Vegan organic agriculture is the organic production of food and other crops using as few animal inputs as possible. It is a type of animal-free agriculture that is organic. It is a type of sustainable agriculture that eliminates the use of animal byproducts, such as manure or bone meal, as fertilizers and soil amendments. It is also known as veganic farming or veganic gardening. It aims to cultivate crops and maintain soil health while avoiding the use of animal-derived inputs. This approach is based on vegan ideals, which prohibit the use of animal products in all aspects of life, including food production.
Animal-free farming methods do not use animal products or byproducts such as bloodmeal, fish products, bone meal, feces, or other animal-origin matter because the production of these materials is viewed as either directly harming animals or as being associated with animal exploitation and consequent suffering.
Key principles and practices of vegan organic agriculture include:
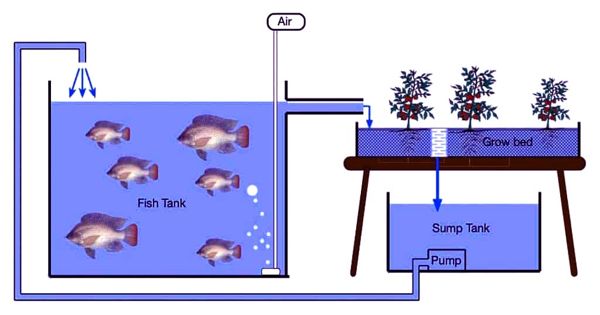
- Plant-Based Fertilizers: Instead of animal manure, veganic farmers use plant-based fertilizers like compost made from plant materials, green manure crops, cover crops, and crop rotation to enrich the soil with essential nutrients.
- Soil Health: Veganic agriculture emphasizes building and maintaining healthy soil using organic matter, mulching, and other natural techniques to improve soil structure and fertility.
- Biodiversity: Promoting biodiversity through intercropping, polycultures, and crop rotation helps control pests and diseases without the use of synthetic chemicals.
- Pest Management: Veganic farming uses integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, such as companion planting, beneficial insect release, and natural predators, to reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
- Non-GMO: Avoiding genetically modified organisms (GMOs) is often a core principle of vegan organic agriculture.
- Ethical Considerations: Veganic agriculture is driven by ethical concerns regarding the treatment of animals and a desire to minimize the environmental impact of farming.
- Sustainability: Veganic farming aims to create a sustainable, regenerative system that minimizes harm to the environment and maintains ecosystem health.
Some of these items are byproducts of animal husbandry, formed during the process of raising animals for meat, milk, skins, furs, entertainment, work, or companionship. The selling of such by-products reduces expenses and improves profits for those involved in animal husbandry, hence supporting the animal husbandry industry, which most vegans find objectionable.
Veganic agricultural practices are becoming more popular as there is a demand for products that adhere to vegan and ecologically conscious standards. Many veganic farms and gardens are already growing a wide range of fruits, vegetables, cereals, and other crops without the use of animal-derived inputs.