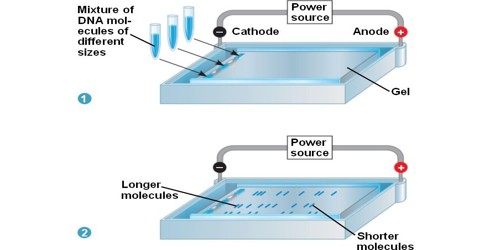
Gel Electrophoresis is a technique used to separate mixtures like DNA and proteins. It is a technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size. The separation is based on how positively or how negatively charged a molecule is, and its size. Electrophoresis involves running a current through a gel containing the molecules of interest. Gel electrophoresis uses a gel (like gelatin) and an electric field is put through the gel. It is a ubiquitous separation technique in nucleic acid biochemistry.
The word electrophoresis comes from – electro, because an electric field is used, and –phoresis, which means movement.
Gel
The gel is made up of large and branched molecules called polymers. Gels for DNA separation are often made out of a polysaccharide called agarose, which comes as dry, powdered flakes. The amount of branches in the gel determines how easily molecules can squeeze through, depending on their size. The end of the gel with the wells is positioned towards the negative electrode.
Charged molecules move through a gel when an electric current is passed across it. If there are a lot of branches, small molecules will be able to move through easily while big molecules will move through slowly or not at all.
Applications
DNA separation
Gel electrophoresis is the most commonly used technique to study DNA. Electrophoresis enables you to distinguish DNA fragments of different lengths. DNA can be broken down into smaller pieces of different sizes and these pieces are then separated using gel electrophoresis. DNA always has a negative charge and moves towards the anode.
In addition to analyzing proteins or DNA, electrophoresis is also used to create purified samples of proteins. Proteins are large and complex molecules made of amino acids. Proteins can be studied by gel electrophoresis in two ways. One way is to take a mixture of proteins and separate them in the gel. The other way is to break down a single protein into smaller pieces. In gel electrophoresis, the molecules to be separated are pushed by an electrical field through a gel that contains small pores.
Medicine
In medicine, there is a special type of electrophoresis called iontophoresis. It is a widely used technique in life science laboratories to separate macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins. Iontophoresis uses the same idea of gel electrophoresis to deliver drugs into the human body through the skin without using needles to inject the drug.