Restoration ecology
Restoration ecology is the study of renewing a degraded, damaged, or destroyed ecosystem through active human intervention. It is the scientific study supporting the practice of ecological restoration, which is the practice of renewing and restoring degraded, damaged, or destroyed ecosystems and habitats in the environment by active human intervention and action. It aims to recreate, initiate, or accelerate the recovery of an ecosystem that has been disturbed. Effective restoration requires an explicit goal or policy, preferably an unambiguous one that is articulated, accepted, and codified. It includes activities to assist the recovery of ecosystem structure and function and the associated provision of goods and services.
Restoration ecology is a scientific discipline that applies ecological theory in order to develop general principles to guide the practice of ecological restoration.
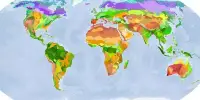
Ecological restoration has a growing role in policy aimed at reversing the widespread effects of environmental degradation. Restoration goals reflect societal choices from among competing policy priorities, but extracting such goals is typically contentious and politically challenging. Common disturbances include logging, damming rivers, intense grazing, hurricanes, floods, and fires.

Ecosystems are dynamic communities of plants, animals, and microorganisms interacting with their physical environment as a functional unit. Natural ecosystems provide ecosystem services in the form of resources such as food, fuel, and timber; the purification of air and water; the detoxification and decomposition of wastes; the regulation of climate; the regeneration of soil fertility; and the pollination of crops. These ecosystem processes have been estimated to be worth trillions of dollars annually. The practice of ecological restoration includes a wide scope of projects including – erosion control, reforestation, removal of non-native species and weeds, revegetation of disturbed areas, the reintroduction of native species, as well as habitat and range improvement for targeted species. There is consensus in the scientific community that the current environmental degradation and destruction of many of the Earth’s biota are taking place on a “catastrophically short timescale”.
The study of restoration ecology has only become a robust and independent scientific discipline over the last two decades. Scientists estimate that the current species extinction rate, or the rate of the Holocene extinction, is 1,000 to 10,000 times higher than the normal, background rate. Habitat loss is the leading cause of both species extinctions and ecosystem service decline.
Restoration ecology is a scientific discipline that applies ecological theory in order to develop general principles to guide the practice of ecological restoration. The commercial applications of ecological restoration have increased exponentially in recent years. The United Nations General Assembly (01.03.2019) declared 2021– 2030 the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration.