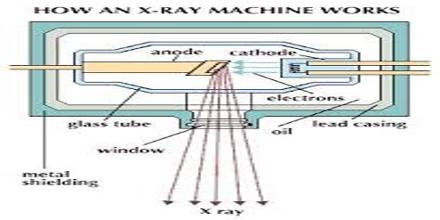
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen discovered X Rays. In an x-ray tube, negatively charged electrons are accelerated across a potential to a positively charged anode (typically made of tungsten). When the electrons impact the target, most of their energy is dissipated as heat, but approximately 1 percent of that energy is transformed into x rays. The window in the x-ray machine directs the x-ray beam toward the body part to be imaged.
How X Rays Work?