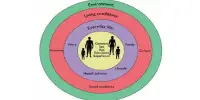
Social innovation is the creation and implementation of new ideas, strategies, and solutions to address social and environmental concerns. These are innovative social practices that strive to better address societal demands than existing alternatives, such as working conditions, education, community development, or health. Unlike traditional innovations, which are primarily concerned with technology developments or corporate procedures, social innovations attempt to improve the well-being of communities and society as a whole. These concepts are developed with the purpose of expanding and strengthening civil society.
Social innovation encompasses both social processes of innovation, such as open source methods and techniques, and social innovations, such as activism, crowdfunding, time-based money, telehealth, cohousing, virtual volunteering, microcredit, or distance learning. There are numerous definitions of social innovation, but they all involve broad requirements such as social purposes, social interaction among actors or actor variety, social outputs, and innovativeness. These innovations can take many different forms, including changes in regulations, practices, or the implementation of creative methods to societal challenges.
Here are some examples and key aspects of social innovation:
- Community-Based Initiatives: Social innovations frequently begin at the grass roots, with communities identifying and addressing their specific concerns. This can include education, healthcare, poverty reduction, and environmental sustainability projects.
- Collaborative Platforms: Many social innovations use teamwork and technology to link people and organizations. Online platforms and networks make it easier to share ideas, resources, and solutions, allowing for a more collaborative approach to issue solving.
- Social Entrepreneurship: Social entrepreneurs start enterprises with the goal of alleviating social or environmental issues. These businesses seek to generate both commercial and social value by tackling issues such as poverty, education, and healthcare access.
- Policy Innovations: Governments and policymakers can drive social innovation by implementing new policies and regulations that address societal challenges. This can involve creating incentives for sustainable practices, promoting social equality, or introducing innovative approaches to governance.
- Technological Solutions: Advances in technology can be harnessed for social good. For example, mobile applications and digital platforms have been used to improve access to education, healthcare, and financial services in underserved communities.
Microfinance, social impact bonds, open-source solutions, fair trade practices, and numerous community-led initiatives are examples of social innovations. As societies encounter new difficulties, the field of social innovation continues to expand, necessitating inventive and adaptive solutions to achieve positive change.
varying definitions include varying mixes and numbers of these qualities (for example, the EU has a definition that emphasizes social purposes and actor interaction). Transformative social innovation not only brings new methods to seemingly intractable issues, but also changes the social institutions that caused the problem in the first place.