Calcium stearate is a carboxylate salt of calcium, classified as a calcium soap. It is a calcium salt of stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid that is commonly used in various industrial and consumer products. The salt is a component of some lubricants, surfactants, as well as many foodstuffs. It is a white waxy powder. It is insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents like chloroform and ethanol
Properties
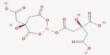
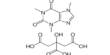
- Chemical formula: C36H70CaO4
- Molar mass: 607.030 g·mol−1
- Appearance: white to yellowish-white powder
- Density: 1.08 g/cm3
- Melting point: 155 °C (311 °F; 428 K)
- Solubility in water: 0.004 g/100 mL (15 °C)
- Solubility: soluble in hot pyridine, slightly soluble in oil, insoluble in alcohol, ether
Production and occurrence
Calcium stearate is produced by heating stearic acid and calcium oxide:
2 C17H35COOH + CaO → (C17H35COO)2Ca + H2O
It is also the main component of soap scum, a white solid that forms when soap is mixed with hard water. Unlike soaps containing sodium and potassium, calcium stearate is insoluble in water and does not lather well. Commercially it is sold as a 50% dispersion in water or as a spray dried powder. As a food additive it is known by the generic E number E470.
Chemical Properties
Calcium stearate is quite stable and not highly reactive, though it can undergo hydrolysis in the presence of water. It can react with strong acids, like hydrochloric acid, to produce stearic acid and calcium chloride.
Applications
Calcium stearate is a waxy material with low solubility in water, unlike traditional sodium and potassium soaps. It is also easy and cheap to produce, and exhibits low toxicity. These attributes are the basis of many of its applications. Related applications exist for the magnesium stearate.
- Lubricant: In the manufacturing process, calcium stearate is used as a lubricant to prevent sticking in molds or equipment.
- Plastic Industry: It is a common additive in plastics, where it acts as a stabilizer, lubricant, and dispersant. It helps to improve the flow of plastic during molding and prevents degradation.
- Cosmetics and Pharmaceuticals: Used as a binder, stabilizer, and emulsifying agent in products such as creams, lotions, and tablets.
- Paints and Coatings: As a stabilizer and dispersing agent, calcium stearate helps prevent the settling of pigments and enhances the durability of paints and coatings.
- Rubber Manufacturing: Acts as a lubricant to prevent the rubber from sticking to molds during the production process.
Safety Considerations
- Toxicity: It is considered non-toxic and is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used in food and cosmetics in low concentrations.
- Handling: While generally safe, it is important to handle the powder form with care to avoid inhalation of fine particles, which can irritate the respiratory tract.