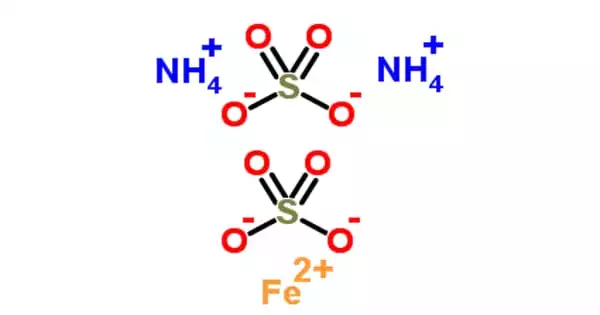
Ammonium iron(III) sulfate, NH4Fe(SO4)•12 H2O, commonly known as ferric ammonium sulfate (FAS) or iron alum, is a double salt in the alum class composed of compounds with the general formula AB(SO4)2•12 H2O. It has the appearance of octahedrical crystals that are slightly violet. The origin of the crystals’ color has been debated, with some attributing it to impurities in the compound and others suggesting it is a feature of the crystal itself.
It is used in the dyeing and printing of fabrics and textiles as a mordant. The chemical is also employed as an analytical reagent and in medicine.
Properties
FAS is hazardous to microbes because it is paramagnetic, acidic, and paramagnetic. It’s a mild oxidizer that can be converted to Mohr’s salt, ferrous ammonium sulfate. The origin of the crystals’ color has been debated, with some attributing it to impurities in the compound and others suggesting it is a feature of the crystal itself.
- Molecular Weight: 266.01
- Appearance: Liquid
- Melting Point: N/A
- Boiling Point: N/A
- Density: 1.050 g/mL
- Solubility in H2O: N/A
- Color: Clear amber
Ammonium iron(III) sulfate is a double salt in the alum class. It is a mild oxidizing agent that can be converted to Mohr’s salt, ferrous ammonium sulfate. It is used in wastewater treatment, tanning, dyestuff manufacture, and as an etching agent in the production of electronic components. It has been employed in a variety of applications, including adiabatic refrigeration equipment, biochemical analysis, and organic synthesis.
Preparation
FAS can be made by crystallizing a solution of ferric sulfate and ammonium sulfate. Iron(II) in ferrous sulfate is oxidized to ferric sulfate by the addition of sulfuric and nitric acid. Ferric ammonium sulfate crystals precipitate after the addition of ammonium sulfate to the solution and damping in of the solution. Equations for these conversions ignore the degree of hydration of the material.
Oxidation: 6 FeSO4 + 2 HNO3 + 3 H2SO4 = 3 Fe2(SO4)3 + 2 NO + 4 H2O
Synthesis: Fe2(SO4)3 + (NH4)2SO4 = 2 NH4Fe(SO4)2
Uses
FAS is used in wastewater treatment, tanning, dyestuff manufacture, and as an etching agent in the production of electronic components. It has been employed in a variety of applications, including adiabatic refrigeration, biochemical analysis, and organic synthesis.