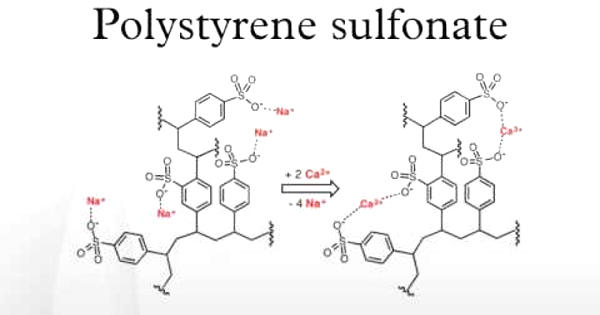
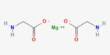
Polystyrene sulfonates are polymers derived from polystyrene by the addition of sulfonate functional groups. They are a group of medications used to treat high blood potassium. Effects generally take hours to days. They are widely used as ion-exchange resins to remove ions such as potassium, calcium, and sodium from solutions in technical or medical applications. They are also used to remove potassium, calcium, and sodium from solutions in technical applications. Additionally, they can be used to remove toxins.
Common side effects include loss of appetite, gastrointestinal upset, constipation, and low blood calcium. It binds itself to potassium in your digestive tract. This helps prevent your body from absorbing too much potassium. These polymers are derived from polystyrene by the addition of sulfonate functional groups. Keep using this medicine even if you feel fine. Hyperkalemia often has no symptoms that you will notice until your potassium levels are very low.
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate was approved for medical use in the United States in 1958. It is in a class of medications called potassium-removing agents. It works by removing excess potassium from the body. It is used to treat high levels of potassium in the blood, also called hyperkalemia. Because it is not absorbed into the bloodstream, this medicine is not expected to be harmful during pregnancy or while nursing a baby.
A polystyrene sulfonate was developed in the 2000s to treat Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea under the name Tolevamer, but it was never marketed.
Medical uses
Polystyrene sulfonate is usually supplied in either the sodium or calcium form. It is used as a potassium binder in acute and chronic kidney disease for people with hyperkalemia (abnormal high blood serum potassium levels). It comes as a suspension and as an oral powder for suspension to take by mouth. The suspension may also be given rectally as an enema. However, it is unclear if it is beneficial and there is concern about possible side effects when it is combined with sorbitol. It works differently from other medicines because it passes into your intestines without being absorbed into your blood stream.
Polystyrene sulfonates are given by mouth with a meal or rectally by retention enema. It can be given as a liquid by mouth, through a stomach feeding tube, or as a rectal enema.
Information Source: