1.1 Historical Background
City Bank Ltd. is one of the first generation private Commercial Banks in Bangladesh, which has started its operations on 27th March, 1983, in DhakaCity. The bank currently has 84 online branches and 5 SME centers spread across the length & breadth of the country that include a full fledged Islami Banking branch. Besides these traditional delivery points, the bank is also very active in the alternative delivery area. It currently has 35 ATMs of its own; and ATM sharing arrangement with a partner bank that has 225 ATMs in place; SMS Banking; Interest Banking and so on. Soon its CustomerCallCenter is going to start operation. The bank has a plan to end the current year with 50 own ATMs.
City Bank is the first bank in Bangladesh to have issued Dual Currency Credit Card. The bank is a principal member of VISA international and it issues both Local Currency (Taka) & Foreign Currency (US Dollar) card limits in a single plastic. VISA Debit Card is another popular product which the bank is pushing hard in order to ease out the queues at the branch created by its astounding base of some 400,000 retail customers. The launch of VISA Prepaid Card for the travel sector is currently underway.
A couple of years ago, CBL took an ambitious objective of becoming the number one private commercial bank in Bangladesh. In order to achieve this goal, CBL is going through a massive restructuring process. In its 25th Anniversary, CBL has come up with a new dynamic brand logo and tagline. The company is expanding very fast with the recruitment and training of highly potential employees, automation of the daily operations and improvisation of its service quality policies.
1.2 Vision
To be the leading bank in the country with best practices and highest social commitment.
1.3 Mission
To contribute to the socioeconomic development of the country
To attain highest level of customer satisfaction through extension of services by dedicated and motivated team professionals
To maintain continuous growth of market share ensuring quality
To maximize bank’s profit ensuring its steady growth
To maintain the high moral and ethical standards
To ensure participative management system and empowerment of human resources
To nurture an enabling environment where innovativeness and performance is rewarded
1.4 Objectives
To become the no.1 private commercial bank in the country in 3 years time. The newly launched logo and the pay-off line of the bank are just one initial step towards reaching that point.
1.5 Business Strategy
As a general practice City Bank will definitely concentrate its business in Trade Finance/ Export–Import business and all types of Commercial Loan, Industrial/ Project Finance / Syndication and structured Finance / SME Financing/ Retail Financing and other specialized programs except otherwise restricted by the Government or indicated as unethical and banned items.
The Bank will give emphasis to diversify its business portfolio commensurate with economic and business trend and cyclic aspect of the economy & appetite for growth of each sector, life cycle of the products, demand supply gap, social and national obligation etc. The Bank’s policies for financing in different major sectors are summarized as follows:
1.6 Organization Structure
City Bank is among the very few local banks which do not follow the traditional, decentralized, geographically managed, branch based business or profit model. Instead the bank manages its business and operation vertically from the head office through 4 distinct business divisions namely:
- Corporate & Investment Banking
- Retail Banking (including Cards)
- SME Banking &
- Treasury & Market Risks
Under a real-time online banking platform, these 4 business divisions are supported at the back by a robust service delivery or operations setup and also a smart IT Backbone. Such centralized business segment based business & operating model ensure specialized treatment and services to the bank’s different customer segments.
Organogram of The City Bank Ltd.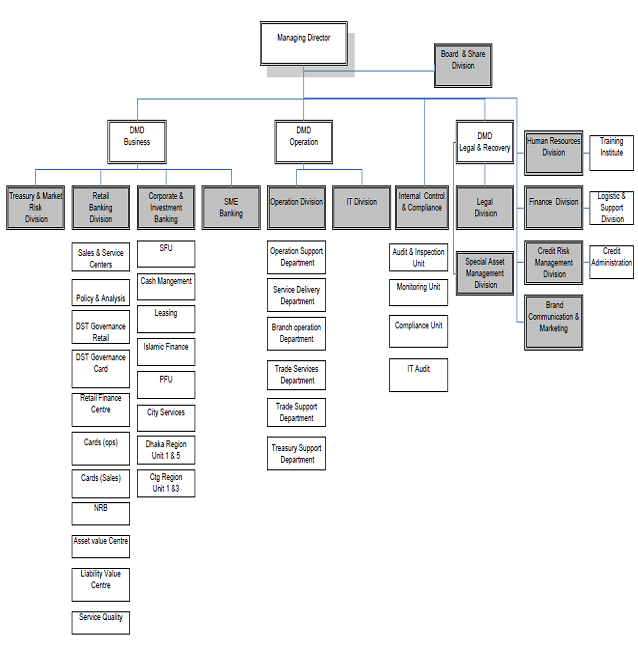
1.7 Functions of Departments
1.7.1 Corporate & Investment Banking: This division of CBL mostly deals with deposits and loans from corporations or large businesses, as opposed to normal individual members of the public (retail banking). The functions of the corporate division may include the following tasks:
- issuing bank drafts and bank cheques
- accepting money on term deposit
- lending money by overdraft, installment loan, or other means
- providing documentary and standby letter of credit, guarantees, performance bonds, securities underwriting commitments and other forms of off balance sheet exposures
- safekeeping of documents and other items in safe deposit boxes
- sale, distribution or brokerage, with or without advice, of insurance, unit trusts and similar financial products as a “financial supermarket”
1.7.2 Retail Banking
The CBL Retail banking division executes transactions directly with consumers, rather than corporations or other banks. Services offered include: savings and checking accounts, mortgages, personal loans, debit cards, credit cards, and so forth.
Recently launched ‘Celtic Project’ (American Express Credit Card) is also the core initiative of City Retail.
1.7.3 SME Banking
SME banking division is engaged in the transactions which are directly connected with small & medium businesses or entrepreneurs with diminutive amount of investment. Services offered include: business loans for plant & machinery purchasing, mortgages and other short term & long term loans.
1.7.4 Treasury & Market Risk Division
Interest Rate Risk Management
To achieve the objective of protecting the Bank from changes in market interest rates, the Bank matches the sensitivity of its assets and liabilities. The Bank’s strategy for implementing the desired matching is to divide the balance sheet into the two broad types of interest rate sensitive assets and liabilities (floating rate and fixed rate) and to align the interest rate profiles of each balance sheet component to the appropriate benchmark.
Currency Risk Management
The agreement establishing the Bank explicitly prohibits it from taking direct currency exchange exposures by requiring liabilities in any one currency (after swap activities) to be matched with assets in the same currency.
Liquidity Risk Management
Bank holds sufficient liquid assets to enable it continue normal operations even in the unlikely event that it is unable to obtain fresh resources from the capital markets for an extended period of time. The Bank’s policy requires maintaining a prudential minimum of liquidity based on projected net loan transfers, contingent liabilities and debt service payments. Equally, the Bank’s policy permits the increase of liquid resources up to an operating level based on the minimum in addition to taking into account undisbursed and irrevocable commitments to take advantage of low cost funding opportunities as they arise.
1.8 Competitive Conditions
HSBC
In Bangladesh, the HSBC Group’s history dates back to 1996 when The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC) Ltd opened its first branch. Today, the HSBC Group offers a comprehensive range of financial services in Bangladesh including commercial banking, consumer banking, payments and cash management, trade services, treasury, and custody and clearing. HSBC provides full range of services with high service quality standard. However, having only 9 branches and 27 ATMS, its current customer base and target market is much narrower compared to other banks in the industry.
Standard Chartered Bank
Standard Chartered Bank originally established its first branch in Chittagong in 1948. Today, Standard Chartered Bank is the largest international bank in Bangladesh with 25 Branches and 50 ATMs; employing over 1,300 people. SCB currently has presence in 6 cities in Bangladesh– Dhaka, Chittagong, Khulna, Sylhet, Bogra and Narayanganj; including the country’s only offshore banking units inside Dhaka Export Processing Zone (DEPZ) at Savar and Chittagong Export Processing Zone (CEPZ). With a moderate level of service quality, SCB is targeting much wider market than HSBC & obviously playing a major role in Bangladesh banking industry.
Dutch-Bangla Bank
Dutch-Bangla Bank started operation as Bangladesh’s first joint venture bank. The bank was an effort by local shareholders spearheaded by M Sahabuddin Ahmed (founder chairman) and the Dutch company FMO. From the onset, the focus of the bank has been financing high-growth manufacturing industries in Bangladesh. The rationale being that the manufacturing sector exports Bangladeshi products worldwide. Thereby financing and concentrating on this sector allows Bangladesh to achieve the desired growth. DBBL’s other focus is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). In the current market scenario, DBBL is the leader in the ATM business with around 170 ATM booths. And with around 80 branches all over the country, it has captured a huge market share in the banking industry.
Dhaka Bank
Dhaka Bank was incorporated as a public limited company under the Companies Act. 1994. The Bank started its commercial operation on July 05, 1995 with an authorized capital of Tk. 1,000 million and paid up capital of Tk. 100 million. The paid up capital of the Bank stood at Tk 1,934,252,875 as on June 30, 2008. The total equity (capital and reserves) of the Bank as on June 30, 2008 stood at Tk 3,424,609,016.
The Bank has 44 branches, 2 SME Service Centers, 1 Business Center, 2 Offshore Banking Units across the country and a wide network of correspondents all over the world. With a very attractive remuneration package, the Bank has plans to open more branches in the current fiscal year to expand the network.
BRAC Bank
BRAC Bank, with its recent achievements like ‘Best Financial Institution of the Year-2008’ for innovation in products, services, financial performance/ productivity and company management, has set an example for other local banks. With almost 350 SME offices all over the country, it claims to be the leader in SME financing. However, the recent downfall of service quality has become a major concern for the bank.
EBL
Eastern Bank Limited (EBL) is one of the modern, fully online and technologically superior private commercial Banks in Bangladesh. Eastern Bank markets a wide range of depository, loan & card products. Eastern Bank has its presence in major cities/towns of the country including Dhaka, Chittagong, Sylhet, Khulna and Rajshahi. Currently it has around 40 branches all over the country. Tracing its origin back to 1992, EBL is serving the individual and corporate clientele alike with remarkable success offering innovative banking services since then.
Prime Bank Ltd.
Prime Bank Ltd. was created and commencement of business started on 17th April 1995. The sponsors are reputed personalities in the field of trade and commerce and their stake ranges from shipping to textile and finance to energy etc. Prime Bank Ltd. has already made significant progress within a very short period of its existence. The bank has been graded as a top class bank in the country through internationally accepted CAMEL rating. The bank has already occupied an enviable position among its competitors after achieving success in all areas of business operation. The bank has consistently turned over good returns on Assets and Capital. During the year 2005, the bank has posted an operating profit of Tk.1520.34 million and its capital funds stood at Tk.3177.32 million. Out of this, Tk.1400 million consists of paid up capital by shareholders and Tk.1777.32 million represents reserves and retained earnings
1.8.1 SWOT Analysis
Strength
ü American Express Credit Card: The City Bank Ltd. has launched both local and dual currency (BDT & Dollar) Amex Credit Cards on 7th November, 2009. According to the claws of the agreement, CBL is going to be the sole provider and dealer of Amex cards in Bangladesh. Brand image of Amex is certainly going to leverage the brand reputation of City Bank Ltd.
ü New management: City Bank’s management team has significantly changed since the year 2007. Personalities and brilliant minds like Mahmood Sattar, Mashrur Arefin, Sohail R K has taken over the new management. New and new departments like NFB (Non funded business), Policy & analysis etc are opened for better operation purposes.
ü Experience: City Bank Ltd. has been in the industry for around 25 years. This long period of existence in the industry has helped CBL to gain in-depth knowledge about the industry trends as well as helped to build up strategic partnership with many corporations which most other banks could not achieve in the shorter period of time.
ü Availability of Branches: Currently CBL has 82 Finacle (Online) branches, 1 full fledged Islami Banking Branch and 5 SME centers throughout the country. This big number of branches is giving easy access to their customer which is a huge advantage of CBL over its customers.
Weaknesses
ü Low remuneration package: Compared to other banks, CBL’s remuneration package is poor. With this lower payment policy, CBL won’t be able to hire the best executives of the country and might even loose their existing brilliant executives to other banks.
ü Lower service quality: Compared to HSBC or SCB, CBL’s service standard is way lower. Except few selected branches (Dhanmondi, Gulshan branch), most other banks don’t even have posh and neat interior decoration. Customers are not treated according to their expectation level and service is very slow.
ü Existing elderly employees: A big percentage of CBL employees are working in this bank over 15 years. The new management is finding it hard to deal with these employees, especially with them who are reluctant to accept new policies and change within the organization. Now it’s a matter of question for the CBL top management that whether to find an appropriate exit strategy for these employees or whether to arrange appropriate training programs to educate them.
ü Poor Brand Image: Prior to the launching of Amex Cards, CBL had negative brand image among its customers which lasted for more than 20 years. Now it would be difficult for this new management to change this brand image all of a sudden.
Opportunities
ü Credit Card Business: The card business of Bangladesh is booming since last few years. ATM’s, Debit cards & Credit cards are becoming a priority product both for the customers and bank itself. A major portion of the Bank’s income comes from card business. CBL has already launched AMEX Credit Cards on 7th November, 2009. This is certainly going to boost their card business and brand image. In addition, CBL is looking forward to include Master Card in their card business. They are hoping to bring Master Card by July, 2010. Both these brands possess huge potential for CBL to grow as the leader in the card business in Bangladesh.
ü Online Banking: With the advancement and availability of technology, the need for online banking is getting more priority. Both foreign and local banks are moving towards online banking to ease the transaction process for the customers. CBL too, has taken some tremendous efforts. They have already converted 83 of their branches into online branch and providing certain services through internet.
ü Automation: Since 2007, one of CBL’s major projects was to automate its operation by using latest technology and software. Currently all of their branches are connected through intranet. This network based banking is making the overall departmental jobs much easier and faster, ensuring better and much faster customer service. CBL employees are also using software called ‘Finacle’ which helps them to track information and data about their customers within a matter of minutes. This move towards automation will certainly provide CBL a big advantage over other banks in the industry.
Threats
ü VISA Credit discounts: We have already mentioned that CBL has undertaken an ambitious project of American Express in the card segment of the banking industry. However, the card segment of Bangladesh is already dominated by Visa credit cards. Moreover, right after the launch of Amex Cards, several banks (i.e. standard chartered bank) has undergone significant discounts in their visa card offerings. Under these circumstances, further promotional efforts in Visa by other banks can possess a devastating effect in CBL’s Amex Project.
ü Failure to establish AMEX brand image: Compared to the existing foreign banks, CBL’s brand reputation is considered somewhat poor. Especially in case of service quality. With the existing brand image of its own, CBL might fail to establish AMEX brand image properly.
ü Maintaining a broad target market: CBL’s target market consist of consumers from lower class to consumers with high net worth. Recently undertaken ‘Celtic Project’ is designed for solely the elite class of Bangladesh. However, with limited training, the existing employees might turn to provide inefficient service to these different classes of people, especially since the expected service quality of the upper class is much different than the lower classes.
ü Management Collision: In the year 2006, a significant change occurred in the history of CBL’s management because of the sudden recruitment of certain personalities like Mahmood Sattar, Sohail R. K. and Mashrur Arefin. Being in the position of MD, Mr. Mahmood Sattar renovated the overall structure of the bank and centralized its operations. He tried to ensure that the new management consists of young and highly talented people of the industry.
After this change in the top management, over 200 employees from different banks (especially from eastern bank ltd.) were recruited. However, a major portion of the bank still comprises of employees who are working here for more than 15 years and finding it hard to match with the pace of this new management. Many of these employees think that under this new management their future prospect of job is zero and to some extent they are neglected in the newly undertaken projects of the bank. On the contrary, the new management is not even ready to agree that there exists some sort of misunderstanding and is trying to convince that only people with high abilities have been chosen for newly undertaken projects. This invisible curtain of misunderstanding between these two groups of employees can cause significant damages in the upcoming projects of CBL.
1.9 Current State of operations:
The Celtic Project: CBL is currently running ‘The Celtic Project’ under which they have brought American Express Credit Cards in Bangladesh. They have launched two variants of American Express Cards (Amex Gold & Blue). Under this project their objective is to sell 15000 Amex credit cards by May 2010. The total amount of investment in this project is around 65 crore taka and the estimated pay back period is around 2 years. In order to achieve this target, the Celtic team has gone through extensive market research and Amex acquisition plan. Currently the card team members of Celtic Team is going through strategic partnerships with different MNC’s and reputed local organizations in Bangladesh.
Service Quality Renovation: CBL has recently implemented many new service quality policies to improvise its customer service level. One stop teller service, mystery shoppers, central complaint system…
Automation: In order to pace up the service delivery process and to reduce the cost and hazard of paper work, CBL is going through massive automation process. Important branches and offices are already being provided with latest model computers, printers, scanners, ID card readers and CCTV’s while other branches are still in the automation process. They have recently implanted ‘Finacle’ software which helps their employees to track down the data of every customer and employees of the organization.
Expansion of operations: CBL is expanding its operation in a rapid pace by opening new branches and departments. CBL has recently opened 3 new branches in Gulshan Avenue, Prabartak and Banani. CBL has also opened 5 new SME centers at Gazipur, Jamalpur, Hobigonj, Kishoregonj and Maijdicourt.
Promotion & Publicity: CBL has undertaken a massive promotional budget in order to promote their new brand image and newly launched product Amex cards. They are basically using print media, billboards and radio coverage to promote their brand. For more successful response, they have renovated their branding department, headed by newly joined Nazmul Karim. The brand & communications department is jointly working with their partner Unitrend Advertising Agency to promote CBL’s new look and brand image.
2.0 Future Directions
Online Banking: CBL has an ambition of becoming most modern and advanced equipped bank in Bangladesh. It believes that a major step toward this goal would be to specializing in online banking. It has already converted 80 percent of its branches into online branches. Although currently customers can get limited service through internet, but CBL believes it will enhance its services through online in the coming years.
Card Business: The City Bank Ltd. believes that Card business is the present and probably the future of banking. That is why they are putting maximum focus in this part of the business. They have introduced American express credit cards, maximized the number of ATM booths and also looking forward to bring other prestigious brands like MasterCard in Bangladesh.
Non Funded Business: This segment of the bank does not require any additional funds; however by taking some important steps it can bring additional income for the bank. Although banks like HSBC, SCB and even local banks like EBL, BRAC already has their non funded income department working; CBL thinks it’s not too late to get into this business. By providing value added services (i.e. visa related services, student counseling, tourism and medical related services) and going for effective strategic partnerships, the NFB department can do a lot for this bank.
2.1 Introduction
City Bank Ltd. is one of the first generation private Commercial Banks in Bangladesh, which has started its operations on 27th March, 1983, in DhakaCity. The bank currently has 83 online branches all around the country, including one full fledged Islami Banking branch. A couple of years ago, CBL took an ambitious objective of becoming the number one private commercial bank in Bangladesh. In order to achieve this goal, CBL is still going through a massive restructuring process and emphasizing a lot in its service quality level.
This internship project solely focuses on the service quality of CBL. This project has tried to assess the new service policies of CBL by surveying its customers and also tried to find out whether its new policies are creating any positive impact in the mind of the consumers.
2.2 Objective
The primary objective of this report is to find out the consumer perception level of service quality of the City Bank Ltd. The first portion of the report (i.e. Organization part) has presented the policies and service quality concepts that have recently been applied by City Bank Ltd (i.e. one stop service, mystery shoppers) in their organization. The following portion of the report (i.e. Project part) tried to measure its effectiveness by means of consumer survey.
2.3 Significance of the Study
Service quality is often considered as a major factor for the success behind a business. In the Banking sector of Bangladesh, the emphasis for continuous improvement in the service quality level has been observed in past few years. Local banks like: BRAC Bank, EBL, Dutch-Bangla Bank and many others have tried to set an example in terms of service quality in the Banking industry. Many banks changed their operating style and converted to Centralized system in order to improvise their monitoring system for service quality.
Service quality has been a major issue for CBL throughout the restructuring process.
To change its prior negative image regarding service quality, CBL has renewed its service quality team and implemented new policies such as: One stop service, mystery shoppers, central complaint system etc. CBL is also arranging training sessions for customer service offices and tellers to improvise overall quality of the service. Branch redesigning, new method of branding and exclusive publicity & promotion are just another way of changing consumer perception of the old CBL’s image into a new dynamic bank. This report would help us to understand whether or not these theoretical models and practical steps are really improvising the service quality standard of CBL.
2.4 Hypotheses
As I have mentioned earlier, the primary objective of this report is to find out the consumer perception level of service quality of the City Bank Ltd. And in order to determine that, it would be helpful if we assume that CBL’s customers are really satisfied/ dissatisfied with the banks service standard. Therefore, this is going to be our principle hypotheses.
H1 (Alternative hypothesis): CBL customers are satisfied with the service standard
HØ (Null Hypothesis): CBL customers are not satisfied with the service standard
Here, Service Quality is taken as the dependant variable (Y). However, there could be a number of independent variables in this scenario. This report is going to consider the following variables as the key independent variables: V1: Tangibles, V2: Reliability, V3: Assurance, V4: Responsiveness and V5: Empathy. The nature of these variables will be discussed in details in the methodology section.
The hypotheses part is divided in two types:
1) Primary hypothesis &
2) Supporting hypotheses
In order to prove the primary hypothesis, a survey was conducted among 120 participants. The participants were asked questions which were based on SERVQUAL model. The responses were gathered and collected data was converted into softcopy in order to analyze it through SPSS software. Chi-Square test, Independent sample t test, ANNOVA and Regression analysis was done in order to prove the primary hypotheses. In each case, I had to count on supporting hypotheses to prove the test.
The following supporting hypotheses were taken into account:
In case of the Chi-Square test, the assumed hypothesis was:
H1 (Alternative hypothesis): Goodness of fit in between gender and age group
HØ (Null Hypothesis): There is no Goodness of Fit in between gender and age group
In case of the Regression Analysis, the assumed hypothesis was:
H1 (Alternative hypothesis): There is a significant linear relationship between y and the independent variables
HØ (Null Hypothesis): There is no linear relationship of y to the independent variables
For Independent sample t test
H1 (Alternative hypothesis): There is a significant difference between the male and female satisfaction of the service quality of city bank ltd
HØ (Null Hypothesis): There is no significant difference between male and female satisfaction of the service quality of city bank ltd
For ANNOVA test, the assumed hypothesis was:
H1 (Alternative hypothesis): There is a significance difference of the mean value of the service satisfaction level of the customers between at least two different branches of CBL
HØ (Null Hypothesis): There is no significance difference of the mean value of the service satisfaction level of the customers between different branches of CBL
2.5 Methodology
2.5.1 Data
The research design includes mainly primary data and a minor portion of secondary data. In order to collect primary data, a survey questionnaire was prepared based on the SERVQUAL model. The questionnaire consisted three sections:
- Demographics
- Perception &
- Satisfaction
In the beginning portion of the questionnaire, customers were presented with questions related to their ‘demographics’ and was presented with check boxes to fill up personal information (i.e. age, sex, monthly income, frequency of visit, visited branch etc.)
The section ‘perception’ was solely designed on the several dimensions of SERVQUAL model. For our better understating, the SERVQUAL model has been discussed below:
SERVQUAL MODEL
SERVQUAL is a multi-item scale developed to assess customer perceptions of service quality in service and retail businesses. SERVQUAL or RATER is a service quality framework. SERVQUAL was developed in the mid eighties by Zeithaml, Parasuraman & Berry. The scale decomposes the notion of service quality into five constructs as follows:
* Tangibles – physical facilities, equipment, staff appearance, etc.
* Reliability – ability to perform service dependably and accurately
* Responsiveness – willingness to help and respond to customer need
* Assurance – ability of staff to inspire confidence and trust
* Empathy – the extent to which caring individualized service is given
SERVQUAL represents service quality as the discrepancy between a customer’s expectations for a service offering and the customer’s perceptions of the service received, requiring respondents to answer questions about both their expectations and their perceptions (Parasuraman et. al., 1988). The use of perceived as opposed to actual service received makes the SERVQUAL measure an attitude measure that is related to, but not the same as, satisfaction (Parasuraman et. al., 1988).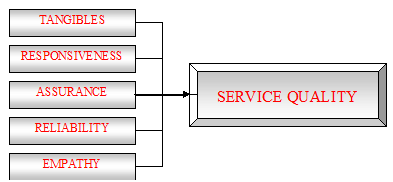
In the ‘Perception’ and ‘Satisfaction’ section, participants were requested to fill up boxes designed in likert scale. The dimensions of service quality –Tangibles, Reliability, Responsiveness, Assurances and Empathy are measured on a 5-point scale where 1 being strongly disagree and 5 being strongly agree.
In the ‘Perception’ section, each of the constructs of SERVQUAL model was used to gather information about consumer perception of the service quality standard. With in the ‘Perception’ section, there were five sub sections based on the SERVQUAL constructs (i.e. tangibles, reliability etc.). From questions 1 to 33, customers were asked questions based on the constructs of the SERVQUAL model.
In the ‘Tangibles’ section, questions like: a) CBL branches has neat and posh interior decoration b) Bank stuffs were consistent with smart and tidy dress-up & five more similar questions were presented.
In the ‘Reliability’ section, questions like: a) Bank statements were error-free b) City Bank performs the service right the first time & four other similar questions were presented.
In the ‘Responsiveness’ section, questions like: a) CBL employees provide prompt services to customers b) CBL employees are always willing to help you & similar questions were asked.
In the ‘Assurance’ section, questions like: a) The behavior of staffs instill confidence in customers b) Customers feel safe and rely on banks expertise & similar five more questions were presented.
In the ‘Empathy’ section, questions like: a) Customers are given individual attention b) City Bank has your best interest at heart & similar four more questions were asked.
Then finally in the ‘Satisfaction’ section, respondents were asked about whether they are really satisfied with the branch and overall banking experience or not. In question number 33, 34 & 35, participants were presented with questions like: a)The service provided by CBL was up to your expectation level b) The service provided by CBL is comparatively better than other top banks of the industry etc.
* A sample copy of the questionnaire is presented in the Appendix section.
2.5.2 Variables
It has been mentioned before in the hypotheses section, that the dependent variable in this report is going to be Consumer Satisfaction (Y). On the contrary, we have five independent variables (i.e. the 5 constructs of SERVQUAL model). The independent variables are following:
X1: Tangibles – physical facilities, equipment, staff appearance, etc.
X2: Reliability – ability to perform service dependably and accurately
X3: Responsiveness – willingness to help and respond to customer need
X4: Assurance – ability of staff to inspire confidence and trust
X5: Empathy – the extent to which caring individualized service is given
The generic formula which is used here is,
Consumer Satisfaction (Y) = α + βtangibles + βresponsiveness + βreliability + βassurance + βempathy
2.5.3 Data Collection
Data collection method consisted ‘structured questionnaires’ and no personal interview or any other data collection method. After obtaining the approval for conducting the project, the survey questionnaire was distributed in more than three branches of CBL, namely Gulshan, Dhanmondi, Motijheel etc. It took around 15 days to collect information from the branches and after that the responses were put into SPSS software. It took 6 more days to complete the data entry part.
On the contrary, Secondary data was collected solely from the banks resources (i.e. department files, memos, approvals and the intranet) and mainly focused on the policies and service related concepts that have already been applied within the organization. Secondary data helped me to understand the organizational structure, functionality of the various departments and ongoing projects of CBL.
2.5.4 Sample
The population for the project is all the customers of The City Bank Ltd. which is significantly large. However, considering our limited time frame, the sample size was reduced to 120 participants. In order to choose valid participants, the following criteria were followed:
i. All participants were CBL customers
ii. None of the participants were employed in any department of The City Bank Ltd.
iii. All participants were customers of CBL for at least one year period
iv. All participants had frequently visited CBL in past 6 months
2.6 Results
2.6.1 Cross tabs and chi square
Age * Gender Cross tabulation
Gender | Total | ||||
| Male | Female | Male | |||
| Age | 18-25 | Count | 13 | 15 | 28 |
| Expected Count | 18.2 | 9.8 | 28.0 | ||
| % within Age | 46.4% | 53.6% | 100.0% | ||
| % within Gender | 16.7% | 35.7% | 23.3% | ||
| % of Total | 10.8% | 12.5% | 23.3% | ||
| 26-35 | Count | 33 | 19 | 52 | |
| Expected Count | 33.8 | 18.2 | 52.0 | ||
| % within Age | 63.5% | 36.5% | 100.0% | ||
| % within Gender | 42.3% | 45.2% | 43.3% | ||
| % of Total | 27.5% | 15.8% | 43.3% | ||
| 36 and above | Count | 32 | 8 | 40 | |
| Expected Count | 26.0 | 14.0 | 40.0 | ||
| % within Age | 80.0% | 20.0% | 100.0% | ||
| % within Gender | 41.0% | 19.0% | 33.3% | ||
| % of Total | 26.7% | 6.7% | 33.3% | ||
| Total | Count | 78 | 42 | 120 | |
| Expected Count | 78.0 | 42.0 | 120.0 | ||
| % within Age | 65.0% | 35.0% | 100.0% | ||
| % within Gender | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | ||
| % of Total | 65.0% | 35.0% | 100.0% | ||
Chi-Square Tests
Value | df | Asymp. Sig. (2-sided) | |
| Pearson Chi-Square | 8.255(a) | 2 | .016 |
| Likelihood Ratio | 8.411 | 2 | .015 |
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 8.185 | 1 | .004 |
| N of Valid Cases | 120 |
a. 0 cells (.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 9.80.
Symmetric Measures
Value | Approx. Sig. | ||
| Nominal by Nominal | Phi | .262 | .016 |
| Cramer’s V | .262 | .016 | |
| Contingency Coefficient | .254 | .016 | |
| N of Valid Cases | 120 | ||
a. Not assuming the null hypothesis.
b. Using the asymptotic standard error assuming the null hypothesis.
Chi square test
H1 (Alternative hypothesis): Goodness of fit in between gender and age group
HØ (Null Hypothesis): There is no Goodness of Fit in between gender and age group
The Chi Square Value of our cross tabulation is 8.255 with 2 degrees of freedom. The Asymptomatic Significance (i.e. the P-value) is 0.016 (which is less than 0.05) which shows that it is significant. Thus there is Goodness of Fit of our cross tabulation between these different categorical data sets (Gender group and age).
The Phi value and Cramer’s Value both tell us the strength of the test. Our values are both .262, which is quite weak. The closer this value is to 1.00, the stronger is our test.
Description
This Cross-Tabulation Test is a Descriptive Statistics Analysis that I have done on two categorical data sets. I have tried to compare the age group of Males and Females customers. My analysis indicates there is Goodness of Fit of the relationship between the cells.
Among the age group of 18-25, 13 Males and 15 Females responded that they fall in the given age category. The expected count for males to respond in this category was 18.2, and for females were 9.8. The actual count for male in this case was lower to the probabilistic expectation. The actual count for female in this case was higher to the probabilistic expectation. Among all respondents who fell in this category, 46.4% were male users, and females were 53.6%. Among total male respondents, 6.9% were from this age group, and among total female respondents 35.7% were from this age group.
Among the age group of 26-35, 33 Males & 19 Females responded that they fall in the given age category. The expected count for male in this category was 33.8 and for females were 18.2. The actual count for both male and female were analogous to the probabilistic expectation. Among all respondents who fell in this category, 63.5% were male users and females were 36.5%. Among total male respondents, 10.8% were from this age group, among total female respondents 12.5% were from this age group.
Among the age group of 36 & above, 32 Males & 8 Females responded that they fall in the given age category. The expected count for male in this category was 26 and for females were 14. The actual count for male in this case was little higher than the probabilistic expectation. The actual count for female in this case was lower than the probabilistic expectation. Among all respondents who fell in this category, 80.0% were male users, and females were 20.0%. Among total male respondents, 65.0% were from this age group, and among total female respondents 35.0% were from this age group.
2.6.2 Regression test
Descriptive Statistics
Mean | Std. Deviation | N | |
| msatisfaction | 2.7583 | 1.08806 | 120 |
| mtangible | 3.1357 | .77605 | 120 |
| mreliable | 3.1750 | .57445 | 120 |
| mresponsiveness | 3.0643 | .66771 | 120 |
| massurance | 3.3917 | .72098 | 120 |
| mempathy | 3.1347 | .70654 | 120 |
ANOVA (b)
| Model | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| 1 | Regression | 117.558 | 5 | 23.512 | 114.927 | .000(a) |
| Residual | 23.322 | 114 | .205 | |||
| Total | 140.881 | 119 |
a Predictors: (Constant), mempathy, mreliable, mtangible, massurance, mresponsiveness
b Dependent Variable: msatisfaction
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval for B | |||
B | Std. Error | Beta | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | B | Std. Error | ||
| 1 | (Constant) | -2.035 | .238 | -8.539 | .000 | -2.507 | -1.563 | |
| mtangible | .057 | .090 | .041 | .632 | .529 | -.122 | .236 | |
| mreliable | .022 | .119 | .012 | .183 | .013 | -.215 | .258 | |
| mresponsiveness | .634 | .132 | .389 | 4.817 | .000 | .374 | .895 | |
| massurance | .214 | .116 | .142 | 1.846 | .045 | -.016 | .445 | |
| mempathy | .598 | .139 | .388 | 4.295 | .000 | .322 | .873 | |
Regression hypothesis
Null Hypothesis (HØ): There is no linear relationship of y to the independent variables
Hypothesis 1 (H1): There is a significant linear relationship between y and the independent variables
In the ANNOVA table, the F value is 114.927 and the significance level of the F value is 0.00.As a result we reject the Null hypothesis that there is no linear relationship of y to the independent variables. The Dependant variable is somehow affected by the independent variables.
In the coefficients table, it is observed that the independent variables that affect the dependant variables (Customer Satisfaction) are Reliability, Assurance, Responsiveness and Empathy as all of their F value significance level is less than 0.05. However, the independent variable that does not have a significant affect on the dependent variable is Tangibility.
In the coefficients table, it is also observed that the independent variables which move in the same direction as dependent variables are all the independent variables – Tangibility, Reliability, Assurance, Responsiveness and Empathy as their unstandardized coefficients B value is positive.
In the Model Summary Table, it can be found out that Adjusted R square value is .827. Thus we can conclude the model has got a very good predictive power. So the Regression model is a very good fit.
2.6.3 Independent sample t Test
Group Statistics
| Gender | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | |
| You are fully satisfied with City Bank’s Service Quality | Male | 78 | 2.40 | 1.313 | .149 |
| Female | 42 | 2.95 | 1.168 | .180 |
Hypothesis 1 (H1): There is a significant difference between the male and female satisfaction of the service quality of city bank ltd
Null Hypothesis (HØ): There is no significant difference between male and female satisfaction of the service quality of city bank ltd
Over here the categorical data is the gender, and the numeric data is service satisfaction level of city bank ltd. The mean of male’s service satisfaction is 2.40 (N=78, Std. Deviation=1.313) and the mean of female’s service satisfaction is 2.95(N= 42, Std. Deviation = 1.168). As the Levene’s Test shows a value of .282, we see the data set of the first row of the t-test for Equality of Means. The t value is -2.294 and the degree of freedom is 118. The P-Value is .024 (i.e. <.05), which means it is significant. So we accept hypothesis 1 which states that there is there is a significant difference between the male and female satisfaction of the service quality of city bank ltd and reject hypothesis 2.
2.6.4 ANNOVA
Test of Homogeneity of Variances
You are fully satisfied with City Bank’s Service Quality
Levene Statistic | df1 | df2 | Sig. |
3.882 | 3 | 116 | .011 |
ANOVA
You are fully satisfied with City Bank’s Service Quality
Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| Between Groups | 128.160 | 3 | 42.720 | 71.994 | .000 |
| Within Groups | 68.832 | 116 | .593 | ||
| Total | 196.992 | 119 |
ANNOVA Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis (HØ): There is no significance difference of the mean value of the service satisfaction level the customers between different branches of CBL
Hypothesis 1 (H1): There is a significance difference of the mean value of the service satisfaction level the customers between at least two different branches of CBL
The mean for the Motijheel branch is 1.85(N=53, std. Deviation = .907). The mean for the Gulshan branch is 3.43(N=35, std. Deviation = .778). The mean for the Dhanmondi branch is 4.22(N=18, std. Deviation = .428). The mean for the other branch is 1.21(N=14, std. Deviation = .426) In the ANNOVA table, the F value is 71.994 with degrees of freedom of 3. The level of significance is .000(< 0.05), and as a result we accept the alternative hypothesis that there is a significance difference of the mean value of the service satisfaction level of the customers between at least two different branches of CBL. Post Hog table is studied below for detailed analysis.
In studying both LSD and HSD, we can see that the significant p –value between all the different groups are less than 0.05. As a result, we can conclude that the customers of CBL experience different level of service satisfaction at different branches.
2.7 Results Discussion
In the Regression Analysis, it is observed that the independent variables that affect the dependant variables (Customer Satisfaction) are Reliability, Assurance, Responsiveness and Empathy. All of these variables have a positive correlation with the dependant variable. However, the independent variable Tangibility also moves in the same direction but does not affect the dependant variable in the linear equation. In the ANNOVA table, the F value is 114.927 and the significance level of the F value is 0.00. In the Model Summary Table, it can be found out that Adjusted R square value is .827 which shows the Regression Model has very good predictive power.
In the Independent Sample t test, it is observed that the mean value of both males and females satisfaction of the service quality vary significantly. The mean value of females is 2.95 whereas the mean value of males is 2.40. It can be concluded the females slightly have a higher degree of satisfaction than males. On a scale of 1 to 5, as the females have a mean value close to 3, it can be said that the females are moderately satisfied whereas the males are lowly satisfied.
In the ANNOVA tests, the service quality satisfaction level in different locations was analyzed. The mean for the Motijheel branch is 1.85(N=53, std. Deviation = .907). The mean for the Gulshan branch is 3.43(N=35, std. Deviation = .778). The mean for the Dhanmondi branch is 4.22(N=18, std. Deviation = .428). The mean for the other branch is 1.21(N=14, std. Deviation = .426). The mean value was different in almost all of the branches.
The mean values for Motijheel and Other branches were very low and below 2. The highest value was found for Dhamondi Branch with a value of 4.22. Gulshan Branch had a moderate value of 3.43 showing moderate levels of satisfaction. In the ANNOVA table, the F value is 71.994 with degrees of freedom of 3.
In the Chi square test, the Chi Square Value is 8.255 with 2 degrees of freedom. The Asymptomatic Significance (i.e. the P-value) is 0.016 (which is less than 0.05) which shows that it is significant. Hence there is a goodness of fit between the data sets. However, the Phi and Crammers values were very low (.262) which showed the test was very weak.
2.8 Recommendations
- Educate employees with the new service policies
- Ensure effective implementation of assumed policies
- Enhance effective branch monitoring
- Offer sufficient training for branch employees
- Motivate employees for outstanding performances
- Blend the expertise of old employees with the creativity of newly recruited staffs.
2.9 Limitations of the Study
- Small sample size compared to large population
- Lack of secondary data in internet, manuals & intranet.
- Limited access to internal office files
- Sheer size of the project compared to limited time frame
- Little assistance from CBL employees due to their busy work schedule
|
Recommendation
On the basis of the problems we can suggest these recommendation-
- The banking should completely be operated through online. Though it is online banking facilities in some branches, but still some works are being done manually, which should be eliminated gradually and it will automatically give more efficiency in service.
- Employees training should be conducted so that they will be more professional and efficient to deal with problem customers and problematic situations.
- Individual attention should be given to customers in order to better understand their needs and better satisfy them.
- City BANK should pursue a positive advertising campaign in order to build up a strong image and reputation among potential customers. TV ads should be aired to reach a wider array of customers. The ads should capitalize on building strong relationship, needs of customers and quality service of the bank rather than features of products.
- CBL should arrange the monthly seminar or workshop on the vest area of Foreign Exchange business and its contemporary issues for the branch’s officer. Certainly this workshop will motivate them.
- Head office of this bank should supply necessary prospectus about the information of the bank for the clients. Although every table of every section is capable of supplying the various information about the bank but this task is generally preformed by the front desk or account opening section. However this section is found always busy. Therefore, if CBL wants to perform this task in more efficiently the branch should keep a Reception Section.
|
Conclusion
The City Bank Ltd. went through a massive restructuring process during the year 2006. During that period, the bank took some important initiatives (i.e. Centralization, one stop service training, know your customer profile, mystery shoppers etc.) to improvise its customer service quality. However, even after taking such steps the bank still could not change its service quality image completely in its consumer minds.
This study shows that except few exceptions, CBL consumers possess very low satisfaction level in terms of customer service. The report also shows that the level of customer satisfaction varies from branch to branch. While Dhanmondi branch, rated as the best customer service provider, other branches scored to be moderate or very low in terms of customer satisfaction. The reason behind this fact is that previously CBL failed to establish a uniform service quality standard within their organization and the branches served their customers according to their own method. However, The City Bank Ltd. has recently been transformed in to a Centralized bank. And performances of branches like Dhanmondi & Gulshan can be taken as ideal examples.



![Thesis Paper on Performance Analysis and Budgetary Control Activities of Trade Vision Limited [Part-2]](https://assignmentpoint.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/images-18-200x100.jpg)












