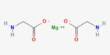
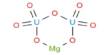
Jadarite is a white, earthy monoclinic silicate mineral, whose chemical formula is LiNaSiB3O7(OH) or Na2OLi2O(SiO2)2(B2O3)3H2O. It is a mineral, sodium lithium boron silicate hydroxide. It is a new lithium sodium borosilicate mineral from the Jadar Basin, Serbia.
It was discovered in November 2006, in drill core from the Jadar Valley in Serbia, from which it is named. The find was located 10 km (6.2 mi) southwest of the Cer mountain. It was confirmed as a new mineral after scientists at the Natural History Museum in London and the National Research Council of Canada conducted tests on it.
General Information
- Category: Nesosilicate
- Formula: LiNaSiB3O7(OH)
- Crystal system: Monoclinic
- Crystal class: Prismatic (2/m) (same H-M symbol)

Fig: Jadarite – earthy monoclinic silicate mineral
Properties
- Formula mass: 219.46 g/mol
- Color: White
- Fracture: Irregular to conchoidal
- Tenacity: Brittle
- Mohs scale hardness: 4 – 5
- Luster: Dull
- Streak: White
- Diaphaneity: Translucent to opaque
- Specific gravity: 2.45
- Optical properties: Biaxial
.Occurrence
It occurs as massive white aggregates, several metres thick, and is relatively free from inclusions and intergrowths; however, individual subhedral (tabular, elongate) to anhedral crystals rarely exceed 5-10 μm in size. It is associated with calcite, dolomite, K-feldspar, rutile, albite, ilmenite, pyrite, and fine-grained muscovite.
Commercialization
The mineral discovery may be commercially important to the presence of Lithium and Boron, both relatively rare industrially important elements, lithium being used for lithium batteries, and boron in alloys, ceramic, glasses, and other applications.
Information Source: