Understanding online shoppers of
Unilever Bangladesh
As known to all, Unilever Bangladesh Limited is one of the leading multinational business firms in the world of FMCG industry. Over the last four decades Unilever Bangladesh Limited (UBL) has been relentlessly bringing new, innovative and world-class products to make the lives of Bangladeshis easier. Over 90% of the country’s households use one or more of UBL products. Unilever currently offers nineteen variety brands in spread across four different categories-Food and Drink, Home care, Personal Care, Water Purifier.
To identify how to make these brands popular amongst the people of Bangladesh is the core objective of the “Consumer and Market Insight department” or in short CMI. (a proactive segment of the Brand Building department of Unilever Bangladesh Limited). CMI is the department where the study of the different marketing mix is done to analyze its effectivity and efficiency. This phase typically comes before the planning phase during which managers do study on different perspectives and analyze the feasibility of different methods.
During my tenure I along with the guidance of my line manager researched on the most popular buzzing topic of the time i.e. internet shopping. As the world is moving with a very fast pace with the help of internet, it’s time that Unilever as a global giant also hit this system to accelerate their growth.
In addition, I have carried out a small-scale research to find out how to penetrate this path and grab success through it. I critically analyzed the pros and cons of online shopping and tried to gather as much real life information as possible by reaching mass people. I have scrutinized different other online shops and thus came out with possible recommendation to make it feasible for Unilever Bangladesh Ltd.
Introduction
The world is moving at a very fast pace with the rapid growth of internet population and increasing dependency on ICT in different sectors. Internet has caused restructuring in the communication pattern which has created huge potentials for the development of trade and commerce. Due to the efficiency, effectiveness and very low operating cost, it has become highly booming and fasted adopted technology till date. The use of internet in business has marked incredible response since its inception. Be it a solo start-up or the government or any MNC, internet marketing or what in business terminology we call e-commerce, is increasingly viewed as a key business modality of the future.
This paper is all about different e-marketing strategies adopted by different companies, how they expand their market, how they reach to their customers and how are they building a better relationship with the customers. This is the high time when we as such a big name in the business world attempt to grab the potentials of this channel where effective promotion of the business can be done by reaching maximum customers with the minimum operating cost. Consumers started depending on online shopping once they got assured with the secured usage of their credit cards in e-business. Now consumers can buy anything and everything just with a click sitting comfortably in a couch at home. Companies also can reach customers all over the world. Not only for buying and selling, internet is increasingly used as a source of advertisements. Companies have created innovative advertising programs.
Internet is truly changing the way we do business, the way we market, sell, service, distribute, communicate etc.
The world trade organization and different round discussions on the trade related issues have opened up a new arena of global competition. Developing country’s technological fitness is must in searching new market and making buyer-seller relationship to achieve the competitiveness in the global market. The World Wide Web (WWW) can be considered as the right way which provides the opportunity to overcome the barrier of time and place in building buyer-seller relationship. Thus, E-Commerce should be adopted as the effective media for marketing and selling of a product or services through the internet.
Background:
E-commerce has become a catchphrase of present technology days. E-commerce consists of all internet users of the world. The members of the community can interact with each other at any time without considering the distance gap. Time, place and national boundary do not make any obstacle to build and maintain the relationship. It refers to the process of conducting any kind of business through digital communication. Due to several environmental barriers like economic depression, changing market trends, unpredictable financial markets and political instabilities; organizations have become harried to come up with strong backups to survive and succeed. E-commerce is such a survival weapon which not only makes the management easy but also offsets operation costs. Considering the ongoing threats and opportunities we should also comply with the advancement like other booming online markets. Now a day’s internet services are available in Bangladesh.
Slowly these services are holding a strong position in every part of our life. This paper will be aiming at examining how we can use this service as a tool of communication and distribution like any other online marketers are doing. There will be focus on the philosophy of the e-commerce and how different online marketers are implementing it in reality. I will also critically analyze the customer’s perception about online shopping, their expectations because our prime concern is our customers. Their ease and comfort has to be taken under consideration if we want to garb the market. Then this paper will suggest measures that must be taken to go online.
Research objective:
The aim of doing this research is to find out the possible opportunities and threats of ecommerce execution in Bangladesh so that we can build the capability to seize the future of this channel. For more precise understanding the objective can be broken into following sub-objectives:
- Analyzing consumer understanding about online shopping.
- Examine the growth pattern of e-commerce in Bangladesh
- Finding out the probable challenges and threats and solutions to those threats
- Finding out the opportunities and discover how to utilize and maximize those opportunities
- Examine the operations of online marketing.
The sub-objectives are detailed below:
- Analyzing consumer understanding about online shopping:
Our prime concern is our consumers. So it is very important to know consumer’s perspective about online shopping to create an effective and efficient channel through it.
What are the consumer’s expectations, the problems they are facing now, the items they buy, when and how much they buy; all these are very important information for us to know.
- Examine the growth pattern of e-commerce in Bangladesh:
It has been a while since the internet has been used widely. And the e-commerce sites are also on the way to boom in our country. In a developing country like Bangladesh it is very important to study the growth pattern of a business because that indicates the effects of different economic, political and environmental barriers on the business. So we will study the growth pattern of e-commerce.
- Finding out probable challenges and threats and solutions to it:
By examining the growth pattern we will be able to identify the pros and cons of implementing e-commerce in Bangladesh. Studying critically the pattern will help us find out the challenges that other online businesses are facing and also the way they defended the challenges. So we can have the idea of the threats and by that we can help ensure the feasibility of the business.
- Finding out the opportunities and ways to utilize those opportunities:
As much the study of challenges is important, the study of opportunities is also equally important. By knowing about the opportunities we could be identify the possibilities of expanding business through utilizing those opportunities and also find out how to maximize these opportunities.
- Examine the operations of e-commerce:
Understanding the operation process of e-commerce is very necessary. What are the different departments for e-commerce, functionalities of different departments how the different departments communicate and how to balance between different departments?
Unilever Global:
Unilever is an Anglo-Dutch company, with a history of colonial exploitation, on which it has gradually built its capital. Today it owns more than 400 of the world’s consumer product brands in food, beverages, cleaning agents and personal care products. Unilever employs more than 174,000 people and had worldwide revenue of €49.800 billion in 2013.
Unilever has two parent companies: Unilever NV in Rotterdam, Netherlands, and Unilever PLC in London, United Kingdom. This arrangement is similar to that of Reed Elsevier, and that of Royal Dutch Shell prior to their unified structure. Both Unilever companies have the same directors and effectively operate as a single business. The current nonexecutive Chairman of Unilever N.V. and PLC is Michael Treschow (May 2007) while Paul Polman (January 2009) is Chief Executive Officer. Unilever’s major competitors include Nestlé and Procter & Gamble.
History of Unilever:
William Hesketh Lever founded Lever Brothers in 1885. Lever established soap factories around the world. In 1917, he began to diversify into foods, acquiring fish, ice cream and canned foods businesses. In the Thirties, Unilever introduced improved technology to the business. The business grew and new ventures were launched in Latin America. The entrepreneurial spirit of the founders and their caring approach to their employees and their communities remain at the heart of Unilever’s business today.
Unilever was formed in 1930 when the Dutch margarine company Margarine Unie merged with British soap maker Lever Brothers. Companies were competing for the same raw materials, both were involved in large-scale marketing of household products and both used similar distribution channels. Between them, they had operations in over 40 countries. Margarine Unie grew through mergers with other margarine companies in the 1920s.
In a history that now crosses three centuries, Unilever’s success has been influenced by the major events of the day –economic boom, depression, world wars, changing consumer lifestyles and advances in technology. And throughout they’ve created products that help people get more out of life–cutting the time spent on household chores, improving nutrition, enabling people to enjoy food and take care of their homes, their clothes and themselves. Through this timeline you’ll see how UBL brand portfolio has evolved. At the beginning of the 21st century, path to Growth strategy focused us on global high-potential brands and Vitality mission is taking us into a new phase of development. More than ever, how brands are helping people ‘feel good, look good and get more out of life’ – a sentiment close to Lord Lever Hulme’s heart over a hundred years ago.
Timeline
19th century: Although Unilever wasn’t formed until 1930, the companies that joined forces to create the business we know today were already well established before the start of the 20th century.
1900s: Unilever’s founding companies produced products made of oils and fats, principally soap and margarine. At the beginning of the 20th century their expansion nearly outstrips the supply of raw materials.
1910s: Tough economic conditions and the First World War make trading difficult for everyone, so many businesses form trade associations to protect their shared interests.
1920s: With businesses expanding fast, companies set up negotiations intending to stop others producing the same types of products. But instead they agree to merge and so Unilever is created.
1930s: Unilever’s first decade is no easy ride: it starts with the Great Depression and ends with the Second World War. But while the business rationalizes operations, it also continues to diversify.
1940s: Unilever’s operations around the world begin to fragment, but the business continues to expand further into the foods market and increase investment in research and development.
1950s: Business booms as new technology and the European Economic Community lead to rising standards of living in the West, while new markets open up in emerging economies around the globe.
1960s: As the world economy expands so does Unilever and it sets about developing new products, entering new markets and running a highly ambitious acquisition program.
1970s: Hard economic conditions and high inflation make the 70s a tough time for everyone, but things are particularly difficult in the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) sector as the big retailers start to flex their muscles.
1980s: The business expands into Central and Eastern Europe and further sharpens its focus on fewer product categories, leading to the sale or withdrawal of two-thirds of its brands.
1990s: The business expands into Central and Eastern Europe and further sharpens its focus on fewer product categories, leading to the sale or withdrawal of two thirds of its brands.
The 21st Centuries: The decade starts with the launch of Path to Growth, a five-year strategic plan, and in 2004 further sharpens its focus on the needs of 21st Century consumers with its Vitality mission.
Unilever Bangladesh LTD:
The history Unilever Bangladesh Ltd is one of the world’s most successful fast moving consumer goods manufacturing companies with local manufacturing facilities, reporting to regional business groups for innovation and business results.
Lever Brothers Bangladesh Ltd. as a subsidiary of Unilever is leading the home care, personal care and food product market of Bangladesh. On 25th February 1964 the eastern plant of Lever Brothers Pakistan Ltd. was inaugurated at Kalurghat, Chittagong with a soap production capacity of approximately 485 metric tons. It was a private limited company with 55% share held by Unilever and the rest by the Government of Pakistan.
After independence the eastern plant was declared abandoned. But on 5th July 1973 it was registered under the name of Lever Brothers Bangladesh Ltd. as a joint venture company of Unilever PLC and the Govt. of Bangladesh with a share arrangement of 60.75% to Unilever and 39.25% to the Bangladesh Govt.
Unilever today:
Unilever brands are trusted everywhere and, by listening to the people who buy them, they’ve grown into one of the world’s most successful consumer goods companies. In fact, 200 million times a day, someone somewhere chooses a Unilever product. UBL have a portfolio of brands that are popular across the globe – as well as regional products and local varieties of famous-name goods. This diversity comes from two of their key strengths:
- Strong roots in local markets and first-hand knowledge of the local culture.
- World class business expertise applied internationally to serve consumers everywhere.
Unilever at a Glance:
- Type of business: Fast Moving Consumer Goods Company with local manufacturing facilities, reporting to regional business groups for innovation and business results.
- Operations: Home and Personal Care, Foods
- Constitution: Unilever – 60.75% shares, Government of Bangladesh – 39.25%
- Product categories: Household Care, Fabric Cleaning, Skin Cleansing, Skin Care, Oral Care, Hair Care, Personal Grooming, Tea based Beverages.
- Brands: Wheel, Lux, Lifebuoy, Fair & Lovely, Pond’s, Close Up, Sunsilk, Taaza, Pepsodent, Clear, Vim, Surf Excel, Rexona, Dove, Vaseline.
Manufacturing
Facilities: The Company has a Soap Manufacturing factory and a Personal Products Factory located in Chittagong. Besides these, there is a tea packaging operation in Chittagong and three manufacturing units in Dhaka, which are owned and run by third parties exclusively dedicated to Unilever Bangladesh.
Employees: Unilever Operations in Bangladesh provide employment to over 10,000 people directly and through its dedicated suppliers, distributors and service providers. 99.5% of UBL employees are locals and they have equal number of Bangladeshis working abroad in other Unilever companies as expatriates.
Unilever’s Growth
Although Unilever has been around since pre-liberation days, the real impetus for growth started from 1999. Since then the sales growth has consistently been in double digits and at more than double the GDP rate of growth. In 2003 UBL was the fastest growing business for Unilever Asia delivering profitable growth of 17%. They have also strengthened the fundamentals of the business and have been able to double the rate of gross margins, which has provided us the necessary fuel for growth. During the last few years the profit after tax has increased more than 8 times and this has resulted in exponential growth in shareholder’s fund now being one of the highest in corporate in Bangladesh.
Organizational Structure
In terms of Unilever, they have two chairmen leading the company worldwide. They have seven top directors leading seven different departments. They have divided their worldwide business into different region and have different business groups to manage them.
Unilever Bangladesh limited falls under the Southeast Asian region. On a more micro scale, Unilever Bangladesh ltd is monitored by Hindustan lever Ltd. which oversees operation in Bangladesh, India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. The chairman of Unilever Bangladesh Limited is known as the managing director. The management staff of the company consists of six layers, starting from junior manager (who are local managers) to manager grade 5 (who are Unilever managers). Apart from this the company also hires many non-management staff as well as operatives to work in the factories.
About e-commerce
E-commerce Concept
E-Commerce is trading products or services over computer networks, and the most popular of all such networks is the Internet. It could be thought of as the modern version of the mail-order purchase by catalogue, and can be conducted by both individuals and firms and almost any good or service can be offered, from books and toys to plane tickets and medical services. It allows 24/7 shopping and many choices for consumers, but limits customer contact and verification by checking the actual goods.
Types of E-Commerce
1) By Licensing Type
On- Premise E-Commerce-On-premise E-commerce software usually requires initial one time purchase investment in terms of licensing fees. Also, it implies extra costs related to hardware and installation and also data migration, and periodical maintenance fees that are commonly charged on a yearly basis for software updates and support.
Advantages:
- Easily customizable;
- High Data security;
- High performance;
- Disadvantages:
- Large initial investment;
- Self-maintenance;
- Difficult to scale
Software as-a-Service (SaaS) E-Commerce- Software as a Service (SaaS)- is a cloud based delivery model in which apps are hosted and managed in a service provider’s datacenter, paid by the business owner on a subscription basis and accessed via a browser over an internet connection.
Advantages:
- Low-cost solution;
- Hosted/upgraded by E-commerce provider;
- Easily scalable
- Disadvantages:
- Limited integration with receiving-end systems;
- Lack of data security;
- Limited control over the system- most of it lie with the service provider
2) By Sales Type
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)-In a Business-to-Consumer E-commerce environment, companies sell their online goods to consumers who are the end users of their products or services. Usually, B2C E-commerce web shops have an open access for any visitor, meaning that there is no need for a potential customer to login in order to make any product related inquiry. Example- Amazon.com
Business-to-Business (B2B)-In a Business-to-Business environment, companies sell their online goods to other companies without being engaged in sales to consumers. In most B2B E-commerce environments, entering web shops will require a log in. B2B web shop usually contains customer-specific pricing, customer-specific offering types and customer-specific discounts. Example- Alibaba.com.
Consumer-to-Business (C2B) -In a Consumer-to-Business environment, consumers usually post their products or services online on which companies can post their bids.
A consumer reviews the bids and selects the company that meets his price. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)-In a Consumer-to-Consumer environment, consumers sell their online goods to other consumers. Example: Ebay.com, Bikroy.com.
E-commerce Practice in Bangladesh
E-commerce in Bangladesh actually stated in the year of 1999 based in USA with some non-resident Bangladeshis. This people opened some Bangladeshi sites focused on providing local news and some transactional things like sending gift items to Bangladesh.
The first ever e-commerce site in Bangladesh is www.munshigi.com. List of different e-commerce-type web sites
- www.bikroy.com
- www.olx.com
- www.kaymu.com
- www.cellbazar.com
- www.clickbd.com
- www.chorka.com
- www.chaldal.com
- www.hutbazar.com
- www.bdjobs.com
- www.shoppingcart.com
- www.upohar.com
- www.ushop.com
- www.hungrynaki.com
- www.foodpanda.com
- www.kroybikroy.com
- www.kholabazar.com
- www.bestway.com
- www.sonalibangla.com
- www.e-bangla.com
- www.bangladeshinfo.com
- www.bdbazar.com
- www.quickezine.com
- www.Webbangladesh.com
- www.deshigift.com
- www.bangla2000.com
- www.banglabaskets.com
Statistics of Bangladesh
The World Bank indicates that 6.5% of our population was internet users in 2013. 111 Internet service providers (ISP) serve the nation with an extra 84 in the central zone. 3 companies provide WiMax and an unknown number of LAN service providers (LSP) serve so called “broadband” internet (which has much faster speeds than the theoretical definition of broadband).
Top 5 e-commerce sites in Bangladesh
Kaymu.com.bd
History:
Founded in December 2012, Kaymu.com.bd is a venture of Rocket Internet AG, one of the world’s largest startup incubators. Since then, growth has been phenomenal and now the site enjoys nearly 500,000 visitors per month. Kaymu.com is also operational in around 40 other countries of the world.
Goal:
The goal of Kaymu.com is to provide a smooth online shopping experience for Bangladeshi customers, as well as providing convenient methods for payment such as the popular cash on delivery, KaymuSafepay and Advance payments. It aims to achieve this goal by bringing reliable sellers and buyers together in a solid B2C platform.
Operation:
Both buyers and shoppers have to register at kaymu.bd, and then shop and post goods: the “and” is here because a registered visitor can buy and sell from the same Kaymu account, if he/she chooses to. Kaymu is also intent on being convenient to the seller, by ensuring that payments are properly made. In keeping with their easygoing vibe, registration for sellers is totally free, but of course, Kaymu receives commissions for the sales made.
Finally, the site also ensures that transactions actually took place by contacting the buyer and seller by phone and email.
- Strength- Convenient measures.
- Weakness- Apparently none: and this is the reason for the rapid rise in popularity.
- Opportunity- Including product suggestions, providing discounts to existing customers
- Threats- Existing Competition- akhoni, ekhanei, bikroy etc.
Comparison of E-Commerce Scenarios
Developed Country Example: United States of America
81% of US citizens use the internet; the country houses some of the biggest ISPs in the whole world, with unrivaled speeds. This is the environment in which E-Commerce giants such as Amazon and Ebay have flourished, and others continue to flourish.
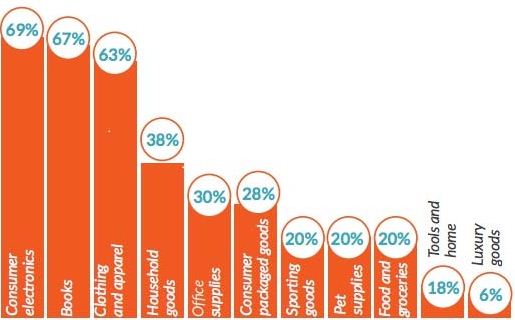
A 2013 study by Walker Sands reveals that nearly 2/3rd of surveyed Americans shop online for at least once per month, thus revealing widespread popularity of online shopping. So what products do American consumers buy online the most? The Top 5 are Consumer Electronics (68%), Books (67%), Clothing and Apparel (63%), Household goods (38%) and Office Supplies at 30%.
What drives such popularity? 80% of consumers would buy if free shipping is provided, and a still-impressive 66% is willing to buy with one-day shipping. 64% of consumers will make a purchase if free returns and lucrative exchange offers are in place.
The same Walker Sands Study tells us that 30% of the surveyed group will spend more than $1000 (77,600 Tk) on an online purchase if it has free shipping and returns, and only 10% will buy a product priced above $1000 online without free shipping and returns. It can be seen that free shipping is deemed very convenient and may facilitate purchases of costlier goods.
Amazon.com
When it comes to USA, it would not do justice to go along without mentioning Amazon.com, one of the most popular online stores on the planet; it was found by an American, Jeff Bezos in Seattle, Washington, America. In the study, it is seen that a whopping 95% of the surveyed sample have bought something from Amazon in the last year, and 40% are willing to buy absolutely any product from Amazon. 37% of the sample disclosed that they would be hesitant to purchase food and groceries from Amazon, and 29% would hesitate to purchase luxury goods. In both of these cases, the majority would still consent to buying these goods from Amazon, as well as all the other categories.
E-Commerce through mobile devices is highly prevalent- 64% of consumers use theirs to research products before buying them. 52% would buy products if the retailer offers instore navigation with a mobile device, and 59% would be willing if the store had checkout via mobile.
Forrester has forecasted that US online retail sales would grow by 57% by 2018; from $263 billion in 2013 to $414 billion in 2014, which shows a whopping annual growth rate of 9.5% compounded. Consumers aged 25-33 years spend the most of all age groups on online shopping in the US-an average of $563 for the last 3 months.
Fast growth creates its own challenges- retailers must ensure smoother and faster checkout, and that too from mobile devices, which from the aforementioned statistics, prove to be the rising means of store access for US online shoppers.
Developing Country Example
Pakistan
In 2013, 10.5% of the population were internet users, and new e-commerce sites keep emerging. Pakistan’s E-Commerce has been valued at Pakistani Rupee 4.5 Billion per year, as of 2013.
In Pakistan, there are 31 million Internet users. 15 million of them browse through mobile devices, according to the Pakistan Telecom Authority. Pakistan’s 125 million active mobile device users, out of population of 190 million, give it the fifth-largest number of mobile phone users in Asia. The market size and large online population lay a strong foundation for Internet retailing.
Internet retailing in Pakistan started in late 1997 with brands such as Liberty Books and Gift Express, with the first payment gateway provided by Citibank and e-store powered by The Cyber Bridge. Since then, several stores have been set up in various categories, including gifts, books, music, movies, consumer electronics, computers, clothing and footwear. Classified sites, such as OLX, DealsToday and Kaymu provide platforms for online trading.
There is no formal estimate on online retail sales in Pakistan, due to cash on delivery being popular and in-case of selling to expatriate Pakistanis, other third-party arrangements are used.
U.S.-based Amazon.com Inc. ships items to Pakistan. Also, U.S. retailers like Macy’s Inc. and J.C. Penny Co. Inc. let customers choose Pakistan as the country of delivery and price items in Pakistani rupees.
Unlike in the USA, where most online consumers pay with credit and debit cards, Pakistani consumers prefer to pay through online banking or through cash on delivery.
There is only one domestic gateway maintained by UBL (United Bank Ltd), which processes Visa and MasterCard transactions.
In Pakistan, online shopping is also not as massively widespread as in USA. Perceptions are therefore on a different rung on the ladder. A 2012 report claims that 43.7% of consumers buy online due to the convenience it provides, 23% buy due to lower prices online, and 18% make purchases resulting from positive reviews from friends and family. Speaking of reviews, another study from 2012 reveals that 60% of the sample discourages online shopping. The same study shows that 70% found online shopping to save time and 49% found it convenient. Opinions of prices being higher, lower or the same as real-world market price was mixed, and 58% of respondents felt secure about making purchases online. The attitudes reflect that of a developing E-Commerce, but overall show a gradually developing positive bent towards online-shopping.
Barriers
- Chances of Fraud
Those who are not shopping online have repeatedly mentioned about the fact that there is a high chance of being trapped in online shops. Many social online sites are there who have been victim of fraud. So they don’t trust this channel for shopping.
- Insecurity:
People are insecure of ordering product online because of chances of getting lower grade products or fake products. They say that when they are ordering online they are not sure of what quality products they will be receiving.
- Payment issue:
Though most of the websites have cash on delivery system of payment. But still there are many sites who demand a certain percentage of money in advance through Bkash or online payment. People say this process involves risks of being victimized of fraud, insecurity of losing credit card information.
- Less disclosure about product:
Another issue that creates obstruction for people to shop online is that during shopping online people don’t get to see detailed specification of the product. And they also don’t get to ask the sales person about it. So there is no direct communication. So many customers don’t prefer going for online shopping because of it.
Future Buying behavior:
12% of the respondents are not ready to buy from online in future because they do not trust this channel. They prefer a physical shopping where they can physically see the product and communicate with the seller directly. According to them physical shopping reduces chances of fraud. 34% of the respondents are willing to buy more in future provided their expectations are met. 54% of the respondents will buy the same in future.
Recommendation
The products we make are the basic necessities of any household. We are a FMCG company and our products moves faster than anything. So for such a very fast moving product it is very important to have a super fast accessibility to customers when we are planning to go online. Our products are readily available in the nearest shops of any person. So for us to seize the e-channel, we have to build a very speedy and fastest delivery system. In a very densely populated country like ours, where human traffic and transport traffic both is at the peak, ensuring fastest delivery is very difficult. So for that I have few recommendations
- To create a central warehouse hub and at least 1 touch point within maximum 4 sq. km. area. The city will be divided into several zones and each zone will have one touch point. Each touch point will take orders from the zonal websites whose data will be centrally coordinated by the central hub. The central database will keep record of the products in the touch points and ensure all time availability by alarming the employee when number of product goes down under certain number.
- To provide post purchase service to the customers so that we can hear to their complains and they don’t feel that they are not able to come in contact with the seller.
- In this way they will be ensured that they are not being betrayed with fake products and will not feel insecure.