Introduction
Goldtex Ltd, is a garments industry, It has been operating its activities in Bangladesh since 2005.In order to identify the different activities that are performed by Goldtex garments, which plays a vital role in our economic development, this research has been intended to be conducted by us for acquiring knowledge of garment industry. In general Goldtex garments has always tried to meet the buyer expectation to do business smoothly and to seek better position in the garments industry This research project has been adopted to identify each of the activities of its operation and how it has build up customer satisfaction & retained its customer by ensuring better quality.
Objective of the Research:
The major objective of this research is to demonstrate the Merchandising, Quality, Operation process, Marketing strategy that contributes to the garments sector for economic development of the country.
The specific objective of this research are:
- To analyze each operational process .
- To analyze the contribution for economic development .
- To identify the process of day by day growth & development
- To maintain customer satisfaction by quality assurance.
- To analyze its Marketing / Merchandising strategy
Scope of the Research :
The findings of this research project will help the customer of the product to know the process of its operation. The manufacturers will also know the desire of the customer which may prompt them to adopt measures for customer satisfaction as per the cota free globalization.
Research Design:
The research project is both descriptive and exploratory in nature. The descriptive research will be conducted to define the basic marketing / merchandising activities of Goldtex garments & enrich its quality for home and abroad. The exploratory research will be conduct to measure the customer’s satisfaction level on the basis of quality by Goldtex garments.
Data and Data Sources:
Both secondary and primary data will be needed to attain the objectives of this research project. There are several method of collecting primary data, particularly in survey and descriptive research these are:
1. Observation method
2. Interview method
3. Through Questionnaires
4. Through schedules, and other method, which include
a) Warranty cards
b) Distributor audits
c)Pantry audit
d) Consumer Panels
e) Using Mechanical devices
f) Through projective techniques
g) Depth Interview
h) Content analysis
The secondary data were collected from the following sources:
1. Company Internal records, Magazines
2. BGMA(Bangladesh Garments Manufacturing Association) directory
3. Company Financial statement, Report 2006-2007 (June ),
4. Custom and BEPZA (Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority) Magazine,
7th Edition,2007
- Reports and publications of various associations connected with business and industry, bank, stock exchange etc.2007,
a. Instrument Of Data Collection:
*For Primary Data: The method of data collection is quite popular, particularly in case of big enquiries. It is being adopted by private individuals, research workers, private and public organizations and even by government. In the method a questionnaire is sent to the person concerned with a request to answer the questions and return the questionnaire. Questionnaire used to gather primary data from 10 Respondents. A well planned undisguised questionnaire was formulated to acquire desired information from sample elements regarding the operation aspects of Goldtex garments .
*Data Processing: The data, after collection, has been processed and analyzed in accordance with the outline laid down for the purpose at the time of developing the research plan. This is essential for a scientific study and for ensuring that we used all relevant data for making contemplated comparisons and analysis. Technically speaking, processing implies editing, coding, classification and tabulation of collected data so that they are amenable to analysis. Data is edited to avoid clarification contradiction, irrelevant, and false responses. Afterwards, the average level of customer satisfaction on each issue of Goldtex garments has been determined by central tendency of statistics, so as to reveal the proportion of satisfaction & dis-satisfaction.
*Data Analysis and interpretation : The term analysis refers to the computation of certain measures along with searching for patterns of relationship that exist among data groups. Thus in the process of analysis, relationships or differences supporting of conflicting with original or new hypotheses should be subjected to statistical tests of significance to determine what validity data can be said to indicate any conclusion. In order to extract meaningful information from the data collected, the analysis will be carried out. After editing the data properly, they will be tabulated by using statistical tools i.e. percentage, average, dispersion etc. alternatively the collected data will also be analyzed by using diagrams, graph etc.
Limitation of the research project:
Time and funds are the major limitation of this research project.
Scheduling:
The entire research project took 90days to conduct, Which were scheduled as below:
A) Data were gathered within 70 days after the acceptance of the proposal by the research guide.
B) Next 5 days were utilized for editing , the data for clearing and recollection.
C) Subsequent 7 days were used to analyze, internet and to prepare the final draft of the report.
D) Final 8 days were required to prepare the final report of the research project.
Europeans began to set up trading posts in the area of Bangladesh in the 16th century; eventually the British came to dominate the region and it became part of British India. In 1947, West Pakistan and East Bengal (both primarily Muslim) separated from India (largely Hindu) and jointly became the new country of Pakistan. East Bengal became East Pakistan in 1955, but the awkward arrangement of a two-part country with its territorial units separated by 1,600 km left the Bengalis marginalized and dissatisfied. East Pakistan seceded from its union with West Pakistan in 1971 and was renamed Bangladesh. To day Bangladesh is playing a roll Model as a developing country for the Global world.
Bangladesh: Country Profile
Name : People’s Republic of Bangladesh
Official Name : Bangladesh
Capital city : Dhaka (pop. 10 million).
Geographical Location : Between 20°34′ and 26°38′ north latitude and between 88°01′ and 92°41′
147, 570 sq. km. (55,813 sq. mi.); about the size of Wisconsin.
east longitude.1,47,570 sq.km. or 57,295 sq.miles.
Boundary : North : India
West : India
East : India and Myanmar
South : Bay of Bengal
Unit of Currency : Taka
Time : GMT+6.00 hours.
Major Divisions : Dhaka, Chittagong, Khulna, Rajshahi, Barisal, Sylhet.
Major Cities : Dhaka (Pop. 10 million), Chittagong (2.8 million),
Khulna (1.8 million), Rajshahi (1 million), Mymensingh, Comilla,
Barisal, Sylhet.
Climate : Winter temp(max 29°C Min 11°C) Semitropical, Monsoonal.
Terrain : Mainly flat alluvial plain, with hills in the northeast and southeast.
Population : 129.2 Million (2001), Growth rate 1.48% (2001)
Language : Bengali but English is widely used.
Principal Industries : Garments, Jute, Cotton, Textile, Tea, Paper, Newsprint, Cement, Fertilizer,
Sugar, Fish, Engineering, Electric Cables, Leather.
Principal Exports : Readymade garments, Jute and jute products, Tea, Leather, Chemical,
Fertilizer and Frozen food etc.
Sea Ports : Chittagong and Mongla.
Airports : Dhaka, Chittagong (International).
Jessore, Rajshahi, Ishwardi, Sylhet, Cox’s Bazar, Syedpur, Barisal (Local).
GEOGRAPHY: : :
Bangladesh is a low-lying, riparian country located in South Asia with a largely marshy jungle coastline of 710 kilometers (440 mi.) on the northern littoral of the Bay of Bengal. Formed by a deltaic plain at the confluence of the Ganges (Padma), Brahmaputra (Jamuna), and Meghna Rivers and their tributaries, Bangladesh’s alluvial soil is highly fertile but vulnerable to flood and drought. Hills rise above the plain only in the Chittagong Hill Tracts in the far southeast and the Sylhet division in the northeast. Straddling the Tropic of Cancer, Bangladesh has a subtropical monsoonal climate characterized by heavy seasonal rainfall, moderately warm temperatures, and high humidity. Natural calamities, such as floods, tropical cyclones, tornadoes, and tidal bores affect the country almost every year. Bangladesh also is affected by major cyclones–on average 16 times a decade. Urbanization is proceeding rapidly, and it is estimated that only 30% of the population entering the labor force in the future will be absorbed into agriculture, although many will likely find other kinds of work in rural areas. The areas around Dhaka and Comilla are the most densely settled. The Sundarbans, an area of coastal tropical jungle in the southwest and last wild home of the Bengal Tiger, and the Chittagong Hill Tracts on the southeastern border with Burma and India, are the least densely populated.
People:
Nationality: Noun and adjective–Bangladeshi(s). Population: 146 million. Annual growth rate: 1.8%.
Ethnic groups: Bengali 98%, tribal groups, non-Bengali Muslims. Religions: Muslim 88.3%; Hindu 10.5%; Christian 0.3%, Buddhist 0.6%, others 0.3%. Languages: Bangla (official, also known as Bengali), English. Education: Attendance– 61%. Literacy– 62.66. Health: Infant mortality rate (below 1)–56/1,000. Life expectancy–62 years (male), 63 years (female).Work force (60.3 million): Agriculture— 62.3%; manufacturing and mining– 7.6%; others—30.1%.
PEOPLE :
The area that is now Bangladesh has a rich historical and cultural past, combining Dravidian, Indo-Aryan, Mongol/Mughul, Arab, Persian, Turkic, and west European cultures. Residents of Bangladesh, about 98% of whom are ethnic Bengali and speak Bangla, are called Bangladeshis. Urdu-speaking, non-Bengali Muslims of Indian origin, and various tribal groups, mostly in the Chittagong Hill Tracts, comprise the remainder. Most Bangladeshis (about 88.3%) are Muslims, but Hindus constitute a sizable (10.5%) minority. There also are a small number of Buddhists, Christians, and animists. English is spoken in urban areas and among the educated. Sufi religious teachers succeeded in converting many Bengalis to Islam, even before the arrival of Muslim armies from the west. About 1200 AD, Muslim invaders established political control over the Bengal region. This political control also encouraged conversion to Islam. Since then, Islam has played a crucial role in the region’s history and politics, with a Muslim majority emerging, particularly in the eastern region of Bengal.
HISTORY:
Bengal was absorbed into the Mughul Empire in the 16th century, and Dhaka, the seat of a nawab (the representative of the emperor), gained some importance as a provincial center. But it remained remote and thus a difficult to govern region–especially the section east of the BrahmaputraRiver–outside the mainstream of Mughul politics. Portuguese traders and missionaries were the first Europeans to reach Bengal in the latter part of the 15th century. They were followed by representatives of the Dutch, the French, and the British East India Companies. By the end of the 17th century, the British presence on the Indian subcontinent was centered in Calcutta. During the 18th and 19th centuries, the British gradually extended their commercial contacts and administrative control beyond Calcutta to Bengal. In 1859, the British Crown replaced the East India Company, extending British dominion from Bengal, which became a region of India, in the east to the IndusRiver in the west.
The rise of nationalism throughout British-controlled India in the late 19th century resulted in mounting animosity between the Hindu and Muslim communities. In 1885, the All-India National Congress was founded with Indian and British membership. Muslims seeking an organization of their own founded the All-India Muslim League in 1906. Although both the League and the Congress supported the goal of Indian self-government within the British Empire, the two parties were unable to agree on a way to ensure the protection of Muslim political, social, and economic rights. The subsequent history of the nationalist movement was characterized by periods of Hindu-Muslim cooperation, as well as by communal antagonism. The idea of a separate Muslim state gained increasing popularity among Indian Muslims after 1936, when the Muslim League suffered a decisive defeat in the first elections under India’s 1935 constitution. In 1940, the Muslim League called for an independent state in regions where Muslims were in the majority. Campaigning on that platform in provincial elections in 1946, the League won the majority of the Muslim seats contested in Bengal. Widespread communal violence followed, especially in Calcutta.
When British India was partitioned and the independent dominions of India and Pakistan were created in 1947, the region of Bengal was divided along religious lines. The predominantly Muslim eastern half was designated East Pakistan–and made part of the newly independent Pakistan–while the predominantly Hindu western part became the Indian state of West Bengal. Pakistan’s history from 1947 to 1971 was marked by political instability and economic difficulties. Dominion status was rejected in 1956 in favor of an “Islamic republic within the Commonwealth.” Attempts at civilian political rule failed, and the government imposed martial law between 1958 and 1962, and again between 1969 and 1971.
Almost from the advent of independent Pakistan in 1947, frictions developed between East and West Pakistan, which were separated by more than 1,000 miles of Indian territory. East Pakistanis felt exploited by the West Pakistan-dominated central government. Linguistic, cultural, and ethnic differences also contributed to the estrangement of East from West Pakistan. Bengalis strongly resisted attempts to impose Urdu as the sole official language of Pakistan. Responding to these grievances, Sheikh Mujibur Rahman in 1948 formed a students’ organization called the Chhatra League. In 1949, Maulana Abdul Hamid Khan Bhasani and some other Bengali leaders formed the East Pakistan Awami Muslim League (AL), a party designed mainly to promote Bengali interests. This party dropped the word Muslim from its name in 1955 and came to be known as Awami League. Mujib became president of the Awami League in 1966 and emerged as leader of the Bengali autonomy movement. In 1966, he was arrested for his political activities.
After the Awami League won almost all the East Pakistan seats of the Pakistan national assembly in 1970-71 elections, West Pakistan opened talks with the East on constitutional questions about the division of power between the central government and the provinces, as well as the formation of a national government headed by the Awami League. The talks proved unsuccessful, however, and on March 1, 1971, Pakistani President Yahya Khan indefinitely postponed the pending national assembly session, precipitating massive civil disobedience in East Pakistan. Mujib was arrested again; his party was banned, and most of his aides fled to India and organized a provisional government. On March 26, 1971, following a bloody crackdown by the Pakistan Army, Bengali nationalists declared an independent People’s Republic of Bangladesh. As fighting grew between the army and the Bengali mukti bahini (“freedom fighters”), an estimated 10 million Bengalis, mainly Hindus, sought refuge in the Indian states of Assam and West Bengal. On April 17, 1971, a provisional government was formed in Meherpur district in western Bangladesh bordering India with Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, who was in prison in Pakistan, as President, Syed Nazrul Islam as Acting President, and Tajuddin Ahmed as Prime Minister. The crisis in East Pakistan produced new strains in Pakistan’s troubled relations with India. The two nations had fought a war in 1965, mainly in the west, but the refugee pressure in India in the fall of 1971 produced new tensions in the east. Indian sympathies lay with East Pakistan, and in November, India intervened on the side of the Bangladeshis. On December 16, 1971, Pakistani forces surrendered, and Bangladesh– meaning “Bengal country”– was born; the new country became a parliamentary democracy under a 1972 constitution. The first government of the new nation of Bangladesh was formed in Dhaka .
Government:
Type: Parliamentary democracy. Independence: 1971 (from Pakistan). Constitution: 1972; amended 1974, 1979, 1986, 1988, 1991, 1996, 2004. Branches: Executive–president (chief of state), prime minister (head of government), cabinet. Legislative–unicameral parliament (345 members). Judicial–civil court system based on British model. Administrative subdivisions: Divisions, districts, subdistricts, unions, villages. Political parties: 30-40 active political parties: largest ones include Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP), the Awami League (AL), the Jatiya Party, and the Jamaat-e-Islami Party.
Suffrage: Universal at age 18.
Fiscal year: July 1 to June 30. Annual GDP growth rate (FY 2006 est.): 6.7%. GDP: $60 billion
Inflation (April 2006): 6.5%. Exchange Rate: FY 2003: 1 $= Taka 57.90 FY 2006: 1 $= Taka 69.43
Annual Budget (FY 2007): $ 10 billion. Per capita GDP (2006): $ 456. Natural resources: Natural gas, fertile soil, water. Agriculture ( 21.8% of GDP): Products–rice, jute, tea, sugar, wheat. Land–cultivable area cropped at rate of 180% in 2004; 176% in 1997; largely subsistence farming dependent on monsoon rainfall, but growing commercial farming and increasing use of irrigation. Industry (Manufacturing; 17% of GDP): Types–garments and knitwear, jute goods, frozen fish and seafood, textiles, fertilizer, sugar, tea, leather, ship-breaking for scrap, pharmaceuticals, ceramic tableware, newsprint.
Trade (FY 2005): Total Imports (FY 2005)- $ 13.4 billion: capital goods, food grains, petroleum, textiles, chemicals, vegetable oils. Total Exports (FY 2005) — $ 8.7 billion: garments and knitwear, frozen fish, jute and jute goods, leather and leather products, tea, urea fertilizer, ceramic tableware.
Exports to U.S. (FY 2005)–$2.5 billion. Imports from U.S. (FY 2005)–$333 million.
Year | GDP – real growth rate | Rank | Percent Change | Date of Information |
2003 | 4.40% | 51 | 2002 est. | |
2004 | 5.30% | 48 | 20.45 % | 2003 est. |
2005 | 4.90% | 84 | -7.55 % | 2004 est. |
2006 | 6.40% | 50 | 30.61 % | 2005 est. |
Back to Bangladesh Economy:
Bangladesh has made significant strides in its economic sector since its independence in 1971. Bangladeshi garments industry is one of the largest and comprehensive industry in the world. Before 1980, Bangladesh’s economy and foreign exchange earnings were driven by the jute industry. However, this industry started to fall dramatically from 1970, when polypropylene products gained popularity over the jute products.
Current GDP per capita of Bangladesh registered a peak growth of 57% in the Seventies immediately after Independence. But this proved unsustainable and growth consequently scaled back to 29% in the Eighties and 24% in the Nineties.
Bangladesh has also made major strides to meet the food needs of its increasing population, through increased domestic production. Currently, Bangladesh is the third largest rice producing country in the world. The land is devoted mainly to rice and jute cultivation, although wheat production has increased in recent years; the country is largely self-sufficient in rice production. Nonetheless, an estimated 10% to 15% of the population faces serious nutritional risk. Bangladesh’s predominantly agricultural economy depends heavily on an erratic monsoonal cycle, with periodic flooding and drought. Although improving, infrastructure to support transportation, communications, and power supply is poorly developed. The country has large reserves of natural gas and limited reserves of coal and oil. While Bangladesh’s industrial base is weak, unskilled labor is inexpensive and plentiful.
Bangladesh Opportunity:
Bangladesh – the country of world famous muslin fabric and the Great Royal Bengal Tiger has now emerged as an child labour free apparel giant in the world textile and apparel market. The country exports its apparel products worth nearly 5 billion US$ per year to the USA, EU, Canada and other countries of the world. At present the country is the 6th largest apparel supplier to the USA and EU countries. The major products are Knit and Woven Shirts and Blouses, Trousers, Skirts, Shorts, Jackets, Sweaters, Sportswear’s and many more casual and fashion apparels.
Back to Bangladesh Economy:
The first ready-made garment factories in Bangladesh aimed at the export market were opened in the late 1970s by investors from other Asian countries whose exports had been restrained by quotas imposed by importing nations. By the mid-1980s, the ready-made garment industry had become a strong export earner. Garment exports brought receipts of only US$3 million in FY 1981, but by 1984 exports had risen to US$32 million, and the following year revenue soared to US$116 million. For FY 1985 and FY 1986, ready-made garments were the second biggest foreign exchange earner for Bangladesh after jute.
In order to stimulate rapid economic growth of the country, particularly through industrialization, the government has adopted an ‘Open Door Policy’ to attract foreign investment to Bangladesh. The Bangladesh Export Processing Zones Authority (BEPZA) is the official organ of the government to promote, attract and facilitate foreign investment in the Export Processing Zones. The primary objectives of an EPZ is to provide special areas where potential investors would find a congenial investment climate, free from cumbersome procedures. We have eight EPZs in Bangladesh.
EPZs of Bangladesh
Dhaka – EPZ
Chittagong – EPZ
Mongla – EPZ
Ishwardi – EPZ
Comilla – EPZ
Uttara – EPZ
Adamjee – EPZ
Karnaphuli – EPZ
Dhaka Export Processing Zone ( EPZ-DAK )
Location :
Savar. 35 kms from Dhaka city centre, 25 kms from Zia-InternationalAirport.
Profile Of Zone :
Zone area : 143.84 hectares (355.34 acres)
Number of industrial plots : 372
Size of each plot : 2000 sqm.
Tariff : US $ 2.00 /sqm /year.
Space of Standard Factory Building : 76000 sqm.
Tariff : US $ 2.50 /sqm /month.
Space of Warehouse : 2356 sqm.
Tariff : US $ 2.50 /sqm /month.
|
YEARS’ PERFORMANCE OF BEPZA:
Banglsdesh EPZ Authority has sanctioned 201 industrial units for EPZs of the country during the last 5 years. Of these 84 are fully foreign owned, 41 under joint venture & 76 are 100% Bangladeshi, Among them 52 are for Chittgong, 51 for Dhaka EPZ, 26 For Mongla EPZ, 16 for Ishwardi EPZ, 34 for Comilla EPZ, & 7 for Uttara, 10 for Adamjee EPZ, & 5 for Karnaphuli EPZ,. BEPZA has sanctioned 29 enterprises in 2001-02 fiscal year, 27 in 2002-03, 55 in 2003-04, 54 in 2004-05 & 36 in 2005-06. Meanwhile, among the 201sanctioned plants 79 have already started production.
The enterprises of EPZs have exporteed goods worth US$ 11839.80 million up to June 2006 where as it was US$ 4823.78 million till June, 2001. During the last 5 years the export volume enhanced to US$ 7016.02 million. The export earnings from EPZs crossed the billion dollar mark in the last five years. In 2001-02 export from EPZs was US$ 1077.03 million, in 2002-03 it was US$1200.22 million, in 2004-2005 US$ 1548.55 million & it was US$ 1836.18 milliuon in 2005-06.Despite worldwide recession, FDI has increased in the EPZs during the last 60 months. In June, 2001 the investment in EPZs was US$ 475.20 million whereas in june 2006 the investment stood at 979.89 million. The volume of investment has rised to US$ 504.69 million in the operating enterprises of EPZs reflects the positive impact of industrialization.
EMPLOYMENT ABOUT 179 THOUSAND:
BEPZA is playing a pivotal role for poverty alleviation through job creation. During the last 5 years 67,825 Bangladeshi nationals have been Employed in EPZs of the countr’y. Employment generation ratio of EPZS proved the significant role of BEPZA for socio- economic development of the country. The operating industries of EPZs have generated employment for 1,78,952 Persons. Of them 1,77,809 are Bangladeshis & 1143 are foreign nationals. Among the Bangladeshi nationals 1,04,155 are employed in Chittagong EPZ & 64636 in Dhaka EPZ while 5787 in nComilla EPZ, 300 in MonglaEPZ, 1250 in UttaraEPZ, 1625 in AdamjeeEPZ, & 56 in IsheardiEPZ, Among the total work force 60% is female.
New Job Creation
The operating enterprises of EPZs have generated new employment for 23,021 Bangladeshi nationls during the fisical year 2005-06. Of them, 9736 persons are employed in chittagong EPZ, 8356 in Dhaka EPZ, 2973 in Comilla EPZ, 95 in Mongla EPZ, 36 in Ishwardi EPZ, 200 in Uttara EPZ, & 1625 in Adamjee EPZ.
EXPORT:
The industrial units of EPZs have exparted goods warth US$ 1836.18 million during the last fisical year which exceeded the target by US$ 236.18 million. Export earnings from Chittagong EPZ stands at US$ 873.03 million while that of Dhaka EPZ US$ 918.30 million, ComillaEPZ US$ 34.99,MongalaEPZ US$ 7.09 million, IshwargiEPZ US$ 2.54 million & AdamjeeEpz US$ 230 thousand.
INVESTMENT:
US$ 112.89 million capital investment rised in the operating 242 enterprises of EPZs during July 2005 to June 2006. Of this total amount, investment in Chittagong EPZ increased to US$ 35.95 million while that of Dhaka EPZ increased in US$ 61.57 million, Comilla EPZ US$ 10.62 million, Adamjee EPZ US$ 4.00 million & Ishwrdi EPZ US$ 760 thousand.
Enterprise & New Plants Sanctioned
BEPZA has sanctionedd 36 new industrial units during the last fiscal year. Of these 20 are fully foreign owned 6 under joint ventures & the rest 10 are bangladeshis. Among the 20 fully foreign owned indusrries 4 will be in Chittigong EPZ, 3 in Dhaka EPZ, 2 in Irshwardi EPZ, 5 in Adamjee EPZ, 2 in Karnaphuli EPZ, 3 in Comilla EPZ & 01 in Mongla EPZ. Among the 6 joint venture industries, 2 will be in Dhaka EPZ, 1 In Chittagong EPZ, 2 in Adamjee Epz & 1 in Karnaphuli EPZ. Among the 10 Bangladeshi owned plants 1 for Ishwardi EPZ, 2 for Dhaka EPZ, 2 for adamjee EPZ, 1 for Comilla EPZ, 2 for Karnaphuli EPZ & the rest 2 for Chittagong EPZ.
Investment Climate in Bangladesh:
The Government of Bangladesh offers great incentives for encouraging the use of local fabrics in the export oriented garment industries. For encouraging textile export, the import of capital machinery is duty-free. Import of cotton is also duty-free. Moreover, the Government has recently implemented several policy reforms to create a more open and competitive climate for foreign investment. Bangladesh is endowed with abundant and cheap labour force that is easily trainable and convertible into semi-skilled and skilled work force. Price, heavily weighted by the labour cost, is one of the main determinants of comparative advantage in the labour-intensive garment industry. The price of labour in our country is lower compared to some of our neighbouring countries as well as some other garment producing countries in South-East Asia and East Europe. Obviously, existence of such cheap but easily trainable labour is one of the advantages that Bangladesh enjoys and will be enjoying over a considerable period in the context of international trade on clothing. An extensive programme of incentives, to expedite investment in the country, are now in place covering :-
- No Ceiling for investment
- Tax holiday of up to 10 years
- Tax-exemption and duty-free importation of capital machinery and spare parts for 100% export oriented industries
- Residency permits for foreign nationals including citizenship
- Easy capital profit and divided repatriation facilities
- Double taxation avoidance
- Tax-exemption on the interest payable on foreign loans
- Taka convertible on current account etc.
Investors can also take advantage of the generalized system of preference which allows duty-free access to European and Japanese Markets.
Backward – Linkage of Apparel Industry Shows Potential for Foreign Investment:
Estimate shows that about 80 percent of garment accessories like cartons, threads, buttons, labels, poly bags, gum tapes, shirt boards, neck boards etc. are now being produced in our country, contributing to the national GDP. But, the textile (Spinning, Weaving, Finishing etc.) industry is just budding.
Prospect for a huge textile industry capable to supply over 3 billion yards of fabrics a year to the export oriented garment industry has also been developed by the industry.
Presently, the total fabric requirement in our captive market is for about 3 billion yards, of which about 85-90 percent we import from countries like China, India, Hong Kong, Singapore, Thailand, Korea, Indonesia, Taiwan, etc.. Fabric requirement is increasing @ 20 percent per annum. This offers a tremendous opportunity for further industrialisation in our country.
Taking the global context within the purview of open market economy by the year 2005, we can exploit the benefit of the potential textile industry of the country by immediately establishing 60 moderate-size composite textilemills, capable of producing 30 million yards of fabrics per year per factory.
The Bangladesh Garments Sector:
The striking successes of readymade garment (RMG) export from Bangladesh over the last two and half decades has surpassed the most optimistic expectation. Today the apparel export sector is a multi-billion-dollar manufacturing and export industry in the country contributing 76% of total export earnings. The overall impact of the readymade garment exports is certainly one of the most spectacular social and economic developments in the contemporary world. Of total 2.2 million workers over one and half million are women employed in semi-skilled and skilled jobs producing clothing for exports. The development of the apparel export industry has had far-reaching implications for the society and economy of Bangladesh. Now Bangladesh earmarks her strong position in the global apparel export market where her product has been well-known for quality, price and competitiveness.
BGMEA at a glance:
Starting in late 70s as a small nontraditional sector of export, Ready-made Garment (RMG) emerged as a promising export earning sector of the country by the year 1983. Bangladesh at that time lacked a sectoral trade body, non-government in nature, free from traditional bureaucracy, to help the sector to boost up the country’s foreign exchange earnings. As a result, 1977 marked the birth of BGMEA. Since its humble inception with only nineteen (19) garment manufacturers and exporters, BGMEA has grown into a strong and dynamic body. Today it is proud to have about 3500 garment manufacturers and exporters as its members.
The fundamental objective of BGMEA is to establish a healthy business environment for a close and mutually beneficial relationship between the manufacturers, exporters and importers in the process ensuring a steady growth in the foreign exchange earnings of the country. To this end, BGMEA has been playing a very strong role to lead the industry in concurrence with the government.
Functions of BGMEA:
The Bangladesh Garment Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) is the largest exporters’ guild in the country, with a membership of 4094, which is no mean achievement considering its inception in 1977 with only 12 members. This spectacular progress has been possible through its total commitment towards promoting a congenial atmosphere of interaction and co-operation at all levels of production and marketing. This sector has provided employment to two million workers and has put to use the invaluable talent of a large female workforce, leading not only to their positive contribution to their family and society, but also to their own self-realization and freedom from age-old economic overthrow. BGMEA is harnessing all the divergent sectors of the garments industry through policy making, marketing and overseeing the interests of the parties involved. It is also involved in facilitating the intercommunication of its member companies with overseas trade bodies and organizations.
Brief about BTMA:
Bangladesh Textile Mills association (BTMA) is the national trade organization representing Yarn, Fabric Manufacturers and Textile Product Processors mills of the country under private sector. BTMA is Registered in 1983 with the Joint Stock Companies as an Association, not for profit, under the Companies Act 1994, with initial membership of 22 mills for the following main objectives:
To organize such factories and workshops for selling or display centers centrally which may be of common benefit for sections which might not be possible or feasible for
Currently the number of membership of BTMA is 810 under:
- Spinning – 222
- Weaving – 458
- Dyeing-Printing-Finishing – 141
Over 2.50 billion EURO has been invested in these mills and about 3.50 million people are currently employed.
QUANTITY AND VALUE OF WOVEN AND KNIT EXPORT DURING 2005 | ||||||
| VALUE IN MN. US$, QUANTITY IN ‘000 DOZ | ||||||
MONTH | EXPORT OF WOVEN AND KNIT | EXPORT OF WOVEN & KNIT | ||||
WOVEN | KNIT | TOTAL | WOVEN | KNIT | TOTAL | |
JANUARY | 296.07 | 221.74 | 517.81 | 7536.75 | 9383.89 | 16920.64 |
FEBRUARY | 292.92 | 196.06 | 488.98 | 7580.54 | 8397.53 | 15978.07 |
MARCH | 264.55 | 231.41 | 495.96 | 6731.88 | 9869.20 | 16601.08 |
APRIL | 236.57 | 215.08 | 451.65 | 6005.58 | 9033.66 | 15039.24 |
MAY | 313.24 | 272.33 | 585.57 | 7935.77 | 11606.30 | 19542.07 |
JUNE | 377.89 | 283.68 | 661.57 | 9771.15 | 12089.91 | 21861.06 |
JULY | 362.79 | 345.25 | 708.04 | 10365.43 | 15010.87 | 25376.30 |
AUGUST | 338.74 | 317.44 | 656.18 | 8095.89 | 13799.13 | 21895.02 |
SEPTEMBER | 265.88 | 256.59 | 522.47 | 6922.93 | 11147.39 | 18070.32 |
OCTOBER | 319.04 | 310.76 | 629.8 | 8461.8 | 13281.57 | 21743.37 |
NOVEMBER | 247.43 | 230.28 | 477.71 | 7595.57 | 10231.91 | 17827.48 |
DECEMBER | 374.48 | 329.92 | 704.40 | 9383.77 | 14339.13 | 23722.90 |
TOTAL | 3689.60 | 3210.54 | 6900.14 | 96387.06 | 138190.49 | 234577.55 |
QUANTITY AND VALUE OF WOVEN AND KNIT EXPORT DURING 2006 | ||||||
| VALUE IN MN. US$, QUANTITY IN ‘000 DOZ | ||||||
MONTH | EXPORT OF WOVEN AND KNIT | EXPORT OF WOVEN & KNIT | ||||
WOVEN | KNIT | TOTAL | WOVEN | KNIT | TOTAL | |
JANUARY | 354.15 | 296.67 | 650.82 | 9509.41 | 12502.99 | 22012.40 |
FEBRUARY | 352.36 | 282.98 | 635.34 | 9374.56 | 12192.85 | 21567.41 |
MARCH | 349.64 | 314.32 | 663.96 | 9316.63 | 13542.16 | 22858.79 |
APRIL | 293.41 | 322.95 | 616.36 | 7739.40 | 13956.32 | 21695.72 |
MAY | 391.06 | 387.68 | 778.74 | 10410.34 | 16789.89 | 27200.23 |
JUNE | 437.11 | 421.37 | 858.48 | 11639.48 | 18228.70 | 29868.18 |
JULY | 451.91 | 452.94 | 904.85 | 12937.59 | 19779.04 | 32716.63 |
AUGUST | 461.89 | 446.91 | 908.80 | 13172.7 | 19604.33 | 32777.03 |
SEPTEMBER | 351.87 | 349.05 | 700.92 | 10044.76 | 15292.34 | 25337.10 |
OCTOBER | 311.38 | 351.68 | 663.06 | 8881.19 | 15368.05 | 24249.24 |
NOVEMBER | 330.3 | 314.96 | 645.26 | 9423.23 | 13766.74 | 23189.97 |
DECEMBER | 459.71 | 447.21 | 906.92 | 13199.67 | 19571.99 | 32771.66 |
| TOTAL | 4544.79 | 4388.72 | 8933.51 | 125648.96 | 190595.40 | 316244.36 |
Dec-06 | ||||||
VALUE AND QUANTITY OF TOTAL APPAREL EXPORT FISCAL YEAR BASIS (VALUE IN MN. US$ QUANTITY IN MN DOZEN) | ||||||
YEAR | TOTAL APPAREL EXPORT IN MN.US$ | TOTAL APPAREL EXPORT IN MN.DZ | ||||
WOVEN | KNIT | TOTAL | WOVEN | KNIT | TOTAL | |
1992-93 | 1240.48 | 204.54 | 1445.02 | 36.05 | 10.66 | 46.71 |
1993-94 | 1291.65 | 264.14 | 1555.79 | 34.35 | 10.81 | 45.16 |
1994-95 | 1835.09 | 393.26 | 2228.35 | 47.21 | 15.30 | 62.51 |
1995-96 | 1948.81 | 598.32 | 2547.13 | 48.82 | 23.18 | 72.00 |
1996-97 | 2237.95 | 763.30 | 3001.25 | 53.45 | 27.54 | 80.99 |
1997-98 | 2844.43 | 937.51 | 3781.94 | 65.59 | 32.60 | 98.19 |
1998-99 | 2984.96 | 1035.02 | 4019.98 | 64.79 | 36.66 | 101.45 |
1999-2000 | 3081.19 | 1268.22 | 4349.41 | 66.63 | 45.27 | 111.90 |
2000-2001 | 3364.32 | 1495.51 | 4859.83 | 71.48 | 52.54 | 124.02 |
2001-2002 | 3124.82 | 1458.93 | 4583.75 | 77.05 | 63.39 | 140.44 |
2002-2003 | 3258.27 | 1653.82 | 4912.09 | 82.83 | 69.18 | 152.01 |
2003-2004 | 3538.07 | 2148.02 | 5686.09 | 90.48 | 91.60 | 182.08 |
2004-2005 | 3598.20 | 2819.47 | 6417.67 | 92.26 | 120.13 | 212.39 |
2005-2006 | 4083.82 | 3816.98 | 7900.80 | 108.82 | 165.02 | 273.84 |
2006-2007 (Dec) | 2368.07 | 2362.29 | 4730.36 | 67.65 | 103.38 | 171.03 |
MAIN APPAREL ITEMS EXPORTED FROM BANGLADESH | |||||
(VALUE IN MN. US$) | |||||
YEAR | SHIRTS | TROUSERS | JACKETS | T-SHIRT | SWEATER |
1993-94 | 805.34 | 80.56 | 126.85 | 225.90 | …. |
1994-95 | 791.20 | 101.23 | 146.83 | 232.24 | …. |
1995-96 | 807.66 | 112.02 | 171.73 | 366.36 | 70.41 |
1996-97 | 759.57 | 230.98 | 309.21 | 391.21 | 196.60 |
1997-98 | 961.13 | 333.28 | 467.19 | 388.50 | 296.29 |
1998-99 | 1043.11 | 394.85 | 393.44 | 471.88 | 271.70 |
1999-2000 | 1021.17 | 484.06 | 439.77 | 563.58 | 325.07 |
2000-2001 | 1073.59 | 656.33 | 573.74 | 597.42 | 476.87 |
2001-2002 | 871.21 | 636.61 | 412.34 | 546.28 | 517.83 |
2002-2003 | 1019.87 | 643.66 | 464.51 | 642.62 | 578.37 |
2003-2004 | 1116.57 | 1334.85 | 364.77 | 1062.10 | 616.31 |
2004-2005 | 1053.34 | 1667.72 | 430.28 | 1349.71 | 893.12 |
2005-2006 | 1056.69 | 2165.25 | 389.52 | 1781.51 | 1044.01 |
VALUE AND QUANTITY OF TOTAL APPAREL EXPORT CALENDAR YEAR BASIS | ||||||
YEAR | TOTAL APPAREL EXPORT IN MN.US$ | TOTAL APPAREL EXPORT IN ‘000 DZ | ||||
WOVEN | KNIT | TOTAL | WOVEN | KNIT | TOTAL | |
1994 | 1544.89 | 341.53 | 1886.42 | 41642.49 | 13768.85 | 55411.34 |
1995 | 1976.40 | 512.18 | 2488.58 | 49377.11 | 19828.10 | 69205.21 |
1996 | 1942.37 | 686.27 | 2628.64 | 47536.84 | 26107.21 | 73644.05 |
1997 | 2621.33 | 810.49 | 3431.82 | 60560.49 | 27997.84 | 88558.33 |
1998 | 2871.06 | 976.29 | 3847.35 | 64229.77 | 34587.54 | 98817.31 |
1999 | 2987.73 | 1169.90 | 4157.63 | 64938.82 | 41303.64 | 106242.46 |
2000 | 3376.49 | 1448.22 | 4824.71 | 71634.03 | 51588.27 | 123222.30 |
2001 | 3162.28 | 1432.72 | 4595.00 | 67724.50 | 50180.09 | 117904.59 |
2002 | 3076.28 | 1573.40 | 4649.68 | 83443.78 | 70714.60 | 154158.38 |
2003 | 3398.84 | 1850.36 | 5249.20 | 85829.29 | 80503.80 | 166333.09 |
2004 | 3686.78 | 2532.62 | 6219.40 | 94223.23 | 104904.34 | 199127.57 |
2005 | 3689.60 | 3210.48 | 6900.08 | 96387.06 | 138190.49 | 234577.55 |
2006 (Dec) | 4544.79 | 4388.72 | 8933.51 | 125648.96 | 190595.40 | 316244.36 |
COMPARATIVE STATEMENT ON EXPORT OF RMG AND TOTAL EXPORT | ||||
YEAR | EXPORT OF RMG | TOTAL EXPORT OF BANGLADESH | % OF RMG’S TO | |
1983-84 | 31.57 | 811.00 | 3.89 | |
1984-85 | 116.2 | 934.43 | 12.44 | |
1985-86 | 131.48 | 819.21 | 16.05 | |
1986-87 | 298.67 | 1076.61 | 27.74 | |
1987-88 | 433.92 | 1231.2 | 35.24 | |
1988-89 | 471.09 | 1291.56 | 36.47 | |
1989-90 | 624.16 | 1923.70 | 32.45 | |
1990-91 | 866.82 | 1717.55 | 50.47 | |
1991-92 | 1182.57 | 1993.90 | 59.31 | |
1992-93 | 1445.02 | 2382.89 | 60.64 | |
1993-94 | 1555.79 | 2533.90 | 61.40 | |
1994-95 | 2228.35 | 3472.56 | 64.17 | |
1995-96 | 2547.13 | 3882.42 | 65.61 | |
1996-97 | 3001.25 | 4418.28 | 67.93 | |
1997-98 | 3781.94 | 5161.20 | 73.28 | |
1998-99 | 4019.98 | 5312.86 | 75.67 | |
1999-2000 | 4349.41 | 5752.20 | 75.61 | |
2000-2001 | 4859.83 | 6467.30 | 75.14 | |
2001-2002 | 4583.75 | 5986.09 | 76.57 | |
2002-2003 | 4912.09 | 6548.44 | 75.01 | |
2003-2004 | 5686.09 | 7602.99 | 74.79 | |
2004-2005 | 6417.67 | 8654.52 | 74.15 | |
2005-2006 | 7900.80 | 10526.16 | 75.06 | |
2006-2007(Dec) | 4730.36 | 6220.61 | 76.04 | |
Garment Division:
History:
Goldtex Limited Garment Division also an offspring company of M/S Golden Crown Head –Wears Factory Ltd, Hong Kong, has gone into commercial production in the year 2005 in Dhaka Export Processing Zone (DEPZ) & has been meeting the growing demand of quality Trouser, Shorts, Skirts, Shirts, Blouse etc of customized designs. The state-of-the-art JUKI & BROTHER brand machineries & highly professional local & expatriate technicians have developed an in-built means for optimum for productivity with superior quality.
Goldtex Limited Garment Division is an WARP Certified Company
Goldtex Limited Garment Division
Product Range of Goldtex Limited Garment Division
– Trouser
– Shorts
– Skirts
– Shirts
– Blouses
– Baby Wears
– Jackets
Production Capacity :
10,000 Pcs per day
Lead Time :
60-90 Days
Fabric Inspection :
4 point system
Garments Inspection:
AQL 2.5 system
Company is specialized in shirt and bottom wear such as chino, Khaki, cargo pants,shorts, etc with all Kinds of washing method and post treatments.
Its workmanship on these product is one of the best in the industry.
Customers of Goldtex Limited Garment Division
Goldtex Limited Garment Division has its own World-class Customer. This customers are also leading buyers of the country
Top Policy Makers
Mr. Ngan Hung Tak
( President )
Mr. Ngan, a national of Great Britain
has over 38 Years of proven Senior
Management experience. He is the
founder of “M/S Golden Crown
Head-Wears Factory Ltd.”, Hong Kong.
The company graded as number one
Cap Exporter of China in 80’s. His
miraculous achievements speak about him.
Mr. Calvin Ngan, Managing
( Director )
Mr. Calvin, a national of Great Britain is a
Highly qualified and widely recognized rising
entrepreneur.
Mr. Leo Tsui
(General Manager )
Mr. Tsui, a national of Hong Kong, has a
Black Belt in fashion designing & management.
Goldtex Limited Garment Division
Total Area Measurment
|
Company vision:
Company vision is to achieve 100% customer satisfaction by producing the right cutting & sewing product with the highest quality and on time delivery, and by providing the best services to the customers for helping them to grow in their business and to maintain leadership in the market.
Mission:
The mission of Goldtex garments is to survive in Garments sector by the assurance of customer satisfaction through better quality & services. Goldtex garments differ from other garments manufacturer because it gives priority to achieve 100 percent customer satisfaction. From sample making ,order placing, production, to post production service, it is dedicated to ensure customers receipt of the highest quality of the production and service.
Goldtex people:
All the people at Goldtex garments are committed to share the vision and the values of the company. This allow everyone at the company to demonstrate the highest level of professionalism and quality in everything they do.
Each department is managed by experienced supervisors from Hong Kong and China.
From cutting to finishing and to packing each of our supervisor has at least 10 Years of experience in their field.
The following are the departments to conduct activities of Goldtex garments.
- The Human Resources Department(HRD)
- Commercial/Shipping Department
- Merchandising Department
- Marketing Department
- Production Department
- Accounts Department
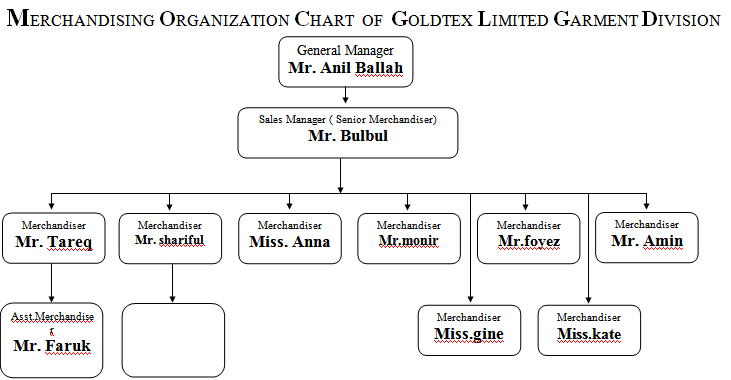
Goldtex Limited Garment Division
Organization Chart
Goldtex Limited Garment Division
Total Manpower Chart
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sister Concerns of Goldtex Limited Garments Division :
Hong Kong Office :
Golden Crown Head-wears Factory Ltd.
Golden Crown is a professional manufacturer of caps and hats with more than twenty years of experience in the field. Golden Crown was established in 1976, and has grown enormously in the past years. It is a Hong Kong based company with 100% self owned factory in China and Bangladesh. It’s goal is to satisfy any customer demand whether in R & D, product quality, shipping schedules or price.
All fabric and accessories they use are the finest that come from most reputable manufacturers meeting AQL world quality standards. They also continually invest on new machines and R&D to ensure & provide the best and most updated product and service to It’s customers. There are no shortcuts taken in every stage of production, and each piece of headwear, they are making is a work of art.
The Company have shipped products to all over the world in the past 30 years. They are proud of producing headwear under license for such world-class companies like Gap, Disney, Major League Baseball (MLB), National Football League (NFL), National Baseball Association (NBA) and National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA).
Golden Crown Head Office was set up in 1976. It is located in Hung Hom, Kowloon which is only 10 mins to the Kowloon Central Train Station. This permits the convenience in traveling to and from our China factories.
The office has 15,000sq.feet space and is well equipped with the latest technologies in computer and communication. This enables It’s staff to have a fast, reliable and economical communication with It’s customers, suppliers and factories. The Company staffed with 40 members of experienced and devoted management team and enthusiastic staff to provide the exceptional service to It’s customers.
Crown Head-wears Factory Ltd
The factory in China is located in Bai Yun District, Guang Zhou. It is about 2 hours travelling time by the Hong Kong – Guang Zhou direct train and a 45 mins car ride from the Guang Zhou train station. It is a 100% self owned factory with 150,000sq.feet space and 500 workers. Beside cap and hat making machines, it is also equipped with 25 embroidery machines for the embroidery production. Monthly production capacity is approx. 30,000dz embroidery caps. In house accommodation and canteen are also provided for our staff and workers.
In addition, the factory also has a medium size production for the 100% knitted wool hat, such as Beret, Beannie, and Gastby Hat. It is equipped with twenty-four Made in Japan Automatic Knitted machines, and production capacity is approx. 4,000dz per month.
In addition, the factory also has a medium size production for the 100% knitted wool hat, such as Beret, Beannie, and Gastby Hat. It is equipped with twenty-four Made in Japan Automatic Knitted machines, and production capacity is approx. 4,000dz per month.
Bangladesh Factory
Actor Sporting Ltd. – Head-wears Division
The factory was established in 1992 and is located in Dhaka Economic Free Zone, Savar. Inside this economic free zone, it is prohibited striking and child labor and unreasonable over time, etc. Thus It can maintain It’s production stability and quality throughout the year. 8Standerd lines in total coverd factory space 8305 Sq. Mtr has created opportunity to employee 2600 persons including a multi-national management staff from Hong Kong, China, Taiwan, Pakistan, and Bangladesh. Similar to our China factory, it is also well equipped with fifteen embroidery machines, and the monthly production capacity is approx. Cap – 85000 dzns & RMG-1,20,000pcs. Furthermore, They also have their own label, bar code printing and box making facility available inside the factory.
In addition, all cotton fabric It use is from It’s 100% self owned Dyeing Mill in Bangladesh. All cotton greige good It purchase is top grade product for the garment industry. Furthermore, their Dyeing Mill is also equipped with in-house washing facility. Using It’s own Dye house and washing facility enables It to have a vertical integration in It’s Head-wears production. Thus It can offer top quality product with competitive price and delivery to It’s customer.
Dyeing Factory:
South China Bleaching & Dyeing Factory Ltd
M/S Golden Crown Head – Wears Factory Ltd, Hong Kong, An Umbrella organization, has Started its operation in the filed of fabric processing in Dhaka Export Processing Zone (Depz), Bangladesh under incorporation in the name of South China Bleaching And Dyeing Factory Limited, as a limited company in 1996 production plant with a workforce of around 250 & Has been Meeting the growing demand of 100% Cotton & T/C Fabric in Bangladesh Readymade Garment Sector Largly. With a production capacity of dyeing & finishing of about 3 million yds in a month.
The company by this short period of operation time in Bangladesh, has already earned a high market reputation for its quality and service. South China by this time became one of the largest exporter of woven fabrics in Bangladesh with garments manufactured from the fabrics produced by it were being exported to the USA, Canada and all EU countries
They are specialized in reactive, vat & pigment dyeing and also in hard, soft & peach finish. Textiles available on different construction of twill, canvas and sheeting having high tensile strength, low shrinkage and excellent color fastness properties.
It’s vision is to provide all customers need, do the right solution in first time and to remain as a leader in this field. It’s goal is to nurture a close and open working partnership with all our customers, regardless of size or location, throughout the world.
South China Bleaching & Dyeing Factory Ltd Goldtex Limited
Weaving Unit
Goldtex Limited Weaving Unit also an Offspring company of M/S Golden Crown Head-Wears Factory Ltd,Hong kong, has gone into commercial production in the year 2005 in Dhaka Export Processing Zone (Depz) & has been meeting the growing demand of 100% cotton greige Fabric Largely.
The state-of-the-art TOYOTA brand Air Jet Loom imported from Japan& installed under direct supervision of experts of supplier company has developed an-built means for optimum productivity with superior quality.
Merchandising & Marketing In Garment Sector :
Merchandising with mandatory regulations in the industry is now crucial Continuous enhancement of product Quality provides a competitive edge in today’s garments market. By monitoring a local factory / supplier & it’s manufacturing process ranging from: fabrics to garments, company structure to management, manufacturing capability to quality systems, working environment to safety polices & other criteria can also be incorporated.
As an international corresponding part of this country, garment industry is the main venue in where we can develop our both inside & outside of human knowledge in any of other foreign areas.
Today garment merchandisers have to move with frequent changes in demand & the developing technologies utilized in manufacturing & production.
To find out customer requirements they regularly visit retail outlets & come up with latest updates from frontline staff. In order to keep an eye on development in sourcing, site visits are made every week to maintend factories to meet suppliers & study production.
In garment merchandising there is no specific rule, So it’s important to be able to think on one’s feet.
Merchandising in garment is not synonymous with merchandising being practiced in consumer product companies. It is much broader in its scope, activites & responsibilities. While in consumer product companies, its merely restricted to POP- ( Point of Purchase ) promotions for product in the stores to make it more cisible & attractive for the customers in order to increase sales: but in Garment it means much more than this.
Goldtex Limited Garment Division
(100% Export Oriented Garment Manufacturing Unit)
Merchandising & Marketing Information:
Dedicated merchandising & marketing team ensures most competitive pricing in the world market, ethical sourcing & on time delivery with shortest possible lead time for all the valued customers round the globe. It’s Hong Kong and Bangladesh office support its merchandising & marketing operations to provide intimate service to its clients.
– Trade Term: FOB
|
L/C Requirement: Irrevocable L/C at sight
– Banker: The Hongkong & Shanghai Banking Corporation Ltd. (HSBC)
SWIFT: HSBCDDH
A/C # 050-000116-096
Merchandising & Marketing of Goldtex Limited Garment Division :
Merchandising & Marketing of Goldtex Limited Garment Division use to play in TWO steps
Merchandising & Marketing system. It’s Hong Kong office maintain the vital role to direct sourcing of buyers or buying houses & other activities also. On the other hand the Bangladesh office basically operate the production development & production procedure to achieve the buyer satisfaction. Now a day of few the local BD office merchandisers are trying to communicate with the buyers & buying houses to collect new orders. Though this forwarding steps are tide with some bounds but it is crystal clear that this tine steps will bring the vision come true in the up coming feature.
Merchandising Policy of Goldtex garments:
Goldtex garments, it is a foreign investment garments industry in EPZ locality, its operate its merchandising & marketing activity in globally since 2005. Its effectively run its merchandising & marketing activities within the world and increasing its Merchandising & marketing activities day by day. The aim of its to identify the customer and try to gain order form them by giving the promotional sample. There are many merchandising office are already taken for marketing in Europe & America region. Merchandising policy of Goldtex garments is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational goals. It holds that achieving organizational goals depends on determining the needs and wants of target markets and delivering the desired satisfactions more efficiently and effectively then competitors do.
Merchandising concept of Goldtex garments dose not mean the company profit, should try to give all customers everything they want. Company must balance creating more value for customers against making more profits for the company. The purpose of merchandising arketing concepts of Goldtex garments is to make profit through customer’s satisfaction.
Goldtex garments implementation their merchandising
strategy according to the following stages.
Marketing Strategies of Introduction Stage:
# Rapid skimming: This strategy makes sense when a large part of the potential market is unaware of the product; those who become aware of the product are eager to have it and can pay the asking price; and the firm faces potential competition and wants to build brand preferences.
# Slow skimming: This strategy makes sense when the marketer is limited in size; most of the market is aware of the product; buyers are willing to pay a high price; and potential competition is not imminent.
# Rapid penetration: This strategy makes sense when the market is large, the market is unaware of the product, most buyers are price sensitive, there is strong potential competition, and the until manufacturing costs fall with the company’s scale of production and accumulated manufacturing experience.
# Slow penetration: This strategy makes sense when the market is large, is highly aware of the product, is price sensitive, and there is some potential competition.
Marketing Strategies of Growth Stage:
The growth stage is market by a rapid climb in sales. early adopts like the product, and additional consumer start buying it. new competitors enter,attraceted by the opportunities, they introduce new product features and expand distribution. during this stage, the firm uses several strategies to sustain rapid market.
It improves product quality and adds new product features and improved styling.
It adds new models and flanker products
It enters new market segments
It increases its distribution coverage and enters new distribution channels
It shifts from product- awareness advertising to product-preference advertising.
It lowers price to attract the next layer of price-sensitive buyers.
Marketing Strategies of Maturity Stage:
The maturity stage divides into three phases such as:
- growth
- stable
- decaying maturity.
In the first phases, the sales growth rate starts to decline. There are no new distribution channels to fill.
In the second phase, sales flatten on a per capita basis because of market saturation.
In the third phase, decaying maturity, the absolute level of sales starts to decline, and customers begin switching to other products and substitutes.
DECLINE STAGE:
Five strategies are available to the firm:
1.incrising the firms investments (to dominate the market or strengthen its competitive position)
2.maintaining the firm investment level until the uncertain sabot the industry are resolved.
3.decrising the firms investment level selectively by dropping unprofitable customer groups, while simultaneously strengthening the firms investment in lucrative niches.
4.harvesting(milking )the firms investment to recover cash quickly.
5.divesting the business quickly by disposing of its assets as advantageously as possible.
Pricing strategy of Goldtex garments:
Pricing strategies:
Company assumes that, price is the amount of money charged for a product or service, or the sum of the values that consumers exchange for the benefit of having of using the product or service. The pricing strategy of Goldtex garments has operated as the major determinate of buyer choice. This is still the case in poorer nations, among poorer groups, and with commodity-type products.
Company always implementation their pricing strategy as per buyer satisfaction. The main aim of pricing policy not gain new customer but also retain existing customer through customer satisfaction, Price is the marketing mix element that producers revenue; the other produce costs. Price is also one of the most flexible elements: it can be changed quickly, until product features and channel commitments. At the same time, price competition is the number one problem facing companies. Yet many companies do not handle pricing well. The most common mistakes are these: Pricing is too cost-oriented; price is not revised often enough to capitalize on market changes; price is set independent of the rest of the marketing mix rather than as an intrinsic element of market-positioning strategy ;and price is not varied enough for different product items, market segments, and purchase occasions. Goldtex garments cover their pricing strategy according to the above pricing Mix to survive effectively over the competitor.
Pricing policy of Goldtex gmts, Factor affecting pricing decisions :
Goldtex garments consider the following factor to implementation the pricing strategy.
Marketing objectives:
Before setting price, the company must decide on its strategy for the product. If the company has selected its target market and positioning carefully, then its marketing mix strategy, including price, will be fairly straightforward. At the same time, the company may seek additional objectives. The clearer a firm is about its objectives, the easier it is to set price. Example of common objectives is survival, current profit maximization, market-share maximization, and product-quality leadership.
Price is only one of the marketing-mix tools that the company uses to achieve its marketing objectives. Price decisions must be coordinated with product design, distribution, and promotion decisions to form a consistent and effective marketing program. Decisions made for other marketing-mix variables may affect pricing decisions. The decision to position the product on high quality will mean that the seller must charge a higher price to cover higher costs.
Costs: Costs set the floor for the price that the company can change for its product, the company wants to change a price that both covers all its costs for producing, distributing, and selling the product and delivers a fair rate of return for its effort and risks.
Pricing Types :Company follow the Different kind of pricing for effective marketing.
Quantity Discounts:
A quantity discount is a price reduction to buyers who pay their bills promptly. A typical example might be “$10 per unit for less than 100 units, $ 9 per unit for 100 or more units.” Quantity discounts must be offered to all customers and must not exceed the seller’s cost savings associated with selling large quantities. These savings include lower selling, inventory, and transportation expenses. Discounts provide an incentive to the customer to buy more from one given seller, rather than from many different sources.
Functional discount: a functional discount (also called trade discount “)is offered by the seller to trade channel members who performs certain function such as selling, storing ,and keeping.
Seasonal Discount:
A seasonal discount is a price reduction to buyers who buy merchandise or services out of season. Seasonal discounts allow the seller to keep production steady during an entire year.
Discriminatory Pricing:
The company often will adjust its basic price to allow for differences in customers, products, and locations. In discriminatory pricing, Goldtex garments sells a product or service at two or more prices, even though the difference in prices is not based on differences in costs. Discriminatory pricing takes several forms:
Under Customer-segment pricing: Different customers pay different prices for the same product or service. For example may charge a lower admission for students and senior citizens. Segment pricing goes by many names. Roberts cross a long time consultant to the airlines calls it revenue management.
Product-form pricing: Different versions of the product are period differently, but not according to differences in their costs. for instance the most expensive black and Decker iron. The top model has a self cleaning feature, yet this extra feature costs only a few more dollars to make.
Local pricing: Different location is priced differently, even though the cost of offering each location is the same. For instance theaters very their seats prices because of audience preferences for certain locations, and state universities charge higher tuition for out of state students.
For discriminatory pricing to be an effective strategy, certain conditions must exit. The market must be segmental, and the segments must show different degrees of demand. Members of the segment paying the lower price should not be able to turn around and resell the product to the segment paying the higher price. Competitors should not be able to undersell the firms in the segment being charged the higher price.
Psychological Pricing:
In using psychological pricing, Goldtex garments consider the psychology of prices and not simply the economics. For example consumers usually perceive higher priced product as having higher quality. when they can judge the quality of a product by examining it or by calling on past experience with it, they can price less to judge quality. Another aspect of psychological pricing is reference prices-prices that buyers carry in their minds and refers to when looking at a given product. The references might be formed by noting current prices, remembering past prices, or assessing the buying situation. Sellers can influence or use these consumers’ references prices when setting price. For example a company could display its product next to more expensive ones in order to imply that it belongs in the same class.
Promotional pricing:
with promotional pricing companies will temporary prices their product below lists price and sometimes even below cost to create buying excitement and urgency. promotional pricing takes several forms. supermarkets and department stores will price a few products as loss leaders to attract customs to the store in the hope that they will buy other items at normal markups. for example super markets often sell disposable diapers at less than cost in order to attract family buyers who make larger average purchase per trip. sellers will also use special event pricing in certain seasons to draw more customers. Thus linens are promotionally priced every January to attract weary Christmas shoppers back into stores.
Geographical Pricing:
Company also must decide how to price its products to customers located in different parts of the world. Its product price is differing place to place. Should the company risk losing the business of more distant customers by charging them higher prices to cover the higher shipping costs. Five geographical pricing strategies are:
FOB-Origin Pricing
Uniform Delivered Pricing:
A geographical pricing strategy in which goods are placed free on board a carrier. the customer pays the freight from the factory to the destination.
Zone Pricing :
A geographical pricing strategy In which the company sets up two more zones. All customer with in a zone pay the same total price. The more distant the zone, the higher the price.
Business-Point Pricing :
A geographical pricing strategy in which the seller designates some city as a basing point and charges all customers the freight cost from that city to the customer.
Freight-Absorption Pricing :
A geographical pricing strategy in which the seller absorbs all or part of the freight charges in order to get the desired business.
Internal Pricing:
Companies that market their products internationally must decide what prices to charge in the different areas in which they operate. In some cases, Gold can set a uniform worldwide price. The price that a company should charge in a specific area depends on many factors, including economic conditions, competitive situations, laws and regulations, and development of the wholesaling and retailing system. Consumer perceptions and preferences also may vary from area to markets for its products or services. “Using merchandising promotion merchandising executive communicates with the target markets to inform and influence their attitudes and behaviors. Marketing communication tells the target customers that the right product is available at the right price and at the right place. Promotion and communication is used synonymously kiln marketing literature. Communication can also be viewed as the transmission of information. Marketing communication is the various tools used to inform and persuade people that a firm directs toward its target markets, channel members, and the public in general. According to our recent study on Operation process of Goldtex garments and its development . In the marketing point of view promotional mix is very important for Goldtex garments.
There are following attempt are taken for promotional activities –
Advertising:
Advertising is defined as any paid form of no personal communication about Goldtex garments product, service, or idea by an identified sponsor. THE NON PERSONAL COMPONENT means that advertising involves mass media (e.g.: TV radio magazines newspaper )that can transmit a message to large groups of individual often at the same time.
Advertising is the best –known and most widely discussed form of promotion, probably because of its pervasiveness. It is also a very important promotional tool, particularly for companies whose products and services are targeted at mass consumer markets. Advertising can be used to create image and symbolic appeals for Goldtex garments selling products and services that are difficult to differentiate on functional attributes. Another advantage of advertising is its ability to strike a responsive chord with buyer when differentiation across other elements of the marketing mix is difficult to achieve.
Direct Marketing:
Direct Marketing in which Goldtex garments communicate directly with target buyer to generate a response and/or a transaction. For example Goldtex garments also sells of its product through direct marketing. Maximum selling systems are direct marketing.
Sales Promotion:
Which is generally defined as those marketing activities that provided extra value or incentives to sales forces, the distributors or the ultimate consumers and can stimulate immediate sales. sales promotion is generally broken into two major categories: consumers oriented and trade orientate activities.
Consumers oriented sales promotion :is targeted to the ultimate users of a product or services and includes couponing, premiums,rebates,sweepstakes ,sample.
Trade oriented sales promotion:
Is target toward marketing intermediaries such as wholesaler,distributors,and retailers.-promotional and merchandising allowance, price deals, sales contests, and trade shows are some of the [promotional tools used to encourage the trade to stoke and promote a company products.
Publicity and Buyer Relations:
Publicity refers to no personal communications regarding Goldtex garments product, service, or idea not directly paid for or run under identified sponsorship. It usually comes in the form of a news story, editorial, or announcement about Goldtex garments and its products and services. Like ad, publicity involves no personal communication to a mass audience, but unlike advertising, the company does not directly pay for publicity.
From the above discussion we see that the tools of marketing are very important. The wide range of communication tools, messages, and audiences make it imperative that Goldtex garments move toward integrated marketing communications. This way good relationship can be maintained successfully, between buyer and seller, marketing academics called “relationship marketing”.
Selecting of Sample Type:
Sampling may be defined as the selection of some part of an aggregate or totally on the basis of which judgments or inference about the aggregate or totality is made. In other words, it is the process of obtaining information about an entire population by examining only a part of it. In most of the research work and surveys ,the usual approach happens to be make generalizations or to draw inferences based on samples about the parameters of population from which the samples are taken. All this is done on the assumption that the sample data will enable him to estimate the population parameters. The item so selected constitute what is technically called a sample, their selection process or technique is called sample design and the survey conducted on the basis of sample is described as sample survey .Sample should be truly representative of population characteristics without any bias so that it may result in valid and reliable conclusions. Though it’s a production based organization, so it is effective for research to select the consequence number of staff, those who are directly involve on production.
Determining Sample Size:
In sampling analysis the most tick list question is :what should be the size of the sample or how large or small should be? If the sample size is too small, it may not serve to achieve the objectives and if is too large, we may incur huge cost and waste resources. As a general rule, one can say that the sample must be of an optimum size i.e.,it should neither be excessively large nor too small. Technically ,the sample size should be large enough to give a confidence interval of desired width and as such the size of the sample must be chosen by some logical process before sample is taken from the universe. Size of the sample should be determined by a researcher keeping in view the following points:
Nature of the universe, Number of the classes proposed, Nature of the study, Type of the sampling, Standard of accuracy and acceptable confidence level, Availability of finace, Other consideration. There are two alternative approaches for determining the size of the sample .the first approach is ‘to specify the precision of estimation desired and then to determine the sample size necessary to insure it’ and the second approach ‘uses Bayesian statistics to weigh the cost of additional information against the expected value of the additional information’. The first approach is capable of giving a mathematical solutions, and as such is a frequently used technique of determining .The limitation of this technique is that it does not analyze the cost of gathering information vis-à-vis the expected value of information. The second approach is theoretically optimal, but it is seldom used because of the difficulty involved in measuring the value of information .Hence ,we shall mainly concentrate here on the first approach. This refers to the number of items to be selected from the universe to constitute a sample.
Company supply chain:
Company own of the best supply chain in the Garments industry in the garments industry in Bangladesh. First ,it own South China Bleaching and Dying mill & Goldtex Textile. It is one of the premium fabrics supplier in the region. Its well known product quality is second to none in the textile industry. Having own fabric mill not only reduces the lead time for production delivery, it also improve its ability in area such as product development and sample making. In addition, it has office in Bangladesh and Hong Kong to assist the source the right material and accessories.
Analysis of Finding :
We found the following answer as per questionnaire basic for above sample to ensure the effective research program.70% of total responses have given their opinion to this answer.
1.What are the minimum qualification requirements of your company for employees?
Ans: Floor level-Primary
Supervisory level- Secondary
Engineer level- Vocational /Diploma
Managerial level- Graduate
2.Do the existing employees fulfill the qualification requirement?
Ans: Yes
3.What percentage of your employees are experienced?
Ans: It is about 80%
4.What is the proportion of your technical and non-technical employees?
Ans: Technical : Non Technical
6 : 1
5.How the company motivate its employees? what is the nature of motivation?
Ans: To motivate the worker company provided the following facilities-
-Performance allowance
-Attendance allowance
-Production incentives
-Promotion
-Medical facilities
-Transport facilities
-Group insurance,etc
6.Do the company provide scope to its employees to participate in decision making? What is the impact of participation?
Ans: Yes, Such as Group meeting, worker representative welfare committee, suggestions Box etc
Its helps to ensure better relationship with management of any employees.
7.Whether company give scope of security for the jobs of employees?.
Ans: Yes, Such as-Provident fund, Group insurance, Gratuity etc.
8.Do the company provide adequate facilities for the health & safety of the employees?
Ans: Yes
9.Is there any promotion policy in the organization ? what is that? How the employee are evaluated?
Ans: Yes, Based on performance
10.Do the company provide training to the rank and file employees of the organization, If so, what are these?
Ans: Yes, Health & Safety, Technical Training, Compliance, Product quality development
11. Do the company require any disciplinary action against its employee? if so, what are those?
Ans: Yes, Show case- inquire-warning –Dismiss
12.Does the company follow programs continuously for improving the quality of production ?Explain.
Ans: Yes,To ensuring better quality of product company arranged pre & post production program. Total Quality Management(TQM) always take initiative program to gain customer satisfaction by ensuring of better quality.
Conclusion:
The term analysis refers to the computation of certain measures along with searching for patterns of relationship that exist among data groups. Thus in the process of analysis, relationships or differences supporting of conflicting with original or new hypotheses should be subjected to statistical tests of significance to determine what validity data can be said to indicate any conclusion. In order to extract meaningful information from the data collected, the analysis will be carried out. After editing the data properly, they will be tabulated by using statistical tools i.e. percentage, average, dispersion etc. alternatively the collected data will also be analyzed by using diagrams, graph etc.