Photosensitivity refers to a condition in which certain individuals have an abnormal sensitivity to light. This can manifest as an allergic reaction to light, or as a symptom of certain medical conditions such as lupus or porphyria. Symptoms of photosensitivity can include skin rashes, itching, and redness, as well as headaches and eye strain. Some people with photosensitivity may also experience seizures triggered by light. It can be treated with medications and by avoiding sun exposure.
Photosensitivity is a high sensitivity to ultraviolet (UV) rays emitted by the sun and other light sources. During prolonged exposure to sunlight, most people are at risk of developing sunburn. UV ray exposure can also cause skin damage and skin cancer. Photosensitive people may develop skin rashes or burns even after only a brief exposure to the sun. This can manifest as an allergic reaction, skin irritation, or other symptoms when exposed to certain types of light or radiation, such as ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun or artificial sources. Photosensitivity can be caused by certain medical conditions, medications, or genetic factors. It is important for individuals with photosensitivity to avoid excessive exposure to light and to protect their skin from sun damage.
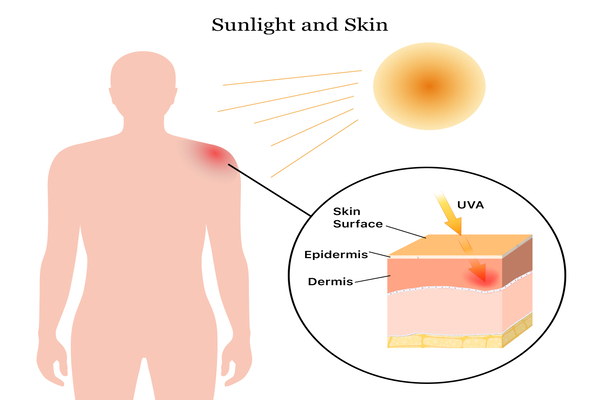
Photosensitivity symptoms range from mild to severe. Exaggerated skin rash or sunburn is the most common symptom. Itching may or may not occur with rashes. Sunburn can be so severe in some cases that blistering develops. Skin weeping and peeling can also occur in severe cases. The amount of sunlight required to cause a reaction varies greatly. Very little sun exposure can cause a rash or burn in some people, while prolonged exposure can cause a reaction in others.
Photosensitivity can be caused by certain medical conditions, medications, or genetic disorders. It can also be a side effect of certain medical treatments, such as chemotherapy. If you experience symptoms of photosensitivity, it is important to consult a doctor to determine the cause and appropriate treatment. Some people have a genetic or acquired condition that makes them more sensitive to light, while others may develop photosensitivity as a side effect of certain medications or treatments. In some cases, photosensitivity can be managed through the use of protective clothing, sunglasses, or other measures, but more severe cases may require medical treatment.