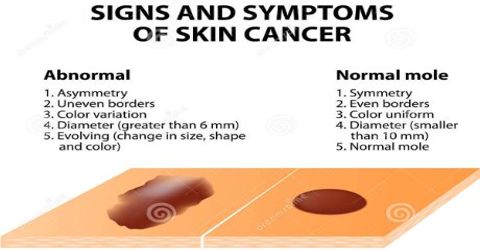
Most skin cancers are caused by revelation to the sun. This may be long-term revelation or short periods of overexposure. This is because ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun damages the DNA (genetic material) in our skin cells.
People who work outdoors have a bigger risk of skin cancer as they are uncovered to the sun for lengthy periods of time. Fair-skinned people have a bigger risk than black- or brown-skinned people. This is because the pigment in darker skin gives protection. Habitually using sunbeds and sunlamps can also enhance the risk of developing some skin cancers.
Other risk factors include earlier skin cancers, earlier radiotherapy treatment, and lowered immunity, overexposure to chemicals at work and rare genetic conditions.
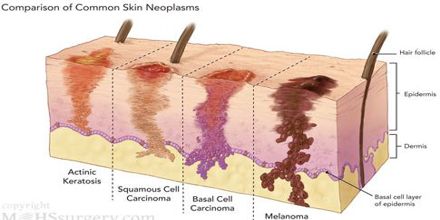
Types of skin cancer
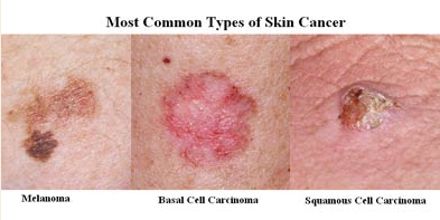
There are three main types of skin cancers: basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and melanoma.
The first two skin cancers are grouped together as non-melanoma skin cancers. Other unusual types of skin cancer include Merkel cell tumors and dermatofibrosarcoma protruberans.
Causes of skin cancer
Sunburn
Sunburn has been related with melanoma, the mainly deadly form of skin cancer.
People are also sun burnt on cooler or overcast days when they wrongly believe UV radiation is not as strong. This is wrong – you can still be sun burnt when the temperature is cool. Sun exposure that doesn’t result in burning can still cause damage to skin cells and increase your risk of developing skin cancer. Evidence suggests that normal exposure to UV radiation year after year can also lead to skin cancer.
Tanning
Tanning is a sign that you have been exposed to enough UV radiation (from the sun or solarium) to harm your skin. This will ultimately cause loss of elasticity (wrinkles), sagging, yellowish discoloration and even brown patches to appear on your skin. Worst of all, it increases your risk of skin cancer.
Family history of skin cancer
Most non melanoma skin cancers don’t run in families. But research has found some families seem to have a higher number than normal. You have an increased risk of developing a squalors cell skin cancer (SCC) if one of your parents has had an SCC. People who have a family history of melanoma have an increased risk of basal cell skin cancer (BCC).
Of course, skin type runs in families. So people from fair skinned families will be more at risk. But there might be some other inherited genes that increase the risk of non melanoma skin cancer in some families.
Other possible causes
Stories about possible causes are often in the media and it isn’t always clear which ideas are supported by facts. There might be things you have heard of that we haven’t included here. This is because either there is no evidence about them or it is less clear.
General Information about Skin Cancer
- Skin cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the skin.
- There are dissimilar types of cancer that start in the skin.
- Skin color and being exposed to sunlight can enlarge the risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer and actinic keratosis.
- Nonmelanoma skin cancer and actinic keratosis often appear as a change in the skin.
- Tests or procedures that examine the skin are used to detect (find) and diagnose nonmelanoma skin cancer and actinic keratosis.
- Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.

How skin cancer is diagnosed
Skin cancer is diagnosed by physical examination and biopsy.
Biopsy is a rapid and easy process where part or all of the spot is removed and sent to a laboratory. It may be done by your doctor or you can be referred to a dermatologist or surgeon. Results may take about a week to be ready.
Treatment of Skin cancer
In choosing the best treatment option, your doctor will judge your age and common health, the type and size of cancer, where it is on your body and what you want. The treatment option will also depend on whether the skin cancer has spread elsewhere in your body.
Types of treatment include:
- surgery
- freezing
- scraping
- radiotherapy
Who is at risk for skin cancer?
Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is utmost for people who have fair or freckled skin that burns simply, light eyes and blond or red hair. Darker skinned individuals are also susceptible to all types of skin cancer, although their risk is considerably lower.
Aside from complexion, other risk factors include having a family history or personal history of skin cancer, having an outdoor job and living in a sunny climate. A history of severe sunburns and an abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles are risk factors unique to melanoma.