Bulimia Nervosa (Causes, Risk factors, and Complications)
Definition: Bulimia nervosa, also known as simply bulimia, is a psychological and severe life-threatening eating disorder described by the ingestion of an abnormally large amount of food in short time period, followed by an attempt to avoid gaining weight by purging what was consumed. Purging refers to the attempts to get rid of the food consumed. This may be done by vomiting or taking laxatives. Other efforts to lose weight may include the use of diuretics, stimulants, water fasting, or excessive exercise.
Most people with bulimia are at a normal weight. The forcing of vomiting may result in the thickened skin on the knuckles and breakdown of the teeth. Bulimia is frequently associated with other mental disorders such as depression, anxiety, and problems with drugs or alcohol. There is also a higher risk of suicide and self-harm.
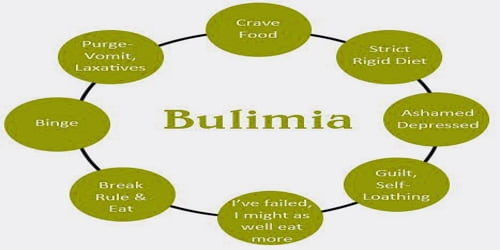
There are two common types of bulimia nervosa, which are as follows:
- Purging type – This type of bulimia nervosa accounts for the majority of cases of those suffering from this eating disorder. In this form, individuals will regularly engage in self-induced vomiting or abuse of laxatives, diuretics, or enemas after a period of bingeing.
- Non-Purging type – In this form of bulimia nervosa, the individual will use other inappropriate methods of compensation for binge episodes, such as excessive exercising or fasting. In these cases, the typical forms of purging, such as self-induced vomiting, are not regularly utilized.
Bulimia is more common among those who have a close relative with the condition. The percentage risk that is estimated to be due to genetics is between 30% and 80%. Other risk factors for the disease include psychological stress, cultural pressure to attain a certain body type, poor self-esteem, and obesity.
The term bulimia comes from Greek βουλιμία boulīmia, “ravenous hunger”, a compound of βοῦς bous, “ox” and λιμός, līmos, “hunger”. Literally, the scientific name of the disorder, bulimia nervosa, translates to “nervous ravenous hunger”.
Causes and Risk factors of Bulimia Nervosa: The exact cause of bulimia is unknown. Many factors could play a role in the development of eating disorders, including genetics, biology, emotional health, societal expectations and other issues.
Some of the main causes of bulimia include:
- Stressful transitions or life changes
- History of abuse or trauma
- Negative body image
- Poor self-esteem
- Professions or activities that focus on appearance/performance
Researchers also believe that this eating disorder may begin with a dissatisfaction of the person’s body and extreme concern with body size and shape. Usually, individuals suffering from bulimia have low self-esteem and fear becoming overweight. The fact that bulimia tends to run in families also suggests that a susceptibility to the disorder might be inherited.

Bulimia nervosa occurs more frequently in developed countries and in cities, with one study finding that bulimia is five times more prevalent in cities than in rural areas. Girls and women are more likely to have bulimia than boys and men are. Bulimia often begins in the late teens or early adulthood.
Factors that increase people risk of bulimia may include:
- Psychological and emotional issues
- Biology
- Dieting
Bulimia is thought to be more prevalent among Caucasians; however, a more recent study showed that African-American teenage girls were 50 per cent more likely than white girls to exhibit bulimic behaviour, including both binging and purging.

Complications of Bulimia Nervosa: Bulimia is more common among those who have a close relative with the condition. The percentage risk that is estimated to be due to genetics is between 30% and 80%. Bulimia may cause numerous serious and even life-threatening complications. Possible complications include:
- Negative self-esteem and problems with relationships and social functioning
- Dehydration, which can lead to major medical problems, such as kidney failure
- Heart problems, such as an irregular heartbeat or heart failure
- Severe tooth decay and gum disease
- Absent or irregular periods in females
- Digestive problems
- Anxiety, depression, personality disorders or bipolar disorder
- Misuse of alcohol or drugs
- Self-injury, suicidal thoughts or suicide
One of the more detrimental and common side effects of bulimia involves dental damage. The negative ways in which teeth are impacted by bulimia is often overshadowed by other major health consequences, such as cardiovascular complications, electrolyte imbalances, gastrointestinal distress, and bone loss.
Information Source: