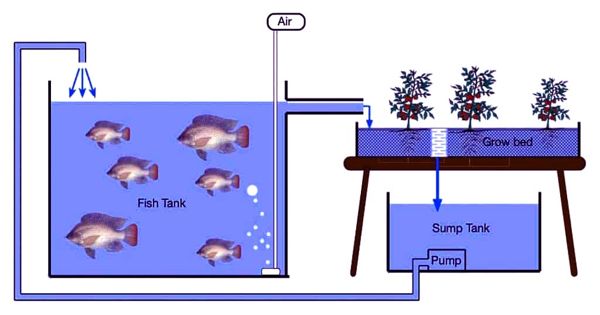
Aquaponics is a combination of aquaculture, which is growing fish and other aquatic animals, and hydroponics which is growing plants without soil. It refers to any system that combines conventional aquaculture (raising aquatic animals such as snails, fish, crayfish, or prawns in tanks) with hydroponics (cultivating plants in water) in a symbiotic environment. In return, the vegetables clean the water that goes back to the fish. Along with the fish and their waste, microbes play an important role in the nutrition of the plants. It is a way to grow your own fish and vegetables at the same time. You feed the fish and the fish will feed your plants through their waste output. In normal aquaculture, excretions from the animals being raised can accumulate in the water, increasing toxicity.
“Aquaponics represents the relationship between water, aquatic life, bacteria, nutrient dynamics, and plants that grow together in waterways all over the world.”
In aquaponics, the nutrient-rich water from raising fish provides a natural fertilizer for the plants and the plants help to purify the water for the fish. In this system, water from an aquaculture system is fed to a hydroponic system where the by-products are broken down by nitrifying bacteria initially into nitrites and subsequently into nitrates that are utilized by the plants as nutrients. Literally speaking, Aquaponics is putting fish to work. It just so happens that the work those fish do (eating and producing waste), is the perfect fertilizer for growing plants. Then, the water is recirculated back to the aquaculture system. These beneficial bacteria gather in the spaces between the roots of the plant and convert the fish waste and the solids into substances the plants can use to grow. The result is a perfect collaboration between aquaculture and gardening.

Aquaponics is a big hope for sustainable organic crop production, aquaculture, and water consumption. It is popular with individuals, entrepreneurs, educators, missions, and governments. The fish waste is recycled and used for plant growth instead of throwing it in the ocean. The water is recirculated in a closed system lowering the consumption of this resource. Furthermore, with this type of indoor farming, you grow substantially more food with less water, land, and labor than traditional agriculture.
Aquaponics represents the relationship between water, aquatic life, bacteria, nutrient dynamics, and plants that grow together in waterways all over the world. As existing hydroponic and aquaculture farming techniques form the basis for all aquaponic systems, the size, complexity, and types of foods grown in an aquaponic system can vary as much as any system found in either distinct farming discipline. It uses the best of all the growing techniques, utilizing the waste of one element to benefit another mimicking a natural ecosystem. It can be done anywhere, providing fresh local food that is free of pesticides, herbicides, and chemical fertilizers. It is safe, easy, and fresh!