Dementia is not a definite disease. It’s in general term that describes a broad range of symptoms connected with a decline in memory or other judgment skills harsh enough to decrease a person’s capability to execute everyday activities.
Memory loss and other symptoms of dementia
While symptoms of dementia can differ greatly, at least two of the following center mental functions must be notably impaired to be measured dementia:
- Memory
- Communication and language
- Ability to focus and pay attention
- Reasoning and judgment
- Visual perception
People with dementia may have troubles with short-term memory, keeping track of a purse or wallet, paying bills, planning and preparing meals, remembering appointments or traveling out of the neighborhood.

Causes
Dementia is caused by spoil to brain cells. This injure interferes with the capability of brain cells to communicate with each other. When brain cells cannot converse usually, thinking, behavior and feelings can be affected.
The brain has a lot of distinct regions, each of which is dependable for diverse functions (for example, memory, judgment and movement). When cells in a particular region are damaged, that region cannot carry out its functions usually.
While mainly changes in the brain that cause dementia are enduring and degenerate over time, thinking and memory problems caused by the following conditions may improve when the condition is treated or addressed:
- Depression
- Medication side effects
- Excess use of alcohol
- Thyroid problems
- Vitamin deficiencies
Is dementia being prevented?
When a person with dementia finds that their mental abilities are declining, they often feel weak and in require of reassurance and support. The people closest to them – including their carers, friends and family – require to do everything they can to help the person to preserve their sense of identity and feelings of self-worth.
However, a healthy lifestyle can help lower your risk of developing dementia when you are older. It can also prevent cardiovascular diseases, such as strokes and heart attacks.
To reduce your risk of developing dementia and other serious health conditions, it’s recommended that you:
- eat a healthy diet
- sustain a healthy weight
- exercise regularly
- don’t drink too much alcohol
- stop smoking (if you smoke)
- make sure to keep your blood pressure at a healthy level
Specific points include:
Weight affects dementia risk: Being overweight can raise your blood pressure, which increases your risk of getting some kinds of dementia. The risk is higher if you are fat. The most systematic way to determine your weight is to calculate your body mass index (BMI).
Exercise to reduce dementia risk: Exercising repeatedly will make your heart and blood circulatory system further proficient. It will also help to lower your cholesterol and keep your blood pressure at a healthy level, decreasing your risk of developing some kinds of dementia.
Stopping smoking could reduce dementia risk: Smoking can cause your arteries to narrow, which can lead to a rise in your blood pressure. It also increases your risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, cancer and dementia.
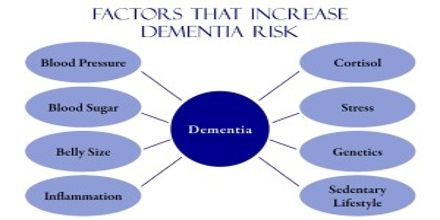
Risk Factor
Some risk factors for dementia, such as age and genetics, cannot be changed. But researchers continue to discover the impact of other risk factors on brain health and impediment of dementia. Some of the mainly active areas of research in risk reduction and prevention include cardiovascular factors, physical fitness, and diet.
Research has identified many risk factors associated with dementia. It’s not possible to get rid of every single one; after all we can’t avoid age, which is the most important. While it is possible to expand dementia early in life, the chances of doing so increase radically with age. One in 50 people between the ages of 65 and 70 have a form of dementia, compared to one in five people over the age of 80.