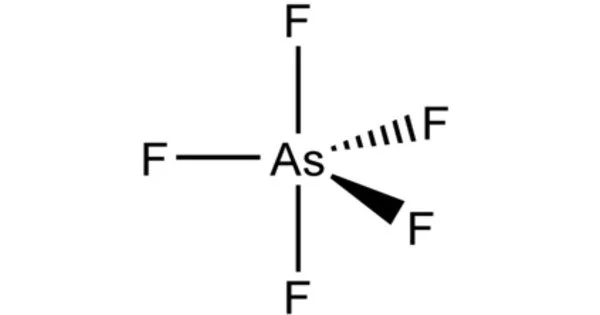
Arsenic pentafluoride is an arsenic and fluorine chemical combination. It is an arsenic fluoride. It is a poisonous, colorless gas. Arsenic has an oxidation state of +5. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas that condenses to a yellow liquid at −53 °C. Although vapor density measurements show some degree of connection, it is a monomeric covalent molecule with a significant degree of coordinating capacity. Because of the potential for significant toxicity, any arsenic compound should be handled with extreme caution.
Synthesis
Arsenic pentafluoride can be prepared by direct combination of arsenic and fluorine:
2As + 5F2 → 2AsF5
It can also be prepared by the reaction of arsenic trifluoride and fluorine:
AsF3 + F2 → AsF5
or the addition of fluorine to arsenic pentoxide or arsenic trioxide.
2As2O5 + 10F2 → 4AsF5 + 5O2
2As2O3 + 10F2 → 4AsF5 + 3O2
Properties
Arsenic pentafluoride is a colourless gas and has a trigonal bipyramidal structure. In the solid state the axial As−F bond lengths are 171.9 pm and the equatorial 166.8 pm. Its point group is D3h.
- Molar mass: 169.9136 g mol−1
- Appearance: colorless gas
- Density: 2.138 kg/m3 (g/L)
- Melting point: −79.8 ˚C
- Boiling point: −52.8 ˚C
- Solubility: Ethanol, Dimethylether, Benzene
Preparation
Fluorination of elemental arsenic or As2O3 can be used to produce arsenic pentafluoride. It is a strong fluoride-ion acceptor and an even stronger Lewis acid than its lighter homolog PF5.
Fluorine is combined with arsenic metal or arsenic trifluoride to produce it. It is employed in the formation of ionic complexes as a strong Lewis acid fluoride and, in conjunction with Brönsted acids, to generate conjugate superacids. It also forms stable intercalation compounds with graphite that have electrical conductivity comparable to silver.
Reactions
Arsenic pentafluoride forms halide complexes and is a powerful acceptor as shown by the reaction with sulfur tetrafluoride forming an ionic complex.
AsF5 + SF4 → SF3– + AsF6–
Safety
Arsenic pentafluoride is a very toxic toxin that primarily poisons liver cells. It has a similar odor to vinyl chloride gas. It is a highly corrosive and toxic gas that damages red blood cells and can cause broad systemic damage. Fluoride toxicity, comparable to hydrogen fluoride, is typical of exposure. Inhalation causes headache, confusion, nausea, vomiting, general malaise, tightness in the chest, and pain in the belly or loins, comparable to arsine gas.