The practice of using plastic materials in agricultural applications is referred to as plasticulture. The plastic materials themselves are referred to as “ag plastics” informally and broadly. It is a farming practice that involves the use of plastic materials in agriculture to improve crop production, efficiency, and resource conservation. It’s also referred to as “plastic mulching” or “plastic farming.”
Soil fumigation film, irrigation drip tape/tubing, plastic plant packaging cord, nursery pots and bales are examples of plasticulture ag plastics, but the term is most commonly used to describe all types of plastic plant/soil coverings. Plastic mulch film, row coverings, high and low tunnels (polytunnels), and plastic greenhouses are examples of such coverings. The use of plastics in agriculture has gained popularity in many parts of the world due to its numerous benefits.
In 2019, 6.7 million tons of plastic were expected to be used in agriculture, accounting for 2% of global plastic production. Because of contamination from agricultural chemicals, plastic used in agriculture is difficult to recycle. Furthermore, the degradation of plastic into microplastics is harmful to soil health, microorganisms, and beneficial organisms such as earthworms.
Current science is unsure whether there are any negative effects on food or once food grown in plasticulture is consumed by humans. Because of these consequences, some governments, such as the European Union under the Circular Economy Action Plan, are beginning to regulate its use and farm plastic waste.
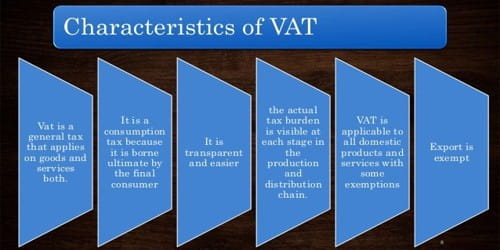
Here are some key aspects and benefits of plasticulture:
- Plastic Mulch: The use of plastic films as mulch is one of the most common applications of plasticulture. Farmers use these films to cover the planting beds by laying them over the soil surface. Plastic mulch helps to retain moisture in the soil, control soil temperature, and create a more favorable environment for plant growth.
- Water Conservation: Plasticulture conserves water by preventing evaporation and runoff. It reduces the amount of water needed for irrigation, making it an efficient method in water-stressed areas.
- Improved Soil Health: Plastic mulches protect the soil from erosion, compaction, and extreme weather exposure. This can lead to better soil structure, more organic matter, and better nutrient retention.
- Disease and Pest Control: Plasticulture can act as a barrier between the soil and the crops, reducing the spread of certain soil-borne diseases and pests.
- Increased Crop Yield: The combination of reduced weed competition, optimized soil conditions, and improved water retention can lead to higher crop yields compared to traditional farming methods.
- Efficient Fertilizer Application: Plastic mulches can help in the precise application of fertilizers, reducing waste and environmental impacts.
However, there are some issues with the use of plasticulture. Improper disposal of plastic materials can cause environmental pollution, and the long-term effects of plastic residues in soil and water are still being researched and debated. Efforts are being made to create more environmentally friendly and biodegradable plastics for agricultural use.