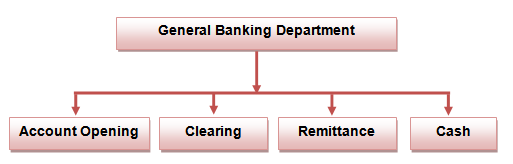
General Banking Department:
General banking department is the ‘Heart’ of all banking activities. The division of general banking plays an important role in a bank. It’s mainly a liability side.
Account Opening:
To become the client of the bank a person need to open an Account. After opening of an account a person becomes a client of a bank. It is a legal contract between the bank and the client. All kinds of deposit and saving schemes are accepted on the Mudaraba principle of Islamic Shari’ah. Under the above principle the clients is the ‘Shaheb-al-mal’ and the bank is ‘Mudareb’. Through this contract a client is ready to deposit any amount of money with purchasing the belief from the bank. Therefore it means the bank is selling their belief and always ready to pay any amount of deposited money to the client. An account opening form is the contractual document. It is the legal basis of Banker-Client relationship.
Prerequisites for opening an Account of Individual
- Photocopy of Passport or National ID Card or Word Commissioner Certificate
- Passport size 2 (two) copies color photograph attested by the introducer.
- Introducing the account by a client who maintaining a current account with this bank.
- Photocopy of Employee ID Card (in case of service holder)
- Nominee form and photo duly attested by account holder.
Prerequisites for opening a Private/Public Limited Company
- Board resolution regarding opening of Account & mentioning authorized persons for
- Operation A/C duly certified by the Chairman..
- Valid & up to date trade license.
- Memorandum & articles of association duly signed by the registrar of joint stock
- Certificate of incorporation.
- Certificate of commencement (in case of public company)
- Certificate of Registration
- TIN & VAT certificate.
- List of all directors along with Designation and specimen signature on the company’s letter head pad.
- Photocopy of latest certified copy of Form-XII
- Passport size 2 (Two) copies color photographs of all the directors.
Prerequisites for opening a Joint Account
- Photocopy of Passport or National ID Card or Word Commissioner Certificate
- Passport size 2 (two) copies color photograph attested by the introducer.
- Introducing the account by a client who maintaining a current account with this bank.
- Photocopy of Employee ID Card (in case of service holder)
- Nominee form and photo duly attested by account holder.
- Joint Declaration
- TIN certificate (if any)
Prerequisites for opening a Partnership Accounts
- Photocopy of Passport or National ID Card or Word Commissioner Certificate
- Passport size 2 (two) copies color photograph attested by the introducer.
- Introducing the account by a client who maintaining a current account with this bank.
- Partnership Deed
- Updated Trade License.
- TIN & VAT certificate.
- Board resolution/ Meeting Minutes
Prerequisites for opening a Societies Account
- Photocopy of Passport or National ID card or Word Commissioner Certificate.
- Board resolution.
- Passport size 2 (two) copies color photograph attested by the introducer.
- List existing Managing Committee.
- Registration (if any).
- Bye Laws/Constitution.
- Updated Trade License.
- TIN & VAT certificate.
- Permission Letter from Bureau of NGO (in case of NGO).
Procedures of opening an Accounts
Before opening an account, the following formalities have to be completed by the customer:
- Apply on a prescribed form.
- An acceptable introduction by an introducer which is acceptable by the bank is required prior to opening of any account.
- Two copies of recent photograph of the account holder(s) duly attested by the introducer must be produced.
- The customer has to give three specimen signatures in the” Specimen signature card”.
- The minimum balance has to be maintained in the current is Tk. 1,000.00 and in Saving Account is Tk. 500.00.
The particulars of the application form for opening Current or Saving Account are as follows:
- Type of the account
- Name of the applicant(s)
- Father’/Mother’s name
- Present address
- Permanent address
- Passport no (If any)
- National ID card no (If any)
- Date of birth
- Nationality
- Occupation
- Telephone/Mobile/E-mail
- Nominee(s)
- Special instruction for operation of the A/C
- Initial deposit
- Specimen signature of the applicant
- Introducer’s Information.
- Name.
- Account number.
- KYC Profile.
- Transaction Profile.
In case of joint account, the following additional headings are in the form:
- Operational instruction of the A/C and signatures or Board resolution
In case of partnership account the following additional headings must be added:
- Partners’ name and signature.
Transaction Profile
The person who wants to open an account have to fill a transaction profile-
| Bank Products Required | No. of Transactions (Monthly) | Maximum Size (Per transaction) | Total Value (Monthly) |
| Outgoing FCY Transfers | |||
| Outgoing LCY Transfers | |||
| Drafts/ Travelers Checks | |||
| Cash withdrawals | |||
| Check Payment | |||
| Pay Link Payments | |||
| FX products | |||
| MM Products (Deposits) | |||
| Letter of credit/Guarantee | |||
| Loan Facilities | |||
| Investment Transactions | |||
| Payroll Cards | |||
| Others (Specify) | |||
| Expected Sources of Fund | |||
| Incoming FCY Transfer | |||
| Incoming LCY Transfer | |||
| Cash Deposits | |||
| Check Deposits | |||
| Cash Collection | |||
| Other station Cash Collections | |||
| Other station Check Collections | |||
| FCY Check Collections | |||
| Export Proceeds | |||
| Other (Specify) |
Note: Please use Additional sheets if required.
I/We, the undersigned, hereby confirm that this: Transaction Profile” truly represents the transactions arising out of the normal course of business of our organization. I/We also confirm to inform you any revision in the “Transaction Profile”, if necessary, from time to time.
01. SIGNATURE: 02. SIGNATURE:
NAME: NAME:
TITLE: TITLE:
DATE: DATE:
Types of Accounts:
There are different types of account in Bank. SIBL has the following types of accounts:
A. Deposit
- Al-Wadiah Current Account.
- Mudaraba Short Notice Deposit
- Mudaraba Saving Deposit
- Mudaraba Term Deposit Receipt
b. Deposit Scheme:
1. Mudaraba Pension Deposit scheme
2. Mudaraba Hajj Deposit scheme
3. Mudaraba Lakhopati Deposit scheme
4. Mudaraba Millionaire Deposit scheme
5. Mudaraba Monthly Profit Deposit scheme
6. Mudaraba Marraige Deposit scheme
7. Mudaraba Bashasthan Deposit scheme
Al-Wadiah Current Account
Al-Wadiah Current Account facilitates the account holder to draw money at any times but no profit is given to this account. These accounts can be of five types. They are:
1. Individual Account
2. Proprietorship Account
3. Partnership Account
4. Limited Company Account
5. Cooperative Account
RULES OF AL-WADIAH CURRENT ACCOUNT
- A minimum initial deposit of Tk.1000/= shall be required for opening a Current Deposit Account.
- Withdrawal of money by the customer from the account shall be allowed only through the leaves of the cheque book issued by the Bank.
- Signature of the customer on the cheque leaf for withdrawal of money shall have to be tailed with the specimen signature recorded with the bank.
- Payment, in no way, shall be allowed against advance/ post dated and torn cheque.
- The statement of account as furnished by the Bank shall be presumed as correct, if no objection to the same is raised by the customer within a week of receipt of the statement.
- Bank shall accept order of the customer for stop payment of a cheque.
- Bank may, at the instruction of the customer, collect proceeds/ money of the cheque etc. for credit into the account but the same shall be accomplished at the risk and responsibility of the customer. Bank shall always take efforts for early collection but shall not be responsible for any delay or loss, if caused in the process of collection. Cheque/ instruments will require to be crossed by the customer before depositing the same in the account. No withdrawal will be allowed against any proceeds not yet collected.
- Bank shall take maximum care and remain alert to record exactly all the transactions of both credit & debit in the Ledger with no fault. However, in case of any mistake/ lapse Bank shall reserve the right to rectify the same and recover the money from the customer without any reference/ notice to the customer. Bank shall not make liable for any loss/ inconveniences caused to the customer due to such error/ mistake/ lapses.
- Any change/ alternation of address/ constitution of the customer must be intimated to the Bank forthwith. In the matters relating to mailing and remittances, Bank shall consider the post office and other courier agencies as representatives of the customer and the Bank shall not be responsible for any delay or no delivery of mails or remittances served through such agents.
- Receipt against any cheque /money/ instruments/ book securities duly signed by the authorized official of the Bank shall be considered as legal one.
- Bank shall reserve absolute right to alter / amend its own rules, regulations as well as rate of profit. This revised rule/ rate of profit shall be applicable upon the customer forthwith. Bank will as per Govt. directives/ notification, realize VAT/ Advance Income Tax/ development surcharge/ other levy at fixed rate at the end of each calendar year on the basis of balance of 30th December or otherwise as decided by Govt. from time to time.
- Bank shall reserve the right to close down any account, if the operation of the same appears to be unsatisfactory. Moreover, Bank may close any account on other genuine grounds without assigning reason thereof.
Mudaraba Short Notice Deposit (MSND)
SIBL offers 5.50% profit on MSND account, which is less than that of saving deposit. Normally various big companies, organizations, government departments keep money in MSND account. For this type of account frequent withdrawal is discouraged. Deposit should be kept for at least seven days to get profit. Prior notice is required for the withdrawal of money from MSND account. The account holder must give notice seven days before the withdrawal that is why MSND is called “Seven-Day-Notice” Current account. The rules of Mudaraba Short Notice Deposit (MSND) Account are same as the rules of Al-Wadiah Current Account.
Mudaraba Saving Account
The saving account is bearing profit. The saving account allows one to have profit income on his/her deposit while the account can be used for transaction purposes. Withdrawal of deposit can be made twice in a week in case of this account. Exceeding this number will forfeit the profit for the month. The SIBL offers 6% profit rate on the account. Profit is applied to the account on half-yearly basis.
RULES OF SAVING ACCOUNT
1. Any person/ persons of the age of majority and sound mind can open account singly or jointly. The balance shall be payable to him/ her/them or the survivor of the joint account. A guardian can open such account on behalf of a minor.
2. Introduction is necessary when opening Saving Account.
3. Every Savings Account shall have a separate account number.
4. Withdrawal of money shall be allowed only through the leave of the cheque book supplied by the Bank.
5. A minimum initial deposit of Tk.500/= shall be required for opening Savings Bank Account.
6. A Depositor shall not be allowed to withdrawal more than twice a week.
7. Profit payable on minimum balance shall be in June and December every year.
8. Signature of the client on cheques for withdrawal of money must tally with the specimen signature recorded within the Bank.
10. In case of closure of any account within 6 months from the date of opening of the same, the Bank shall deduct Tk.100/= from the account as closing charge.
11. The Bank reserves the absolute right to alter/amend these rules of Saving Account as well as rate of profit from time to time.
12. The Bank reserves the right to close any account if the operation appears to be unsatisfactory or on other genuine grounds without assigning any reason thereof.
Mudaraba Term Deposit Receipt (MTDR)
Mudaraba Term Deposit Receipt (MTDR) is a different type of account. Any body can open this account there is different amount of profit on the time schedule. At the time of opening the deposit account the banker issues a receipt acknowledging the receipt of money on deposit account. It is popularly known as MTDR.
Necessary documents for opening a MTDR in SIBL are as follow.
- MTDR Form
- Nominee information
- Photographs of applicant & nominee
- Photocopy of National ID card of Applicant & Nominee
After fill up the MTDR form the party deposits the amount. The party can pay the amount in two ways-
A) By Cash-
When the party pays the money in cash then the MTDR is issued immediately.
B) By Cheque-
When a party gives the Cheque then at first the cheque is send to the clearing house then when the cheque comes from the clearing house successfully then the MTDR is issued.
After fulfilling the MTDR Form and depositing the amount, MTDR Account is opened and MTDR receipt is issued and it is recorded in the MTDR Register. The MTDR Register contains the following information:
- Issued date
- MTDR Account Number
- Name of the MTDR holder
- MTDR Amount
- Mudaraba Deposit Receipt Number
- Maturity Period
In case of Mudaraba Term Deposit Account, the bank need not hold a cash reserve to repay money to the customer. The payment will be made after completion of a certain period of time.
The Profit rate offered by SIBL for Mudaraba Term Deposit Account is as follows:
| Time Period | Rate of Profit |
| 1 month 3 months 6 months 1 year & above
| 8.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00%
|
Normally a customer is not allowed to withdraw money before the maturity of the fixed period in case of MTDR. If any customer withdraws money before maturity date, the customers will not get any profit.
Excise Duty
The excise duty for MTDR is different for different amount of MTD. These are as follows-
| EXISE DUTY | |
| Amount (Tk.) | Charge (Tk.) |
| Tk.10, 000/= to Tk.1, 00,000/= | 120 |
| Tk.1, 00,001/= to Tk.10, 00,000/= | 250 |
| Tk.10, 00,001/= to Tk.1, 00, 00,000/= | 550 |
| Tk.1, 00, 00,001/= to Tk. 50, 00, 00,000/= | 2500 |
| Above Tk. 50, 00, 00,001/= | 5000 |
Profit payment procedure
For 3 months or 6 months
If a person make a MTDR for 3 (three) months or 6 (six) months then the profit will be charge compound basis. That is if the person make a MTDR on 01/05/09 for three months then the MTDR will be mature on 01/08/09. At the end of the maturity if the person do not withdraw the profit and give the instruction “To be renewed automatically” Then after the end of another three months the person will get profit on “Principal +Profit”. It means the profit will be charge on the current balance.
For 1 year, 2 year, 3 year
Under these MTDR, profit is charged on simple basis. If a person make a MTDR for 1 year and at the end of the 1 year if the person do not withdraw the profit amount then after the end of another 1 year he/she will get profit only on the “principal + profit” amount.
Encashment procedure of MTDR
When the party wants to encash the MTDR then the MTDR slip have to be submitting. Then a credit voucher is made-
Amount of profit paid to Mr. X against MTDR no#…………… Cr.
Accounting Procedure
Most of the days some MTDR become matured. So, at the end of the day which MTDR are mature vouchers are made for them. These are as follows-
Exp A/C Profit paid on MTDR ……………………………………Dr.
Exp A/C Profit paid on MTDR (broken days)……………………Dr.
Profit payable on MTDR……………………………………………Cr.
MTDR…………………………………………………………………Dr.
Tax on profit…………………………..………….……………….…Cr.
Excise duty.………..…………………………….………….……Cr.
Client A/C/ P.O ……….……………………………………………..Cr.
Calculation of broken Days Profit
1. For 3 (Three) months:
Principal x Rate x No of days x Quarter –90
(360 x 100) or 36000 x 90
2. For 6 (Six) months:
Principal x Rate x No of days x Half year –180
36000 x 180
3. For 1 (One) Year:
Principal x Rate x No of days x 360
36000 x 360
Important factors of MTDR Account
Some other important factors of MTDR Account are as follow
MTDR is not a negotiable Instrument.
The legal position of a banker regarding a fixed deposit is that of a debtor which bound to repay the money only after the maturity of the fixed period.
Cheque books are not issued for MTDR Account
Transfer of an Account
An account holder can transfer his account from one branch to another branch of Social Investment Bank Limited. For this, he/she must apply with proper reason to the manager of the branch where he is maintaining the account. There are some rules and regulation and some charge have to pay for transferring the account from one branch to another branch of Social Investment Bank Limited.
Closing of an account:
A client can close his account any time by submitting an application to the branch. There must be a signature of the client in the application and the account-opening officer will verify it. The account officer then checks the client’s account position. The client is then asked to draw a final cheque for the credit amount in the account excluding account close charge Tk. 100.00 for saving and Tk. 200.00 for current account. The client then surrenders remaining cheques to respected officer who will tear off these cheques. Vouchers are then issued with debiting the particular account and crediting Incidental charges account.
Incidental charge …………………………………………… Dr.
Account No ………………………………………………….Cr.
In case of joint account the application for closing the account should be signed by all the joint account holders, even if the account is operated by either of them. The last cheque for withdrawal of the available balance in the account should also be signed by all the joint account holders.
Revised Profit Rates on Deposits:
The management of Social Investment Bank Limited has approved revision of Profit Rates on deposits of the Bank with effect from April 16, 2009. The revised profit rate structure is set beneath for information, record & necessary actions –
| SL NO. | Types of Deposits | Period | Rate of Profit P/A | Remarks |
| 01. | Savings | – | 6.00% | Profit will be calculated on half yearly basis on available balance. |
| 02. Mudaraba Short Notice Deposit (MND) | ||||
| 2. A)
| Mudaraba Short Notice Deposit
|
–
| 5.50%
| Profit will be paid @ 5.50% pay to the accounts having average balances minimum balance of Tk. 500 during the month. |
| 03. Mudaraba Term Deposit Received (MTDR) | ||||
| 3. A) 3. B) 3. C)
| MTDR
| 3 m 6 m 1 year
| 10.00% 10.00% 10.00%
| In case of pre-mature encashment of fixed deposit, profit to be paid at the rate equivalent to the prevailing Savings Profit Rate, provided the deposit has been kept with the Bank for a minimum period of 01 month. |
Issuing Cheque-Book:
After the completion of above formalities, the bank provides the client a Deposit Book and cheque book. The cheque book can be of 10 or 25 pages. It will depend on the type of the account. The 10 pages cheque book is issued to the Saving A/C holder and 10, 20, 25 pages cheque book is issued to the Al-Wahdia Current or MSND A/C holder. The client has to fill up the Requisition Slip for cheque book. Then the officer will take a new cheque book with filling up account number of the client and the branch name in each page of the cheque book. The name and the account number of the client are then registered in the “Cheque book issue register”. The serial number of the cheque book is also entered in the computer for proper maintenance of records.
Cash Counter Section:
Cash department is the most important part of General banking. Cash is the key instrument of all financial transaction. The cash section plays a significant role. It is a very sensitive part of the bank because it deals with most liquid assets. Social Investment Bank Limited, Banani Branch has a well-equipped cash section. This section receives cash from depositors and pays cash against cheques, Demand Draft, Pay Order and Pay-in-Slip over the counter. This section deals with all types of negotiable instrument and it includes Vault, used as the store of cash and instruments. Operation of this section begins with the banking hour. The cash officer begins transaction with taking money from the Vault, known as “Opening Cash Balance”. Vault is kept in most secured place. The amount of opening cash balance is entered into a register. After whole days’ transaction, the money remains in the cash counter is deposited back into the Vault, known as the closing balance. The main functions of this section are cash receipt and cash payment. Some register books uses in the cash department are mentioned bellow:
Receiving Cashier’s Book
Payment Cashier’s Book
Cash Balance Book
Vault register
Key register
Remittance Register
Cash Receipt
Cash is the blood of a branch. It is the life of a bank.
At first depositor fills up the deposit amount in slip.
After filling the required deposit amount in slip, depositor deposits the money.
Officer of the cash counter receives the money, counts it, enters the amount of money in the scroll register, makes seal the deposit in slip and sign on with the date.
Then this slip is passed to another officer for counter sign in the deposit slip.
Then the cash officer keeps the bank’s part of the slip. Other part is given to the depositor.
The cash in charge gives posting through computer from the deposit slip in the client’s account and write a transaction number.
Cash Payment
When a client comes to the bank to cash a cheque, he/she gives it to the cash counter.
The cash officer receives the cheque and checks it very carefully.
The cash officer checks the date of the cheque, name, the account number of the cheque, amount in ward in figure and also verifies the signature through computer.
If the instrument is free of all kinds of errors the respected officer will ask the cheque bearer to sign on the back of it.
He/she will then put his/her initial beside the bearer’s signature.
There must be two signatures in cash payment cheque. If it is a big amount, cheque must be verified in front of the cash officer.
The cash officer will then enter the scroll number in his/her register and will pay the money to the bearer.
Then the cash in-charge gives posting of the cheque through computer and writes a transaction number.
Every employee in the cash counter maintains register. After receiving payment they fill up the following particulars-
- Ø Serial No
- Ø Account Number
- Ø Amount
- Ø Initial
After giving the payments they fill up the following particulars-
- Ø Serial No.
- Ø Account Number
- Ø Cheque Number
- Ø Amount
- Ø Initial
Cheque Counter
There is also a counter called Cheque counter. Under this counter three types of Cheque are received-
1) Transfer-
Transfer means inter Bank transfer that is same bank same branch.
2) Clearing-
When Cheque comes from the different Bank located in same clearing zone then it is send to the Bangladesh Bank Clearing House for clearing. Normally it takes 2 to 3 days for clearing a Cheque.
3) Collection-
When A Cheque is collected which are from different bank located in different district then it is sending for collection. The Cheque is then send to that bank. From that Bank it is verified and than checked that if there are available fund or not. If there is available fund then it is send to Social Investment Bank Limited.
Counter Limit
There is a counter limit in every Bank. The SIBL can keep in the counter only Tk. 25.00 Lac. The Bank can not keep more than that amount.
Vault Limit
Social Investment Bank Limited can keeps in the vault only Tk. 60.00 Lac.
Remittance
Remittances represent transfer of funds one place to another through official channel. Remittance facilities are very well known and popular service. The word “Remittance” means sending of money from one place to another through Courier service and Telegraph/Telex. A bank provides this facility to its customers by receiving money from one branch of the bank and making arrangement for payment to same/another bank within the country. For giving this facility, the bank uses some instruments, which are used instead of liquid cash. To transfer the cash from one place to another is very much risky that is why; this department uses some transferable instruments instead of cash.
Remittance department uses the following transferable instruments:
- Pay Order (PO)
- Demand Draft (DD)
- Telegraphic Transfer (TT)
- Outward Bill for Collection (OBC)
- In ward Bill for Collection (IBC)
Pay Order (PO)
Pay Order means Payment Order. Pay order is an instrument that contains an order for payment to the payee only in case of local payment whether on behalf of the bank or its constituents. Like cheque, there is no possibility of dishonoring PO. The Pay Order is only en-cashed through the issuing branch that means in case of PO the issuing and paying branch are the same.
Pay Order Issuing Process
In the beginning stage, PO was issued only to effect the local payment of bank’s own obligations. But at present, it is also issued to the customers, which they can purchase to deposit as security money or earnest money. PO is in form of receipts and issued by joint signature of two officers. It ensures payment to the payee as the money is deposited by the purchaser of PO is kept in a temporary account named “Pay Order A/C.” For issuing a Pay Order, following formalities are to be maintained:
- Carefully filled up the Pay Order application form by the customers.
- Deposit money either in cash or by cheque with necessary charges. That is commission and VAT on remittance 15%.
- Prepare the instrument where the pay order number, payee’s name, date, amount in number and amount are written.
- Before delivering the instrument to the customer, customer’s signature to be taken on the back of the counter part and to be properly scrutinized.
Pay Order Working Procedure
- Purchaser purchases the pay order by filling up pay order application form.
- Purchasers can purchase pay order in favor of a person or a company.
- The beneficiary then can deposit the pay order in his account wit SIBL or any other bank.
Accounting Entry for PO Issue
If the customer purchases the PO by depositing cash in the counter then the procedure are as follows:
Cash A/C ————————————Debit
Pay Order A/C——————————-Credit
Commission A/c—————————–Credit
Vat on Remittance A/C———————Credit.
If the customer wants to transfer the pay order amount from the beneficiary’s account with SIBL by debiting his account then the procedures are as follows:
Party A/C ————————————-Debit
PO A/C —————————————Credit
Commission A/C —————————Credit
Vat on Remittance ————————- Credit.
Pay order is a current liability on the part of bank, which is required to be discharged by the beneficiaries against payment in cash or through an account.
Payment of pay order
Payment of PO is made from the branch it has been issued. It is not transferable and therefore it can only be paid to:
- The payee on identification.
- The payee’s banker, who should certify that the amount would be credited PO to the payee’s account.
- The payee must authenticate a person holding a letter of authority from the payee.
As the bank issues the pay order, it is crossed when it is paid over to the customer. On the other hand the amount is transferred to the payee’s account. To transfer the amount the payee must duly stamped the pay order. The account entries will be:
PO Payable A/C —————————–Debit
SIBL General A/C ————————–Credit
Before the payment is made, it is the duty of the issuing bank to examine whether endorsement was given or not. Payment procedure of PO is described bellow:
- The payee deposits it to the collecting bank.
- Collecting bank sends the PO to the issuing bank through clearing house arrangement.
- Payment is given and registered in PO register.
- The PO is passed and cancelled in the deposit section.
Demand Draft (DD)
Demand Draft is an instruction payable on demand. It is a negotiable instrument issued by a particular branch of a bank containing an order to another branch of the same bank to pay a fixed sum of money to a certain person or order on demand. This instrument can be purchased by a customer from a particular bank’s branch for himself or for beneficiary and can be handed over to the purchaser for delivery to the beneficiary. The payee or the beneficiary will claim the amount of money in the instrument by producing the same to the concerned paying branch. Demand Draft may be paid in cash to the payee on proper identification of the amount may be credited to his account (In case of A/C holder of the bank). Bank issues Drafts for a nominal commission.
Issuance of Demand Draft
While issuing a Demand Draft an officer must be confirmed about the existence of the branch where the DD is to be issued or drawn as asked for by the applicant or purchaser. The applicant fills up the Demand Draft Application Form. After that the commission is computed correctly and applicant is asked to deposit the amount mentioned in the DD. On receipt of cash, a voucher is passed and scrolled by at least two officers. Then the DD is issued and recorded in the “Demand Draft Issue Register” filling the appropriate columns. The accounting treatment will be as follows:
Cash/ Customer A/C —————————–Debit
SIBL General A/C ——————————-Credit
Commission A/C ——————————– Credit
Vat on Remittance A/C ————————-Credit
After giving this entry an Inter Branch Credit Advice (IBCA) is prepared which contains the controlling number, depicted that the branch is credited to whom it is issued.
Payment of Demand Draft
The paying bank as and when it responds to the relative advice receive proceeds so Demand Draft. On receipt of the DD advice from the different branches, the paying bank will verify the genuineness of the advice by way of verifying test numbers and signatures. After receiving the instrument, the IBCA lodgment is done by the branch. Necessary entries are given in DD Inward Register. The controlling number of the IBCA should match with the serial number of this register application. Issuing branch then sends an Inter Branch Credit Advice (IBCA) to the drawn branch against previously issued IBCA. After that the following entries are given below:
SIBL General A/C. ———————————-Debit
Client’s A/C —————————————–Credit
The payment of DD is made with following two procedures. Procedures are as under:
Before getting Advice (IBCA)
When the paying branch of DD receives the DD before receiving the IBCA then the accounting procedures are:
DD Payable without Advice A/C —————–Debit
Party A/C ——————————————–Credit
After receiving the advice, the accounting will be:
SIBL General A/C ———————————-.Debit.
DD Payable without advice A/C —————–Credit.
After getting Advice (IBCA):
When the DD paying branch receives the DD and IBCA at a time then the accounting procedure will be:
SIBL General A/C ————————Debit.
Party A/C ———————————Credit.
Stopping Payment of the Draft
The banker cannot stop the payment of draft. Then on receiving instruction from the purchaser after delivery of the draft. This is for simple reason that issuing a bank draft the banker takes upon himself a commitment in favor of third party (the payee) to pay a certain amount of money. This is because a bank draft is as good as a promissory note issued by a banker and it is accepted by all because of the goodwill and the reputation of the banker.
Loss of the Draft
A bank can stop payment of a draft in those cases where either the purchase of the draft or the payee of the draft has reported about the draft being lost or stolen. However in such cases bank should maintain extreme caution. It should immediately inform the drawee branch about the loss and enquire whether the draft still remains unpaid and also request the drawee branch to exercise caution if and when the draft is presented for payment.
Issue of Duplicate Draft
In case a draft is reported lost and a duplicate draft is required to be issued, the banker should take some steps.
Demand Draft Charge
Bank charges a commission on DD. SIBL, charges 0.15% commission on DD Amount Their minimum commission is Tk. 25.00. The bank charges 15% Vat on Commission Amount. Before making the payment of DD, the paying branch will ascertain the genuineness of its issuance as well as the genuineness of the payee. Open draft may be paid on proper identification of the payee and crossed drafts can never be paid in cash over the counter.
Telegraphic Transfer (TT)
Telegraphic Transfer is another widely used instrument for remittance of fund from one branch to another. TT is quicker than a transfer of amount by DD. Sometimes the customer wants to transfer his money from one branch to another within a very short time. In that case the TT issuing branch uses telephone to transfer the order of paying a certain sum of money immediately to the TT paying branch to its (TT paying branch) client’s account. Telegraphic Transfer is the most rapid and convenient but expensive method. The TT issuing branch takes the telex charge from its customer. It also charges commission and vat from its customer. The drawer and the payee should have accounts with SIBL. After all the formalities of TT are done by the TT issuing branch with its customer, it prepares an Inter Branch Credit Advice (IBCA) for the confirmation of the TT and the bank posts that IBCA to the TT paying branch by Post office at the end of that particular working day.
In case of issuing a TT the following procedures must be considered:
- The customer fills up the TT application form.
- The officer then prepares Credit vouchers of Commission, VAT on Remittance, Telex charge based on the TT amount.
- Then the customer goes to the cash counter for depositing the TT amount along with commission, Vat and telex charge.
- After receiving the cash, the cash officer puts “Cash Receive” seal on all the vouchers and gives back all the vouchers to the customer.
- Then the customer submits all the vouchers to the Remittance officer.
- The customer gets cost memo containing serial number, date, to which branch the TT amount will be remitted, TT amount, commission, and Vat and Telex charge.
- Then the officer makes sure all the necessary entries in the “TT Issue Register”
- Finally, the remittance officer gives Test No and sends the TT form to the manager of that branch. Then the manager gives the Test Number again.
- After getting all the test numbers the remittance officer makes a phone call to the TT paying branch and sends the TT massage containing the following information:
- TT serial number
- TT Payment date
- TT Amount in word and in number
- IBCA No
- Test Number
- Party’s account name and number
It is important to mention here that SIBL, Principal Branch uses Telephone for sending TT massage instead of Telex.
Accounting Entry for TT Issue
Cash A/C / Client’s A/C …………………………Debit
SIBL General A/C …………………………………Credit
Commission A/C …………………………………Credit
Vat A/C……………………………………………Credit
Telex A/C …………………………………………Credit
Procedure of Incoming TT
After receiving the Telex it is recoded on the TT Receiving Form. The TT serial number, test number are verified. Makes sure all the necessary entries in the TT Payable Register. Finally, Credit Voucher in favor of the beneficiary’s account is prepared and passed.
Accounting Procedure of Incoming TT
SIBL Gen. A/C………………………………………Debit
TT Payable………………………………………….Credit
TT Payable………………………………………….Debit
Party account ……………………………………….Credit
Telegraphic Transfer Charge
Bank charges commission on TT.SIBL, charges 0.15% commission on TT Amount Their minimum commission is Tk. 25.00. The bank charges 15% Vat on Commission Amount. Tk. 30 is taken as Telex Charge.
Outward Bills for Collection (OBC)
If the bill is beyond the clearing range, it is collected by outer bill collection mechanism. Customer deposits cheques, DD, PO etc. for collection, attaching with their deposit slip. Instruments outside the clearing range are collected through OBC. As for example, a customer of SIBL Banani Branch deposits a cheque of a bank, Agrabad Branch, Chittagong, as a collecting bank. Now, SIBL, Banani Branch will perform the following tasks:
- Cash department receives the cheque, DD, PO with deposit slip. Then they verify the received cheques, DD or PO. If the instruments are dishonored, those will be returned back to the customers. If the instruments are OK then the cash department will send them to the Local Remittance Department (LRD).
- The officer concerned of LRD first keeps the necessary entries in the OBC register.
- Endorsement “Payee’s Account Will Be Credited on Realization” is given.
- Collecting bank can collect it either by its branch in Agrabad or by the drawer’s bank. They will forward the bill to that particular branch. OBC number is given in the forwarding letter. At the time of preparing OBC forwarding letter, the LRD officer keeps a carbon copy of that particular forwarding letter. He also keeps the deposit slip with the carbon copy of the forwarding letter.
- At last, he/she attached the cheques /DD/PO with the original OBC forwarding letter and sends them by curare service.
- Collecting branch will receive an IBCA from SIBL Agrabad branch.
- When ever, the IBCA of the collecting branch’s OBC comes then the following procedure should be undertaken:
¨ Entry out the bill from the OBC Register.
¨ Respond the IBCA.
¨ Write an statement “Credited to A/C No……..on ……2004 “ on the carbon copy of previously kept OBC forwarding letter.
¨ Makes a debit advice for the party.
¨ Makes three credit vouchers like commission A/C, Vat on remittance A/C and postage charge A/C.
Inward Bills for Collection (IBC)
There is a vice versa relationship between OBC and IBC. A branch of a bank sends OBC for collecting their bill from its branch. Then OBC getting branch responds that OBC and considers that OBC as IBC for them. The procedure of responding OBC (IBC) is as follow:
Credit Voucher of SIBL General A/C
Write down the IBC number and other information in the IBC register.
To prepare IBCA.
Give posting to the computer.
Accounts Department
Accounts Department is one of the most important departments in a bank. Each and every department is closely related with this department. Accounts Department maintains all the records of transactions and all types of statements. At the end of the transaction hour all concerned departments send all kinds of vouchers of transactions to this department. This Department compares all the figures, amount and contains of transaction with supplementary statements automatically arranged by the computer. If any discrepancy arises regarding any transaction then this department reports to the concerned department to repair the mistake. Then Accounts Department does another important task, which is called Voucher Sorting. In this task, the account officer rearranges all the vouchers department wise and divides all the vouchers in to Debit and Credit. After rearranging all the vouchers, the officer concerned counts the vouchers of various departments and ensures that the numbers of the vouchers are equal to the number of vouchers shown in the supplementary statements. Another vital task of this department is to prepare the extract. The extracts statement shows the Inter Branch Transactions during the end of a particular day. The Officer concerned then separates the Inter Branch Transaction Vouchers as Originating and responding basis. The responding IBCA and IBDA have a duplicate sheet for each of them. These duplicate sheets must be separated from the originals and must be kept individually as ‘Extract’. Then the next task is to divide all the Inter Branch Transaction vouchers in to Debit and Credit. Except voucher sorting, Account Department does some other vital tasks.
This Department records its accounts daily, weekly and monthly. We can divide these daily tasks in to two types. They are:
Before End of the Day:
Recording the daily transaction in the cash book.
Recording the daily transaction in general and subsidiary ledgers.
Preparing the daily position of the branch comprising of deposit and cash.
Preparing the statement of Originating and Responding.
Making payment of all the expenses of the branch.
Making Trial Balance.
Taking Backup through computer.
After End of the Day
Preparing Statement of Affairs.
Statement of back page of affairs.
Statement of provisional income.
Statement of provisional expenditure.
Preparing Monthly Report:
Individual account balance statement.
Preparing profit and loss report.
Periodical Tasks:
- Preparing the monthly salary statements for the employees publishing the basic data of the branch.
- Preparing the monthly position for the branch, which is sent to the Head Office to maintain the Statutory Liquidity Requirement (SLR)
- Preparing and Extract which is a summary of all the transactions of the Head Office account with the branch to reconcile all the transactions held among the accounts of all the branches.
Statement of Affairs
Account section prepares the Statement of Affairs for finding the profit/loss as well as amount of assets and liabilities of concerned branch per day. Theoretically m it is called financial statement. It has following two parts:
Income and Expenditure Account.
Statement of Assets and Liabilities.
Depreciation
- Depreciation is the process of cost allocation of assets, not a process assets valuation.
- Fixed asset have been shown at cost less accumulated depreciation.
- Depreciation has been charged on straight line method or reducing method at the following rate on cost of assets for the full year irrespective of their date of purchase.
| Particulars of Assets | Percentage |
| Furniture and Fixture | 10% |
| Office Equipment | 20% |
| Office Decoration | 12% |
| Automobile | 20% |
Besides the above, the accounts department has to prepare some internal statements that are submitted to the central bank.
Clearing Department
Clearing stands for mutual settlement of claims made in among member banks at an agreed time and place in respect of instruments drawn on each other. Clearing House is an arrangement under which member banks agree to meet through their representatives, at the appointed time and place to deliver instruments drawn on the other and in exchange to receive instruments drawn on them. The net amount payable or receivable as the case may be, is settled through an account kept with the controlling bank (Bangladesh Bank/ Sonali Bank).
Social Investment Bank Limited, Banani Branch’s cheques are collected through “Clearing”. Social Investment Bank Limited is a scheduled bank. According to the article 37(2) of the Bangladesh Bank Order, 1972, the banks that are members of the Clearing House are called “Scheduled Banks”. The scheduled banks clear the cheques drawn upon one another through the Clearing House. This is an arrangement by the Central Bank where everyday the representatives of the member banks sit to clear the cheques. The place where the banks meet and settle their dues is called “The Clearing House”. The Clearing House sits for two times in a working day. Everyday the first hour starts at 9.30 AM and returns house at 5.00 PM. If the cheque is dishonored, it is returned with the prescribed ‘Return Memo’ showing the cause for dishonoring the cheque and for necessary action. SIBL, Banani Branch clears its cheques as well as cheques of other banks.
The Social Investment Bank Limited, Banani Branch cheques of its client are received for collection from other banks. In case of receiving cheques the following points should be checked very carefully:
- They should not carry a date older than the receiving date for more than six months. In that case it will be ‘Stale cheque’ and it will not be allowed for collection. Again the date of cheque should not be more than one day’s forward than the receiving date that is the cheque should not be ‘Post Dated’ one.
- The amount both in words and figures in deposit slip should be same and also it should be inconformity with the amount mentioned in words and figures in the cheque.
- The name mentioned both in the cheque and the pay-in-slip should be the same.
- The cheque must be crossed.
- The collection bank must check whether endorsement is done properly or not.
Reference:
Books:
Theory and Practice of Banking (B-101), BangladeshInstitute of Bank Management, Dhaka, 2000.
Andley, K. K & Mattoo, V. J., Foreign Exchange Principles and Practices, Sultan Chand & Sons, New Delhi, 1996.
Balchandran, P., Foreign Exchange: A Mannual for Managers, Skylark Publications, New Delhi, 1991.
Chakraborty, P., The Negotiable Instrument Act, 1881, Swarna Prokashani, Dhaka.
Choudhury, T. A., An Overview of Banks and Their Services, Reading Materials on Banking Service.
Web Site:
- www.sibl.com.bd/
- www.scribd.com/
- www.privatebanking.com/bangladesh/banks/social-sislam-bank-ltd.