology is additionally a practical elective whenever the odds of having the option to buy enough offers and gain sufficient help from investors to mount an unfriendly takeover are somewhere close to thin and none.
The purchase allows the firm to combine the target company’s key skills and assets. As a result, the acquirer can boost revenue or lower operational expenses. The executives will likewise consider the means expected to effectively close a resource procurement procedure and regardless of whether there is a drawn-out social fit concerning the workforce. That way, the effect on monetary influence, and the organization’s asset report is as yet decent.
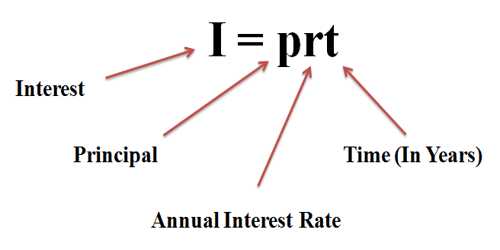
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) specifies the purchase price paid for the assets and how it should be distributed among the assets, stating that the purchase price should be allocated using the residual method. While the specific interaction for dealing with the resource securing may require gradually overseeing key resources and debilitating the objective until selling is the main genuine choice, a painstakingly created obtaining of resources can bring about producing a generous measure of benefit over the long haul. However, there may be tactics that the target firm might employ to avoid such purchases and takeovers. Poison pills are a common term for these tactics.
Information Sources: