Price Discounts
The definition of discount is reduced prices or something being sold at a price lower than that item is normally sold for. An example of something described as the discount is a purse sold for 50 percent off its normal price or a store that focuses on selling designer items at below-market prices.
Stores will often sell items for a discounted sales price. The store will discount an item for a percent of the original price. For example, an item that originally cost $20 may be discounted by 25%.
- To find the amount of discount calculates 25% of $20. ($20.00*25/100=$5.00)
- Subtract the discount from the original price to find the sale price. ($20.00-$5.00=$15.00 sales price).
- Terms you may see for discounted items are 50% Off; Save 50%; Discounted by 50% etc.
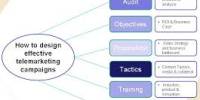
Most Common Types of Price Discounts
The following points highlight the six most common types of price discounts. The types are:
- Quantity Discounts
- Trade Discounts
- Promotional Discounts
- Seasonal Discounts
- Cash Discounts
- Geographical Discounts

Quantity Discounts:
The reason for quantity discounts lies in the general assumption of economies of scale. If a seller of a product can sell more of a product to a given buyer, various cost savings may occur. It can produce more and thus reduce unit costs of production. Distribution and marketing expenses are also reduced.
Trade (or Functional) Discounts:
Trade discounts are normally provided to middlemen for the functions they accomplish in the distribution of commodities. For this purpose, trade discounts are often called functional discounts. For example, booksellers in India get such discounts from publishers at the rate of say 20%, 25%, 33V3% on order of say 5-50, 51-100,101 and above, respectively. Such successive discounts represent a system of graded incentives.
Promotional Discounts:
Such discounts are given to distributors as “an allowance for the distributors’ efforts to promote the manufacturer’s product through local advertising, special displays, or other promotions. These allowances may take the form of a percentage reduction in the price or they may be an outright cash payment either to the distributor or to the promotional vehicle, e.g., a local newspaper”.
Seasonal Discounts:
Business conditions never run smooth. To the periodic fluctuations in the levels of business activity, the name business cycle is given. And, in reality, industries that are characterized by significant but regular fluctuations in volume may offer a discount to consumers who purchase the goods (or service) at non-peak hours.
Cash Discounts:
A cash discount is a reward for the payment of an invoice or account within a specified time period. For example, the Calcutta Electric Supply Corporation provides a discount to all customers who pay their bills on or before a scheduled date. From the seller’s viewpoint, immediate payment is preferred so that the seller can invest the money for the period. Thus, the seller may offer a discount for an immediate cash payment.
Geographical Discounts:
Geographical discount structures introduce to price differentials based on buyers’ (or markets’) location. They’ are important when transport costs are high relative to the selling price since the manufacturer can then gain from differences in transport costs due to varying distances between the locations of plants and the customers.
Information Source: