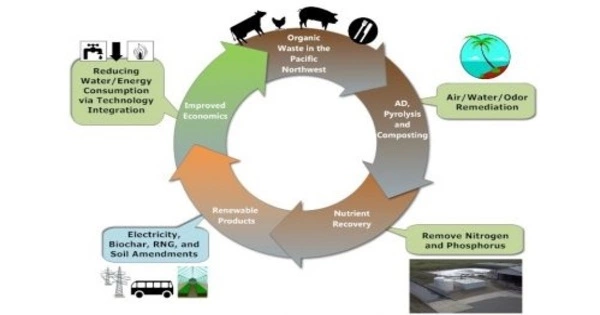
Resource recovery is the process of utilizing trash as an input material to create valuable items as new outputs. It is the process of recovering valuable resources or energy from waste materials, wastewater, or other results of industrial, commercial, or residential activity. The goal is to limit the amount of garbage generated, hence minimizing the requirement for landfill space and optimizing the values obtained from waste. The purpose of resource recovery is to reduce waste generation, reduce the environmental effects of trash disposal, and save resources.
The utilization of raw resources in the manufacturing process is postponed due to resource recovery. Materials recovered from municipal solid waste, construction and demolition waste, commercial garbage, and industrial waste can be used to create new materials and products. Waste can contain valuable materials such as plastic, paper, aluminum, glass, and metal.
Here are some key aspects of resource recovery:
- Materials Recovery: This entails gathering, classifying, and recycling waste products. Metals (such as aluminum and steel), plastics, paper, glass, and organic compounds are common commodities targeted for recovery. These materials can be recycled and used to make new items.
- Energy Recovery: Various processes, such as incineration, gasification, and anaerobic digestion, can be used to extract energy from waste materials. These methods transform biological waste into heat, electricity, or biogas, which can then be utilized to create electricity or heat homes and businesses.
- Biological Resource Recovery: Composting or anaerobic digestion are common methods of organic waste resource recovery. These technologies convert organic matter into usable compost or biogas while minimizing waste volume.
- Water Resource Recovery: In wastewater treatment, resource recovery includes the extraction of valuable resources such as phosphorus and nitrogen, which can be used as fertilizers or in other industrial applications. Advanced wastewater treatment technologies aim to recover these resources and reduce the environmental impact of effluent discharge.
- Waste-to-Energy (WTE): Waste-to-energy plants are built to burn solid waste to generate electricity or heat. This contributes to the reduction of landfill-bound garbage and the generation of renewable energy.
- Circular Economy: The concepts of resource recovery are consistent with those of a circular economy, in which materials and resources are utilized efficiently and waste is reduced. Products and materials in a circular economy are developed with recycling and recovery in mind.
- Environmental Benefits: The environmental impact of trash disposal can be considerably reduced by resource recovery. It decreases greenhouse gas emissions and pollution associated with landfilling by utilizing waste’s energy potential.
Economic Benefits
By producing revenue from the sale of recovered materials or energy and lowering trash disposal costs, resource recovery can generate economic opportunities. While resource recovery has numerous advantages, it also has certain drawbacks, such as the requirement for advanced technologies, environmental concerns with particular recovery methods, and the significance of effective waste separation and recycling programs.
Resource recovery is an important part of waste management and environmental responsibility. It aids in the conservation of natural resources, the reduction of pollution, and the advancement of a more sustainable and circular economy.