Executive Summary
The Garment industry of Bangladesh has been the key export division and a main source of foreign exchange for the last 25 years. At present, the country generates about $5 billion worth of products each year by exporting garment. The industry provides employment to about 3 million workers of whom 90% are women. Two non-market elements have performed a vital function in confirming the garment industry’s continual success; these elements are (a) quotas under Multi- Fibred Arrangement1 (MFA) in the North American market and (b) special market entry to European markets Bangladesh’s industrial base, which has remained stagnant over the past two decades, is very narrow, contributing to about 11.5 percent of the GDP (BBS, 2001). Within this narrow industrial sector, however, the ready-made garments (RMG) industry has flourished as its most dynamic sector. Since its modest beginning in the early 1980s, the industry has contributed to the economy appreciably in terms of employment, output, and foreign exchange earnings. Moreover, employing as it does more than 1 million young women, the industry has brought about a noticeable change in society as well as in intra-household gender relations.
The phasing out of the MFA by the end of 2004, together with ever-increasing globalization, will exert intense competitive pressure on Bangladesh’s RMG industry. As the future of the manufacturing sector and the overall economy crucially depends on the performance of this industry, a matter of serious concern is how far, and in what manner, the RMG industry will face up to the challenge of the post-MFA trading scenario.
Investigate whether the reduction in wage rates and worsening of working conditions in the RMG industry figure as strategies to continue to be competitive in the world apparel market.
1.1 Objective :
The garment industry of Bangladesh has been the key export division and a main source of foreign exchange for the last 25 years. At present, the country generates about $5 billion worth of products each year by exporting garment. The industry provides employment to about 3 million workers of whom 90% are women. Two non-market elements have performed a vital function in confirming the garment industry’s continual success; these elements are (a) quotas under Multi- Fibred Arrangement1 (MFA) in the North American market and (b) special market entry to European markets, Bangladesh’s industrial base, which has remained stagnant over the past two decades, is very narrow, contributing to about 11.5 percent of the GDP (BBS, 2001). Within this narrow industrial sector, however, the ready-made garments (RMG) industry has flourished as its most dynamic sector. Since its modest beginning in the early 1980s, the industry has contributed to the economy appreciably in terms of employment, output, and foreign exchange earnings. Moreover, employing as it does more than 1 million young women, the industry has brought about a noticeable change in society as well as in intra-household gender relations.
The phasing out of the MFA by the end of 2004, together with ever-increasing globalization, will exert intense competitive pressure on Bangladesh’s RMG industry. As the future of the manufacturing sector and the overall economy crucially depends on the performance of this industry, a matter of serious concern is how far, and in what manner, the RMG industry will face up to the challenge of the post-MFA trading scenario. In this connection, there is growing apprehension as to whether the industry, in order to remain competitive, will see both a reduction in the already very low wage levels and a further deterioration of the already very poor working conditions. This study aims to:
Investigate whether the reduction in wage rates and worsening of working conditions in the RMG industry figure as strategies to continue to be competitive in the world apparel market.
1.2 Methodology:
There are two types of sources of methodology. One is primary and another is secondary sources while conducting the study both primary and secondary information were explored. But hardly any primary information could be found. In the absence of primary information the majority of the study has been based on secondary information. For the procurement of data, we had to take support of some specific methods as follows:
Then we went for the answers in the analytical point of view, which provides the mitigation of our requirements.
- Interviewing:
Some times we went for personal interviews of some of the personnel who are treated as specialist in respective assignments. They assisted us with primary and secondary information and otherwise showed us clues for where about of our requirements.
- Computer Sections:
While conducting the study both primary and secondary information were explored. But hardly any primary information could be found. In the absence of primary information the majority of the study has been based on secondary information. For the procurement of data, we had to take support of some specific methods as follows:
Using both of the two sources has collected data.
The “Primary sources” are as follows:
– Face to face conversation with the officer and employees.
– File study of different section of deskwork.
– Face-to-face conversation with clients visited the organization.
– Relevant field study as provided by the officer concern.
The “Secondary Sources” of data and the information are:
– Website of the Delta Composite.
– Various book articles.
– Different procedure manual published by Delta Composite.
– Books
1.3 Limitation:
Bangladesh garment industry still now is not that much developed. When we prepare the report in Delta Composite they don’t even have their garments profile.
We found so many difficulties in searching information.
Foreign buyers English is not that much clear.
There are many code names in garments industry that is very important for production process, and we have memorized those codes.
In garments factory most of the employees doesn’t have any educational background they do their job only with experiences.
1.4 Scope:
During preparing our report we have got chances to visit many buying house, supervise many production process, & completed many sample program. This report gives a narrative overview of the delta composite knitting industries Ltd. and its operation
2.1 Organizational Behavior
Organizational Behavior is the study and application of knowledge about how people as individual or as groups act within organizations.
2.2 Goals of organizational behavior
There are some goals of organizational behavior which are as follows:
Describe: The first goal is to describe, systematically how people behave under a variety of conditions. Achieving this goal allows managers to communicate about human behavior at work using a common language.
Understand: A second goal is to understand any people behave as they do. The managers would be frustrated if they could talk about behavior of their employees, but not understand the reasons behind those actions.
Predict: The managers would have capacity to predict which employees might be dedicated and productive or which ones might have absent, cause problem. And thus the managers could take preventive actions.
Control: The final goal of OB is to control and develop some human activity at work. Since managers are held responsible for performance outcome, they are vitally interested in being able to make an impact on employee behavior, skill development, team effort, and productivity. Managers need to be able to improve results through the actions they and their employees take, and organizational behavior can aid them in their pursuit of this goal.
2.3 Organizational Behavior Model
Five basic models have been developed on which organizational behavior is based. Autocratic Model: This is the most common model on which most garments factories are based. Here the managers or the leaders are firmly in control, and obedience is considered to be a virtue. All decisions come from the management and the rest just follow the instructions.
Custodial Model: Here the management acts as a custodian of the welfare of its employees. They are provided money and security, and the employees in turn follow the diktats of the organization. The orientation is towards providing security, and less towards providing them an opportunity to be independent and leaders
Supportive Model: As is evident from the name, here the emphasis is on support being provided by the managers to the employees. Here the employees are encouraged to improve their performance, and they are awarded recognition for their achievements. This results in an overall improvement, since a good result is praised and rewarded.
Collegial Model: Here the emphasis is on partnership between all parts of an organization. Self-discipline and responsibility are encouraged and employees are encouraged to achieve the goals that they set for themselves. Teamwork is emphasized.
The System Model: Managers and employees don’t see the business only rather they work together for the better product for society, environment, etc.
2.4 Management
Management is a process of coordination to achieve a goal in an effective and efficient way.
2.5 Vision
A possible and desirable future.
2.6 Mission
More descriptive and less future oriented.
2.7 Goal
Target with in set period time.
2.8 Empowerment
Provides greater antinomy to employee through sharing of relevant information and providing more antinomy in work.
2.9 Participation
Mental and emotional involvement of people in decision making.
2.10 Group Dynamics
The social process by which employees interact face to face in small groups.
2.11 Conflict
Conflict is any situation in which two or more employees feel themselves in opposition.
2.12 Levels of conflict
a. Intrapersonal conflict: Conflict with in an individual.
b. Interpersonal conflict: Conflict between two persons.
c. Inter group conflict: With in organization conflict between two groups or different departments.
2.13 Stress
Stress is the pressure employee feel in life.
2.14 Counseling
Counseling is exchange of ideas and feelings between two people. It is discussion with an employee of a problem that usually has emotional content in order to help the employee cope with it better. Counseling seeks to improve employee mental health and well being.
DELTA COMPOSITE KNITTING INDUSTRIES LTD. starts its journey in garment industry 1996. With interests in trading, Delta Composite is a 100% export oriented composite garments industry. The company is constantly providing customers across the world with garment sourcing solution, with manufacturing facilities. Bangladesh entered in readymade garments business in early 1980s. At that time there were very few local entrepreneurs who knew the trade. Mainly the foreign entrepreneurs directly operated their business for the cheap labor. But during late 1980s and early 1990s the scenario of Garment Sector of Bangladesh started changing. Local expert and entrepreneurs started experiencing the knowledge of the trade.
In the above context Delta Composite is a privately owned company was established in 1996. The owners possess a vast experience in dyeing, finishing, knitting of Fabric.
3.1 FACTORY ORGANOGRAM
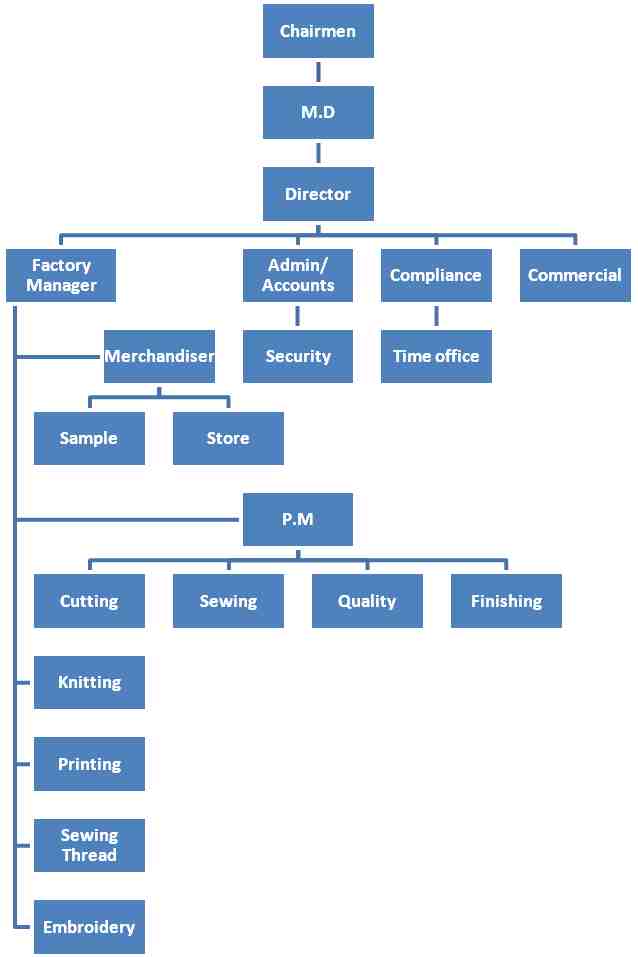
3.2 Our Concerns:
- M/S. DELTA KNITTING LTD
- M/S. DELTA SEWING THREAD
- M/S. DELTA PRINTING
- M/S. DELTA EMBROIDERY
- M/S. DELTA ACCESSORIES.
- M/S DELTA DYEING
The Company is organized into six divisions:
Our total numbers of employee are 4300. However, we are still looking towards further development and expansion in order to cover all branches of the industry, taking into consideration the availability of the raw material – cotton, competitive labor, and low power cost.
We have directed, hardworking, and efficient workforces, supervised and directed by a well-coordinated supportive management team. Not only we ensure the top quality of our products but also we treat safety, security, and hygiene as our priority area. We are equipped with fire fighting services and have a medical team of doctors and nurses to render services to our employees. We hope and believe that we can satisfy our buyers maintaining good-quality products in the most competitive market price.
3.3 List of machineries
LIST OF SEWING MACHINS
Our mission is to provide not only the highest possible product quality but also a total service.
SL. NO | DESCRIPTION | QUANTITY | BRAND |
01 | Plain Machine | 240 | ZOJE |
02 | Over Lock | 144 | ZOJE |
03 | Flat Lock | 110 | ZOJE |
07 | PMD | 04 | ZOJE |
13 | Button Hole | 06 | ZOJE |
14 | Button Attach | 06 | ZOJE |
15 | Rib Cutter | 08 | ZOJE |
| 8 | Kansai | 08 | ZOJE |
Other logistic Machineries
| 1 | Cutting | 04 |
| 2 | Auto Boiler | 02 |
| 3 | P.P Belt Machine | 02 |
| 4 | Vacuum Table | 12 |
| 5 | Steam Iron | 12 |
| Embroidery Machine (20 head) | 02 | |
| 7 | Sewing Thread Machine (72 cone) | 01 |
We have created world-class facilities to ensure better quality control and faster deliveries, the way the market is demanding today.
3.4 WORKING ENVIRONMENT:
Next to its security measures, the factory is will equipped and furnished with enough fire-fighting equipment, fire alarms systems and trained personnel for facilitating emergency evacuation. All of which contribute to minimizing the fire- risks. The factory environment, with excellent lighting and ventilation, is one of the very best of its kind in Bangladesh.
3.5 Our products

- Knitting of fabrics in 100% cotton, blends and 100% polyester
- Dyeing and finishing fabric of 100% cotton, blends and 100% polyester.
- We are manufacturer and exporter of readymade garments like T-shirts, polo shirts, sportswear, underwear, and sweatshirts, casual wear, night wears, lingerie & polar fleece jacket etc.
- Different type of printing like Pigment, Rubber, Flock, Foil, Sugar, Dicsas , Deactive, Embross, Plastic sole, Glitter, Hidensi , Transper, Gel, Stone print.
- All type of embroideries.
- Besides, we have very strong marketing division for all kinds’ of ready-made garments to expand market to Europe, U.S.A, Canada and all over the world.
3.6 Our customer
Customer | Blues Clothing, Padma , Lankstone,I.C.S-UK | |
| Gowitex, S.A Beechins & Texim, -Fabrimode, | ||
| Publi Shirt-Belgium ,Heusel GMBH-Trio GMBH, | ||
| H B PromotionGermany | Zara-Spain | |
| Super Sports Sa-France, | DIGO (BELGIUM) | |
| Setter House-Netherlands. |
Dhaka Office
House# 389, Road# 6
DOHS Baridhara, Dhaka- 1206
Tel: 02-8813636-7, 8824092
Fax: 880-2-8813635
Factory Address
Delta Composite Limited
Zarun (South), Kashimpur
Gazipur, Bangladesh.
Website address
www.deltagroup.com
SWOT Analysis
Strength:
- ISO 9001:2000/DKU-TEX/WRAP certified.
- Easily accessible infrastructure like sea road, railroad, river and air communication
- Accessibility of fundamental infrastructure, which is about 3 decade old, mainly established by the Korean, Taiwanese and Hong Kong Chinese industrialists.
- FDI is legally permitted
- Moderately open Economy, particularly in the Export Promotion Zones
- GSP under EBA (Everything But Arms) for Least Developed Country applicable (Duty free to EU)
- Improved GSP advantages under Regional Cumulative
- Looking forward to Duty Free Excess to US, talks are on, and appear to be on hopeful track
- Investment assured under Foreign Private Investment (Promotion and Protection) Act, 1980 which secures all foreign investments in Bangladesh
- OPIC’s (Overseas Private Investment Corporation, USA) insurance and finance agendas operable
- Bangladesh is a member of Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) under which protection and safety measures are available
- Adjudication service of the International Centre for the Settlement of Investment Dispute (ICSID) offered
- Excellent Tele-communications network of E-mail, Internet, Fax, ISD, NWD & Cellular services
- Weakness of currency against dollar and the condition will persist to help exporters
- Bank interest@ 7% for financing exports
- Convenience of duty free custom bonded w/house
- Readiness of new units to enhance systems and create infrastructure accordant with product growth and fast reactions to circumstances
- Energy at low price
Weakness.
- Lack of marketing tactics
- The country is deficient in creativity
- Absence of easily on-hand middle management
- A small number of manufacturing methods
- Low acquiescence: there is an international pressure group to compel the local producers and the government to implement social acquiescence. The US GSP may be cancelled and purchasing from US & EU may decrease significantly
- M/c advancement is necessary. The machinery required to assess add on a garment or increase competence are missing in most industries.
- Lack of training organizations for industrial workers, supervisors and managers.
- Autocratic approach of nearly all the investors
- Fewer process units for textiles and garments
- Sluggish backward or forward blending procedure
- Incompetent ports, entry/exit complicated and loading/unloading takes much time
- Speed money culture
- Time-consuming custom clearance
- Unreliable dependability regarding Delivery/QA/Product knowledge
- Communication gap created by incomplete knowledge of English
- Subject to natural calamities
Opportunity
- Bangladesh is included in the Least Developed Countries with which US is committed to enhance export trade
- knitwear are very economical even with china and is the prospect for Bangladesh
- If skilled technicians are available to instruct, prearranged garment is an option because labor and energy cost are inexpensive.
- Foundation garments for Ladies for the FDI promise is significant because both, the technicians and highly developed machinery are essential for better competence and output
Threat
- The exporters have to prepare themselves to harvest the advantages offered by the opportunities
Table 3.8.1: Labor costs in selected countries (in US $/hour)
Countries 1991 1993
Bangladesh NA 0.16
India 0.25 0.27
Pakistan 0.24 0.27
Sri Lanka 0.39 0.35
China 0.24 0.25
Indonesia 0.18 0.28
Thailand 0.59 0.71
Italy 13.5 NA
UK 7.99 NA
US 6.77 NA
Sources: Internet
“Productivity, Competitiveness and Job Quality in Garment Industry in India,” a discussion
paper prepared for the Sub-regional Meeting on Productivity, Competitiveness and Job Quality
DELTA COMPOSITE KNITTING INDUSTRIES LTD.
Observing the overall function of Delta Composite Knitting Industries Ltd. including its procedure of providing customers across the world with garment sourcing solution, with manufacturing facilities. There are following findings can be illustrated:
- Delta Composite Knitting industry is an organization. It is yet establish a good control in all aspect of its field.
- Corporate Relation.
- Communication and Promotion
- Employees of this industry are in huge pressure of work. The number of employee is actually not adequate.
- The training procedure of employees is not adequate.
- Delta Composite Knitting industry established excellent internal control and audit system.
Delta Composite Knitting industry is very committed to consumers. This industry has pool of expertise that is well equipped with sophisticated facilities to strengthen the actual judgment in terms of fairness, promptness and reliability. It could be more sensible if We get enough time for the company study.
QUESTIONNAIRE
Q1. Are you aware about OB in your Organization?
Ans: My organization practice OB, because of my company is certified from efficient organization, according to the certification, they maintain the different employment facilities and concern the normal employee.
Q2. Which model of OB do you follow?
a. Autocratic b. Custodial
c. Supportive d. Collegial
e. System
Ans: My organization is not following the specific organization model. I always maintain the mixed management.
Q3. Do you practice the application of motivation?
Ans: Yes.
Q4. How then?
Ans: Already I said my factory whole organization procedure is certified by world renounced organization. According to their rules and regulation we practices in OB. Also you know Garment sector has 25% worker secrecy for to ensure the better worker or employee quality rationally we practice in OB and that is giving application of motivation.
Q5. In your point of view which factor influence employee more?
- Hygiene factor
- Motivational factor
Ans: Hygiene factor. International Buying house are always emphasis on Hygiene factor (Environment, safety, standard wage, medical facilities), that’s why also we concern on Hygiene factor.
Q6. Do you think motivation increase the output of your employee?
Ans: Yes.
Q7. Which managerial role do you prefer in your organization?
- Manager
- Leader
Ans: Manager
Q8. Why you prefer this role? Kindly express.
Ans: Well, Manager(s) are always dealing with the buying house. They know all strict management and better quality managerial role is more preferable for us.
Q9. What kind of leadership style you practice?
- positive leader
- negative leader
- Autocratic leader
- consultative leader
- Participative leader
- Employee oriented leader
- Task oriented leader
Ans: Positive leader.
Q10. According to the Black & Mouton’s managerial grid what kind of leader you are?
- country club leader
- Authoritarian leader
- Impoverished leader
- Team work leader
Ans: I think Team work leader.
Q11. Do you allow employee participation in management decision?
Ans: No. Because most of the Garment workers are getting the wages and most of the time it depends on per hour basic. If we allow the participation, they can’t concentration on their performance but sometime we encourage for participation especially in critical situation in production.
Q12. Do you give empowerment to the employees?
Ans: No, employees have no empowerment because of always run the designed management.
Q13. Do you think that participation can generate better idea?
Ans: No.
Q14. Why then?
Ans: In this sector most the performing framework is fixed. So, participation can’t provide any effective result. But Human management is most important.
Q15. How do you handle informal groups like trade union?
Ans: In our company have no trade organization because of trade organization gives the flexibility of worker but flexibility is the fully opposite in Garments sector.
Q16. Do you manage conflict in your organization?
Ans: Yes, We highly emphasis on conflict management our composite is integration of different department. So, conflict management is mandatory here.
Q17. What might be the sources of conflict you think that may rise in your organization?
Ans: The conflicting sources might be:
— Production
— Procurement
— Knitting
— Dying
— Finishing
These sources might rise in my organization.
Conclusion:
Garment industry is controlled by the transfer of production. The globalization of garment production started earlier and has expanded more than that of any other factory. The global economy is now controlled by the transfer of production where firms of developed countries swing their attention to developing countries. The garment industry of Bangladesh has been the key export division and a main source of foreign exchange for the last 25 years. Many people have earned their livelihood through this industry. Their may be gender discrimination, low wage level exist in the garments industry, but still, they supply employment for all of theses people who come here to live. The Ready Made Garment industry in Bangladesh is made up of 3,486 manufacturers and accounts for 76% of total foreign exchange earnings. It employs about 180,000 managers and 1.5 Million workers, of whom 1.2 Million are women. In Bangladesh, the RMG industry has emerged as a major economic sector and has had its impact on the financial services sector, communications, transportation, and on other related industries. The RMG industry has had a major social impact. It has empowered 1.2 million women with employment and economic independence, which in turn has earned for Bangladesh recognition as a modern and enlightened society.
Garment industry is controlled by the transfer of production. The globalization of garment production started earlier and has expanded more than that of any other factory. The global economy is now controlled by the transfer of production where firms of developed countries swing their attention to developing countries. The garment industry of Bangladesh has been the key export division and a main source of foreign exchange for the last 25 years. Many people have earned their livelihood through this industry. Their may be gender discrimination, low wage level exist in the garments industry, but still, they supply employment for all of theses people who come here to live. The Ready Made Garment industry in Bangladesh is made up of 3,486 manufacturers and accounts for 76% of total foreign exchange earnings. It employs about 180,000 managers and 1.5 Million workers, of whom 1.2 Million are women. In Bangladesh, the RMG industry has emerged as a major economic sector and has had its impact on the financial services sector, communications, transportation, and on other related industries. The RMG industry has had a major social impact. It has empowered 1.2 million women with employment and economic independence, which in turn has earned for Bangladesh recognition as a modern and enlightened society.