Leifite is a rare tectosilicate. It a mineral consisting of a rare fluoride and silicate of sodium and aluminum. It is a rather rare and obscure beryllium silicate mineral. Tectosilicates are built on a framework of tetrahedra with silicon or aluminum at the center and oxygen at the vertices; they include feldspars and zeolites. It is a member of the leifite group, which includes telyushenkoite (Cs, Na, K)Na6(Be2Al3Si15O39) and eirikite KNa6Be2(Si15Al3)O39F2.
Leifite was discovered in 1915, and named after Leif Ericson who was a Norse explorer who lived around 1000 AD and was probably the first European to land in North America, nearly 500 years before Christopher Columbus. It is a rare mineral that occurs at its type locality in the Narssarssuk pegmatite in Greenland, at Mont Saint-Hilaire and the Strange Lake complex in Canada, and in the Kola Peninsula in Russia.
General Information
- Category: Silicate mineral
- Formula: Na7Be2(Si15Al3)O39(F,OH)2
- Crystal system: Trigonal
- Crystal class: Hexagonal scalenohedral (3m)
- Colour: white, colorless to pale violet.
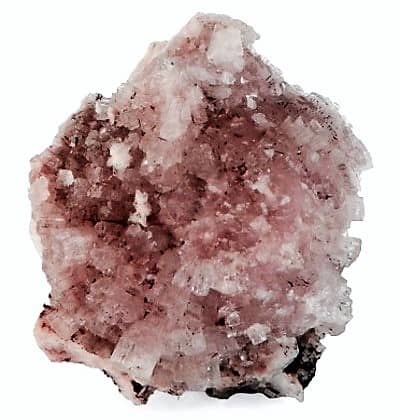

Fig: Leifite
Properties
Leifite is generally white or colorless, with a white streak and a silky or vitreous luster. It occurs as fine needles making up radiating aggregates and rosettes. It is found in pegmatites, alkali massifs, and in a gabbro-syenite complex. Individual crystals are deeply striated hexagonal prisms that are transparent to translucent. It is brittle, with an uneven to splintery fracture.
- Formula mass: 425.47 g/mol
- Crystal habit: Typically radiating aggregates of fine needles
- Twinning: None
- Cleavage: Distinct on {1010}
- Fracture: Uneven to splintery
- Tenacity: Brittle
- Mohs scale hardness: 6
- Luster: Silky to vitreous
- Streak: White
- Diaphaneity: Transparent to translucent
- Specific gravity: 2.6
- Optical properties: Uniaxial (+)
Occurrence
The type locality is the Narsaarsuk pegmatite on the Narsaarsuk Plateau, Igaliku, Narsaq, Kujalleq, Greenland and type material is kept at the University of Copenhagen, Denmark, and at the National Museum of Natural History in Washington DC, US. Leifite occurs in cavities in alkali-pegmatite veins. In Greenland, it occurs in a pegmatite with microcline, calcite, zinnwaldite, and acmite. In Russia, it occurs in the Lovozero Massif associated with albite and natrolite. In Norway, it occurs in a nepheline syenite pegmatite on the southeastern part of the island of Vesle Aroya.
Association: Microcline, aegirine, zinnwaldite, calcite (Narss^arssuk, Greenland); albite, natrolite (Lovozero massif, Russia); rhodochrosite, s¶erandite (Mont Saint-Hilaire, Canada).
Information Source: